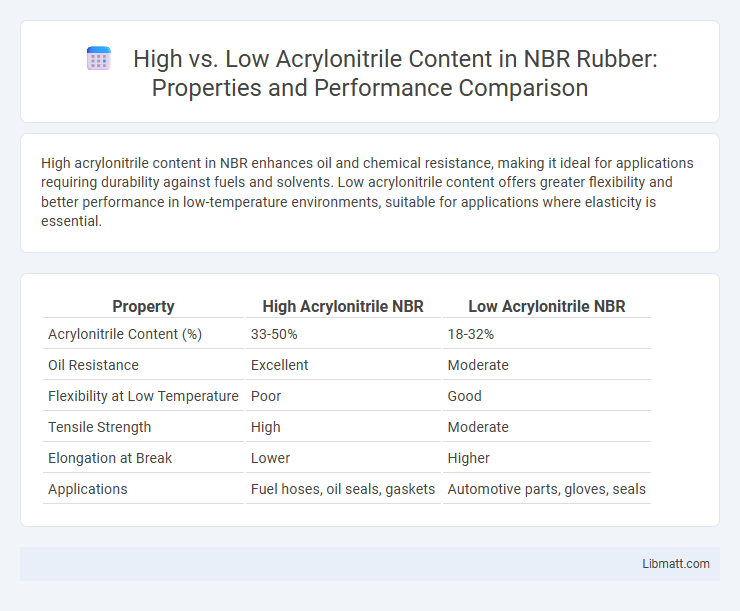
High acrylonitrile content in NBR enhances oil and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability against fuels and solvents. Low acrylonitrile content offers greater flexibility and better performance in low-temperature environments, suitable for applications where elasticity is essential.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High Acrylonitrile NBR | Low Acrylonitrile NBR |
|---|---|---|
| Acrylonitrile Content (%) | 33-50% | 18-32% |
| Oil Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Flexibility at Low Temperature | Poor | Good |
| Tensile Strength | High | Moderate |
| Elongation at Break | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Fuel hoses, oil seals, gaskets | Automotive parts, gloves, seals |
Understanding Acrylonitrile Content in NBR
Acrylonitrile content in NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) significantly influences its chemical resistance and flexibility; high acrylonitrile content (up to 50%) enhances oil and fuel resistance but reduces elasticity and low-temperature performance. Low acrylonitrile NBR (around 18-30%) offers better flexibility and low-temperature resilience but sacrifices some resistance to oils and solvents. Selecting the appropriate acrylonitrile level is crucial for optimizing NBR's performance in applications requiring specific balances of chemical resistance and mechanical properties.
High vs Low Acrylonitrile NBR: Composition Differences
High acrylonitrile content in NBR significantly enhances oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications requiring durability against hydrocarbons. Low acrylonitrile NBR offers greater flexibility and better performance in cold temperatures but has reduced chemical resistance. Selecting the appropriate acrylonitrile concentration in your NBR depends on balancing chemical resistance versus low-temperature flexibility for optimal material performance.
Mechanical Properties: Low vs High Acrylonitrile NBR
Low acrylonitrile NBR exhibits superior flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring excellent elasticity and cold temperature performance. High acrylonitrile NBR provides enhanced oil, fuel, and chemical resistance due to its increased polarity but tends to be less flexible and more rigid. Your choice between low and high acrylonitrile content directly impacts mechanical properties such as tensile strength, hardness, and elongation, tailoring the material to specific operational environments.
Oil and Chemical Resistance Comparison
High acrylonitrile content in NBR significantly enhances oil and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications involving exposure to aggressive hydrocarbons and fuels. Low acrylonitrile content NBR offers greater flexibility and low-temperature performance but sacrifices some resistance to oils and solvents. Your choice depends on balancing chemical exposure requirements with mechanical and environmental conditions, where higher nitrile levels ensure improved durability in harsh oil and chemical environments.
Temperature Performance of High and Low NBR
High acrylonitrile content in NBR significantly enhances temperature resistance, enabling elastomers to maintain flexibility and mechanical properties at temperatures up to 120degC. Low acrylonitrile content NBR exhibits superior low-temperature flexibility but has reduced heat resistance, typically performing well up to 90degC. The balance between acrylonitrile content determines NBR's suitability for applications requiring specific thermal performance ranges.
Flexibility and Compression Set in NBR Variants
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) with high acrylonitrile content exhibits superior resistance to oils and fuels but compromises flexibility, making it stiffer compared to low acrylonitrile variants. Low acrylonitrile NBR offers enhanced flexibility and lower compression set, improving its ability to return to original shape after deformation, which is critical in sealing applications. The balance between acrylonitrile content and performance parameters like flexibility and compression set directly affects the selection of NBR compounds in automotive and industrial sealing solutions.
Typical Applications: Choosing the Right Acrylonitrile Content
High acrylonitrile content in NBR enhances oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for automotive seals, fuel lines, and hose applications exposed to aggressive hydrocarbons. Low acrylonitrile content offers superior flexibility and low-temperature performance, suitable for products like gloves, gaskets, and general-purpose seals requiring elasticity in colder environments. Selecting the right acrylonitrile level depends on balancing chemical resistance with flexibility demands specific to the intended industrial or consumer application.
Processing and Cost Implications
High acrylonitrile content in NBR significantly enhances oil resistance and tensile strength but increases processing temperature requirements and resin viscosity, leading to higher energy consumption and potential equipment wear. Low acrylonitrile NBR offers easier processability with lower viscosity and reduced curing times, resulting in cost savings on manufacturing and less stringent processing conditions. Selecting acrylonitrile content balances performance demands with production efficiency and overall material costs in industrial applications.
Industry Standards for High and Low Acrylonitrile NBR
Industry standards for high acrylonitrile NBR generally specify acrylonitrile content ranging from 33% to 50%, offering superior oil resistance and mechanical strength for automotive and chemical applications. Low acrylonitrile NBR, with acrylonitrile content typically between 18% and 33%, meets industry benchmarks for flexibility and low-temperature performance, essential in food processing and medical equipment. Both classifications adhere to ASTM D2000 and ISO 1629 standards to ensure quality, consistency, and suitability for targeted industrial uses.
Selecting NBR: Key Factors Based on Acrylonitrile Content
Selecting NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) depends significantly on its acrylonitrile content, which ranges from low (18-30%) to high (31-50%). High acrylonitrile NBR offers superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for automotive and industrial sealing applications, while low acrylonitrile NBR provides better flexibility and cold temperature performance suited for dynamic sealing and lighter duty environments. The choice balances resistance requirements against flexibility and cost, optimizing rubber formulation for specific operational conditions.
Acrylonitrile content: high vs low NBR Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com