Robotic dispensing offers precise fluid application, ideal for adhesives and sealants, enhancing your production accuracy and efficiency. Robotic welding provides consistent, high-quality welds, improving structural integrity and reducing manual labor in manufacturing processes.
Table of Comparison
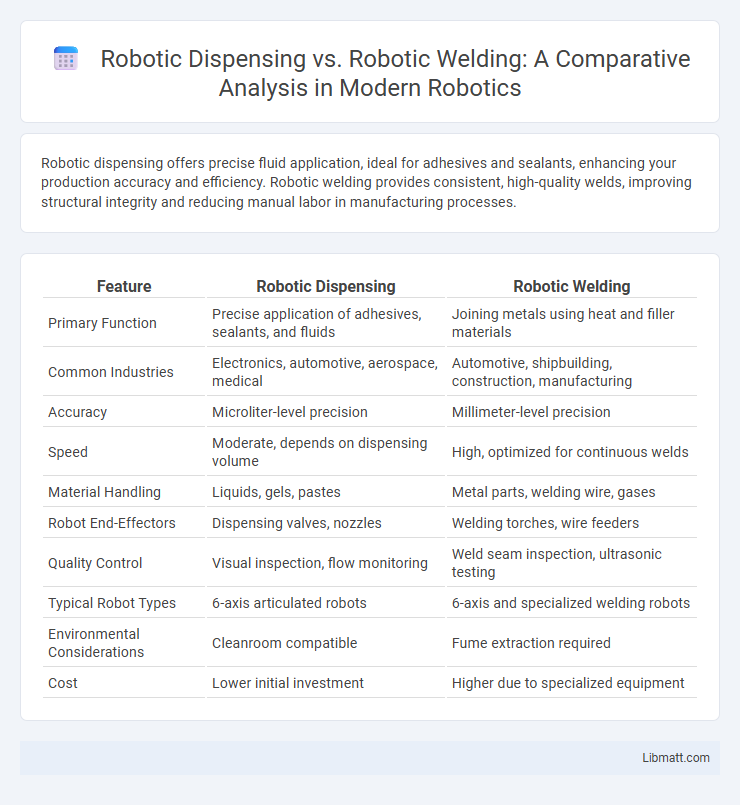
| Feature | Robotic Dispensing | Robotic Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Precise application of adhesives, sealants, and fluids | Joining metals using heat and filler materials |
| Common Industries | Electronics, automotive, aerospace, medical | Automotive, shipbuilding, construction, manufacturing |
| Accuracy | Microliter-level precision | Millimeter-level precision |
| Speed | Moderate, depends on dispensing volume | High, optimized for continuous welds |
| Material Handling | Liquids, gels, pastes | Metal parts, welding wire, gases |
| Robot End-Effectors | Dispensing valves, nozzles | Welding torches, wire feeders |
| Quality Control | Visual inspection, flow monitoring | Weld seam inspection, ultrasonic testing |
| Typical Robot Types | 6-axis articulated robots | 6-axis and specialized welding robots |
| Environmental Considerations | Cleanroom compatible | Fume extraction required |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher due to specialized equipment |
Introduction to Robotic Dispensing and Robotic Welding
Robotic dispensing involves the automated application of adhesives, sealants, or other fluids with high precision to improve product quality and consistency in manufacturing processes. Robotic welding uses programmable robots to perform welding tasks such as spot welding, arc welding, and laser welding, enhancing speed, accuracy, and safety in metal fabrication. Both technologies optimize production efficiency, reduce labor costs, and ensure repeatable, high-quality results in various industrial sectors.
Core Principles and Processes
Robotic dispensing involves precise application of adhesives, sealants, or fluids through automated nozzles following programmed paths and volumes, ensuring consistency and accuracy in manufacturing processes. Robotic welding utilizes robotic arms equipped with welding torches to perform controlled joining of metals via processes such as MIG, TIG, or spot welding, optimizing speed and quality in metal fabrication. Both technologies rely on automation, but dispensing emphasizes fluid control and patterning, whereas welding focuses on heat application and material fusion.
Key Differences in Technology
Robotic dispensing utilizes precise fluid control technology to apply adhesives, coatings, or sealants with high accuracy, relying on pumps, valves, and specialized nozzles for material deposition. Robotic welding employs advanced arc or laser-based systems to join metal components, integrating sensors and real-time monitoring to ensure consistent weld quality and penetration. Your choice between these technologies should consider factors such as material type, required precision, and production speed to optimize manufacturing efficiency.
Application Areas Across Industries
Robotic dispensing is widely used in electronics manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and automotive industries for precise application of adhesives, sealants, and lubricants. Robotic welding finds extensive applications in automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery sectors, enabling consistent, high-strength welds on metal components. Both technologies enhance production efficiency but target distinct processes--dispensing focuses on fluid materials application, while welding centers on joining metal parts.
Precision and Accuracy Comparison
Robotic dispensing systems excel in precision by delivering exact volumes of adhesives, sealants, or lubricants with microliter accuracy, ensuring consistent application across complex geometries. Robotic welding emphasizes positional accuracy and repeatability, often within +-0.1 mm, to maintain weld quality and strength, but may face challenges with intricate joint configurations compared to dispensing tasks. Both technologies employ advanced sensors and vision systems to enhance accuracy, yet dispensing robots typically achieve finer control over fluid applications than welding robots achieve in heat and material fusion.
Cost Efficiency and ROI Analysis
Robotic dispensing systems typically offer higher cost efficiency in applications requiring precise fluid or adhesive application, reducing material waste and rework costs compared to manual processes. Robotic welding, while involving higher initial investment and maintenance expenses, delivers significant ROI through faster cycle times, consistent weld quality, and reduced labor costs in high-volume production environments. Analyzing ROI for both technologies depends on factors such as throughput requirements, defect reduction, and overall operational savings specific to the manufacturing context.
Safety and Risk Factors
Robotic dispensing systems significantly reduce human exposure to hazardous chemicals by automating fluid application processes, minimizing the risk of spills and inhalation injuries. In contrast, robotic welding involves high temperatures, intense light, and fumes, necessitating advanced shielding and ventilation to protect workers from burns, eye damage, and respiratory hazards. Both automation types improve workplace safety but require different risk management protocols tailored to their specific operational hazards.
Integration with Smart Manufacturing
Robotic dispensing systems offer precise control of fluid applications essential for smart manufacturing integration, enabling real-time monitoring and adaptive process adjustments through IoT connectivity. Robotic welding integrates seamlessly with Industry 4.0 technologies by utilizing advanced sensors and data analytics to optimize weld quality and reduce downtime in automated production lines. Both technologies enhance smart factory environments by improving operational efficiency and contributing to predictive maintenance strategies.
Future Trends in Automation
Robotic dispensing and robotic welding are both advancing with AI integration and machine learning to enhance precision and adaptability in manufacturing. Future trends emphasize collaborative robots (cobots) that work alongside humans, improving flexibility and safety in complex tasks. Your facility can benefit from these innovations by adopting hybrid systems that combine dispensing and welding capabilities for streamlined automation.
Choosing the Right Robotic Solution
Selecting the appropriate robotic solution depends on the specific manufacturing needs; robotic dispensing excels in precision fluid application, ideal for adhesives, sealants, and coatings, while robotic welding offers high-strength joining capabilities essential for metal fabrication and automotive industries. Factors such as material compatibility, process speed, accuracy requirements, and production volume must guide the decision between robotic dispensing and robotic welding. Integrating the right technology enhances operational efficiency, reduces errors, and ensures consistent product quality across diverse industrial applications.
Robotic Dispensing vs Robotic Welding Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com