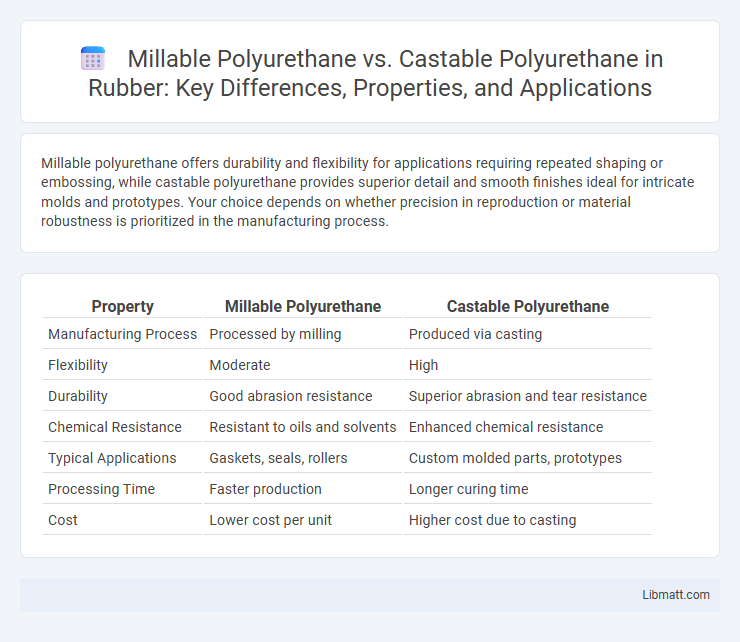
Millable polyurethane offers durability and flexibility for applications requiring repeated shaping or embossing, while castable polyurethane provides superior detail and smooth finishes ideal for intricate molds and prototypes. Your choice depends on whether precision in reproduction or material robustness is prioritized in the manufacturing process.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Millable Polyurethane | Castable Polyurethane |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Processed by milling | Produced via casting |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance | Superior abrasion and tear resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils and solvents | Enhanced chemical resistance |
| Typical Applications | Gaskets, seals, rollers | Custom molded parts, prototypes |
| Processing Time | Faster production | Longer curing time |
| Cost | Lower cost per unit | Higher cost due to casting |
Introduction to Polyurethane Elastomers
Polyurethane elastomers are versatile polymers known for their durability, flexibility, and impact resistance, commonly used in manufacturing and prototyping. Millable polyurethane is processed through milling and compression molding, offering excellent mechanical properties and easier fabrication for flexible parts. Castable polyurethane, produced via casting into molds, provides high detail accuracy and is ideal for complex shapes with superior surface finish and dimensional stability.
Understanding Millable Polyurethane
Millable polyurethane is a specialized elastomer designed for easy processing through milling and compression molding, offering excellent durability, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals. Unlike castable polyurethane, which cures in molds to form solid parts, millable polyurethane starts as solid sheets or pellets, allowing precise control over thickness and shape during fabrication. Its ability to maintain performance in dynamic applications makes it ideal for seals, gaskets, and impact-resistant components in industrial settings.
Overview of Castable Polyurethane
Castable polyurethane is a versatile material known for its excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and superior abrasion resistance, making it ideal for components requiring durability and precision. It cures through a chemical reaction allowing for intricate moldability and is widely used in prototyping, tooling, and small-batch manufacturing due to its ease of casting and dimensional stability. Your projects benefit from castable polyurethane's ability to produce detailed, resilient parts that maintain structural integrity under stress.
Key Differences Between Millable and Castable Polyurethane
Millable polyurethane is a rubber-like material that can be processed using traditional milling and molding techniques, offering excellent tear resistance and flexibility for applications like gaskets and seals, whereas castable polyurethane is a liquid resin that cures into a solid form through casting, allowing for complex shapes and precision in parts such as prototypes and intricate molds. Millable polyurethane typically provides higher durability and is better suited for dynamic mechanical stress, while castable polyurethane excels in producing detailed, customized components with fine surface finishes. The choice between millable and castable polyurethane depends on the required mechanical properties, manufacturing process, and design complexity of the end product.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Millable polyurethane is produced through a rubber compounding process where ingredients are mixed and milled into sheets before curing, enabling precise control over hardness and elasticity. Castable polyurethane involves liquid raw materials poured into molds, curing through chemical polymerization, which allows for complex shapes and detailed features with minimal post-processing. Each manufacturing process impacts the final product's performance, with millable polyurethane favoring flexibility and durability in rollable forms, while castable polyurethane excels in intricate, high-precision applications.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Millable polyurethane exhibits higher tensile strength and flexibility, making it ideal for custom gaskets and seals requiring durability under repetitive stress. Castable polyurethane offers superior hardness and abrasion resistance, suited for applications demanding rigidity and wear resistance such as industrial components. Both materials differ significantly in elongation at break, with millable grades providing greater elasticity compared to the stiffer castable variants.
Typical Applications of Millable Polyurethane
Millable polyurethane is commonly used in applications requiring flexibility and durability, such as seals, gaskets, vibration isolators, and automotive parts. Its ability to be processed through milling and molding makes it ideal for producing custom components with high abrasion resistance and elasticity. You benefit from millable polyurethane in industries needing strong, wear-resistant parts that maintain performance under dynamic mechanical stress.
Typical Applications of Castable Polyurethane
Castable polyurethane is commonly used in prototyping, mold making, and low-volume production due to its excellent flexibility and high tear strength. Its ability to withstand mechanical stress and chemical exposure makes it ideal for producing functional parts such as gaskets, seals, and automotive components. You can rely on castable polyurethane for applications requiring durable, impact-resistant materials with precise dimensional stability.
Cost and Performance Considerations
Millable polyurethane offers cost-effective solutions for high-volume production with excellent abrasion resistance and elasticity, suitable for industrial parts requiring durability and flexibility. Castable polyurethane, while generally more expensive, provides superior precision, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for custom, intricate components and prototypes. Selecting between millable and castable polyurethane depends on balancing budget constraints with required performance specifications such as wear resistance, dimensional accuracy, and application environment.
Choosing the Right Polyurethane for Your Needs
Millable polyurethane offers superior elasticity and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility and impact resistance, while castable polyurethane provides excellent precision and hardness for detailed, high-strength components. Your choice depends on whether you need a resilient material for dynamic use or a rigid substance for intricate parts and high-load environments. Selecting the right polyurethane ensures optimal performance and longevity tailored to your specific project requirements.
Millable Polyurethane vs Castable Polyurethane Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com