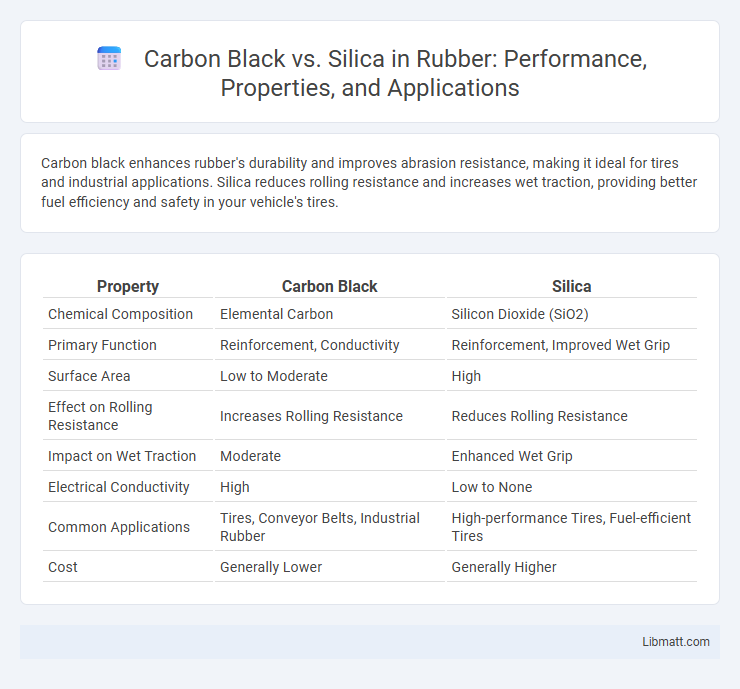
Carbon black enhances rubber's durability and improves abrasion resistance, making it ideal for tires and industrial applications. Silica reduces rolling resistance and increases wet traction, providing better fuel efficiency and safety in your vehicle's tires.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Black | Silica |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Elemental Carbon | Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) |
| Primary Function | Reinforcement, Conductivity | Reinforcement, Improved Wet Grip |
| Surface Area | Low to Moderate | High |
| Effect on Rolling Resistance | Increases Rolling Resistance | Reduces Rolling Resistance |
| Impact on Wet Traction | Moderate | Enhanced Wet Grip |
| Electrical Conductivity | High | Low to None |
| Common Applications | Tires, Conveyor Belts, Industrial Rubber | High-performance Tires, Fuel-efficient Tires |
| Cost | Generally Lower | Generally Higher |
Introduction to Carbon Black and Silica
Carbon Black is a fine black powder primarily used as a reinforcing filler in rubber products, especially tires, due to its excellent strengthening properties and electrical conductivity. Silica, a silicon dioxide compound, is widely utilized as a reinforcing filler in tire treads to improve wet traction and reduce rolling resistance, enhancing fuel efficiency. Both materials play crucial roles in the rubber industry but differ significantly in their chemical composition, structure, and performance characteristics.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Carbon black consists primarily of elemental carbon arranged in a fine particulate form with a high surface area, while silica is composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2) with a crystalline or amorphous structure. The molecular arrangement in carbon black features a network of fused aromatic rings, contributing to its conductivity and strength, whereas silica's tetrahedral silicon-oxygen framework provides excellent thermal stability and insulation properties. Understanding these differences in chemical structure and composition helps optimize Your choice based on application requirements such as reinforcement or thermal resistance.
Historical Uses in Industry
Carbon black has been extensively used in the tire and rubber industries since the early 20th century due to its reinforcing properties and ability to improve durability. Silica's industrial application dates back to the 1950s, gaining prominence as a filler in rubber compounds to enhance wet traction and reduce rolling resistance in tires. Both materials have evolved with advancements in polymer technology, but carbon black remains dominant in heavy-duty applications, while silica is preferred for performance-oriented and environmentally-friendly products.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Carbon Black exhibits a high surface area with particle sizes typically ranging from 10 to 500 nanometers, offering exceptional reinforcement in rubber and plastics, while Silica particles are generally larger, around 20 to 500 nanometers, providing superior opacity and gloss in coatings. Carbon Black has a density of approximately 1.8 to 2.1 g/cm3, compared to Silica's lower density of about 2.2 g/cm3, affecting the weight and mixing behavior in composites. Your choice between Carbon Black and Silica will depend on the specific physical properties needed, such as color strength, durability, or surface texture, for your application.
Role in Rubber and Tire Manufacturing
Carbon black serves as a reinforcing filler in rubber and tire manufacturing, significantly enhancing tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and durability, which improves overall tire performance and lifespan. Silica is used as a functional filler to reduce rolling resistance and improve wet traction, contributing to better fuel efficiency and safety in tires. Combining carbon black with silica optimizes the balance between mechanical strength and performance characteristics, making it a preferred choice for advanced tire compounds.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon black production generates significant carbon emissions and relies heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to environmental pollution and resource depletion. Silica, especially when sourced sustainably or produced via green methods, tends to have a lower carbon footprint and better biodegradability, enhancing its sustainability profile. Choosing silica-based materials can reduce your project's environmental impact through improved recyclability and reduced reliance on non-renewable resources.
Performance Differences in Applications
Carbon black enhances the durability and UV resistance of rubber products, making it ideal for tires and industrial applications, while silica offers superior wet traction and lower rolling resistance, improving fuel efficiency in automotive tires. Your product's performance can be optimized by selecting carbon black for toughness and abrasion resistance or silica for enhanced grip and energy savings. The choice directly impacts wear, handling, and environmental sustainability in composite materials.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Carbon black generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to silica due to its lower production expenses and widespread availability. While silica provides superior performance in certain applications, its higher manufacturing costs can increase overall material expenses. Evaluating your project's budget against performance needs helps determine the most economical filler choice.
Future Trends in Filler Materials
Carbon black and silica are evolving as key filler materials in the tire and rubber industries, with future trends emphasizing sustainability and performance enhancement. Carbon black continues to dominate due to its reinforcing properties and conductivity, but silica offers advantages in rolling resistance reduction and wet traction, making it a preferred choice for eco-friendly tires. Your selection of filler material will increasingly depend on balancing environmental regulations, cost efficiency, and desired mechanical properties to optimize product innovation.
Choosing Between Carbon Black and Silica
Choosing between carbon black and silica depends on your specific application requirements, such as durability, reinforcement, and compatibility with the base material. Carbon black offers excellent abrasion resistance and UV protection, making it ideal for automotive tires and heavy-duty rubber products. Silica provides enhanced rolling resistance and wet traction, often preferred in tire treads for improved fuel efficiency and safety.
Carbon Black vs Silica Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com