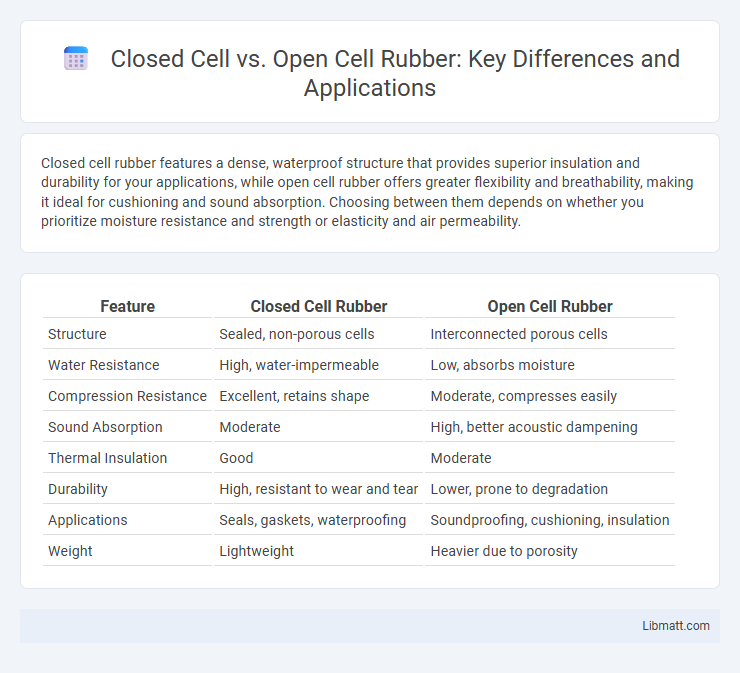
Closed cell rubber features a dense, waterproof structure that provides superior insulation and durability for your applications, while open cell rubber offers greater flexibility and breathability, making it ideal for cushioning and sound absorption. Choosing between them depends on whether you prioritize moisture resistance and strength or elasticity and air permeability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Closed Cell Rubber | Open Cell Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Sealed, non-porous cells | Interconnected porous cells |
| Water Resistance | High, water-impermeable | Low, absorbs moisture |
| Compression Resistance | Excellent, retains shape | Moderate, compresses easily |
| Sound Absorption | Moderate | High, better acoustic dampening |
| Thermal Insulation | Good | Moderate |
| Durability | High, resistant to wear and tear | Lower, prone to degradation |
| Applications | Seals, gaskets, waterproofing | Soundproofing, cushioning, insulation |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to porosity |
Introduction to Closed Cell and Open Cell Rubber
Closed cell rubber consists of cells that are completely enclosed and not interconnected, providing superior insulation, moisture resistance, and higher durability, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. Open cell rubber features interconnected cells that allow air and moisture to pass through, resulting in softer, more flexible materials suitable for sound absorption and cushioning. Your choice between closed cell and open cell rubber depends on the specific requirements for insulation, flexibility, and environmental exposure.
Understanding Cell Structure Differences
Closed cell rubber features tightly packed, intact cells filled with gas, providing superior water resistance, higher insulation, and greater structural rigidity. In contrast, open cell rubber consists of interconnected, porous cells that allow air and moisture to pass through, resulting in increased flexibility and better sound absorption. Understanding these structural differences helps you choose the right material for applications requiring durability, cushioning, or environmental resistance.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Closed cell rubber features a dense, impermeable structure offering superior insulation, higher tensile strength, and enhanced resistance to moisture and chemicals compared to open cell rubber. Open cell rubber is characterized by its porous, flexible composition, providing excellent sound absorption and cushioning but lower durability and moisture resistance. These key physical properties determine their applications in insulation, sealing, and acoustic control industries.
Insulation and Thermal Performance
Closed cell rubber offers superior insulation and thermal performance due to its dense structure, which minimizes heat transfer and prevents moisture absorption. Open cell rubber, with its porous composition, provides lower thermal resistance and is less effective in moisture control, making it suitable for applications where breathability is needed. Your choice depends on the need for high insulation efficiency or flexibility in airflow and vapor permeability.
Water and Moisture Resistance
Closed cell rubber offers superior water and moisture resistance due to its dense, non-permeable structure that prevents water absorption and inhibits mold growth. Open cell rubber, characterized by its porous and interconnected structure, allows moisture to penetrate, making it less effective in wet environments. When selecting rubber for waterproofing or moisture-sensitive applications, your choice should prioritize closed cell rubber to ensure long-lasting protection and durability.
Applications and Typical Uses
Closed cell rubber is widely used in insulation, sealing, and cushioning applications due to its high resistance to moisture and air permeability. Open cell rubber, with its softer and more flexible structure, is typically employed in soundproofing, shock absorption, and packaging to provide enhanced cushioning and noise reduction. Your choice between these materials depends on whether you prioritize durability and moisture resistance (closed cell) or flexibility and sound insulation (open cell).
Cost Considerations and Budget Impact
Closed cell rubber typically involves higher upfront costs due to its denser material and superior durability, which can lead to long-term savings by reducing maintenance and replacement expenses. Open cell rubber generally offers a lower initial price, making it attractive for projects with tight budgets, but may incur higher costs over time due to its lower resistance to moisture and wear. Considering your project's budget, closed cell rubber often provides better value through extended lifespan and enhanced performance, whereas open cell rubber suits cost-sensitive applications requiring less durability.
Durability and Longevity
Closed cell rubber offers superior durability and longevity due to its dense structure, which resists moisture, chemicals, and physical degradation more effectively than open cell rubber. Open cell rubber, with its porous nature, is more prone to wear and tear over time as it absorbs water and contaminants, reducing its lifespan. When selecting materials for long-term applications, you should consider closed cell rubber for enhanced resilience and extended service life.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Closed cell rubber offers superior resistance to moisture and chemicals, resulting in longer product lifespan and reduced material waste, which enhances its environmental sustainability. Open cell rubber, due to its porous structure, promotes breathability but tends to degrade faster, leading to increased frequency of replacement and higher environmental footprint. Choosing closed cell rubber often supports eco-friendly applications by minimizing resource consumption and contributing to sustainability goals in insulation and sealing industries.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Needs
Closed cell rubber offers superior water resistance and insulation due to its dense, airtight structure, making it ideal for applications requiring moisture protection and thermal stability. Open cell rubber, with its porous and flexible composition, excels in cushioning and sound absorption, suited for environments needing shock absorption and noise reduction. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific requirements such as durability, environmental exposure, and mechanical performance.
Closed Cell vs Open Cell Rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com