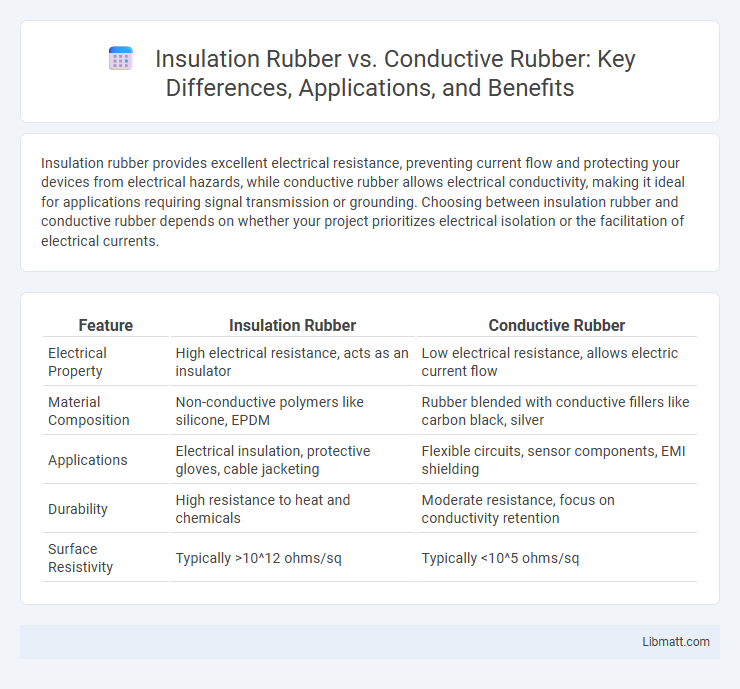
Insulation rubber provides excellent electrical resistance, preventing current flow and protecting your devices from electrical hazards, while conductive rubber allows electrical conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring signal transmission or grounding. Choosing between insulation rubber and conductive rubber depends on whether your project prioritizes electrical isolation or the facilitation of electrical currents.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Insulation Rubber | Conductive Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Property | High electrical resistance, acts as an insulator | Low electrical resistance, allows electric current flow |
| Material Composition | Non-conductive polymers like silicone, EPDM | Rubber blended with conductive fillers like carbon black, silver |
| Applications | Electrical insulation, protective gloves, cable jacketing | Flexible circuits, sensor components, EMI shielding |
| Durability | High resistance to heat and chemicals | Moderate resistance, focus on conductivity retention |
| Surface Resistivity | Typically >10^12 ohms/sq | Typically <10^5 ohms/sq |
Introduction to Insulation Rubber and Conductive Rubber
Insulation rubber is designed to prevent the flow of electric current, providing high resistance and protecting against electrical shocks and short circuits in various applications. Conductive rubber contains conductive fillers like carbon or metal particles, enabling it to facilitate electrical conductivity for use in sensors, electromagnetic shielding, and flexible electronics. Both types of rubber are engineered with distinct material compositions to meet specific electrical performance requirements in industrial and electronic environments.
Key Differences Between Insulation and Conductive Rubber
Insulation rubber primarily acts as an electrical barrier, preventing the flow of current due to its high resistivity and dielectric strength, making it essential for safety in electrical applications. Conductive rubber is engineered with conductive fillers like carbon or metal particles, allowing it to transmit electricity effectively and enabling its use in sensors, flexible circuits, and EMI shielding. The key difference lies in their electrical properties: insulation rubber resists conduction, while conductive rubber promotes controlled electrical flow.
Composition and Material Properties
Insulation rubber is primarily composed of non-conductive polymers like EPDM or silicone, featuring high dielectric strength and excellent resistance to heat, moisture, and electrical current, making it ideal for electrical insulation applications. Conductive rubber typically incorporates conductive fillers such as carbon black, metal particles, or graphene within a flexible elastomer base, enabling efficient electrical conductivity while maintaining elasticity. The key difference lies in their material properties: insulation rubber prioritizes electrical resistance and safety, whereas conductive rubber balances conductivity with flexibility for grounding and shielding purposes.
Electrical Characteristics and Performance
Insulation rubber possesses high electrical resistivity and excellent dielectric strength, making it ideal for preventing electrical current flow and protecting against voltage spikes. Conductive rubber, infused with conductive fillers like carbon or metal particles, provides controlled electrical conductivity for applications requiring electrostatic discharge (ESD) shielding or electrical grounding. The performance difference is characterized by insulation rubber minimizing current leakage, whereas conductive rubber enables reliable current flow while maintaining flexibility and durability.
Applications of Insulation Rubber
Insulation rubber is widely used in electrical and electronic applications to prevent electrical shock and ensure safety by providing effective resistance against current flow. Common applications include cable insulation, protective gloves for electricians, and insulating mats in power plants. Your equipment and personnel rely on insulation rubber to maintain operational safety in high-voltage environments.
Applications of Conductive Rubber
Conductive rubber is widely utilized in applications requiring electrical conductivity, such as flexible circuits, electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, and pressure-sensitive switches. Its ability to conduct electricity while maintaining elasticity makes it essential in wearable electronics, sensor technology, and anti-static components. Your choice of conductive rubber ensures reliable performance in environments demanding both flexibility and electrical functionality.
Safety Considerations and Standards
Insulation rubber is designed to prevent electrical conduction, providing essential protection against electric shocks and ensuring safety compliance with standards such as ASTM D257 and IEC 60093. Conductive rubber, used for electromagnetic interference shielding and static dissipation, must meet specific resistivity and grounding criteria outlined in standards like MIL-STD-883 and ISO 8031 to maintain safe operation. Your choice between these materials should prioritize the required safety ratings and regulatory certifications to ensure proper protection in electrical applications.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Insulation rubber offers superior durability with excellent resistance to heat, moisture, and chemicals, making it ideal for harsh environmental conditions. Conductive rubber, while durable, is more susceptible to wear and degradation due to its embedded conductive fillers that may react under extreme stress or environmental exposure. Your choice depends on the specific application demands, balancing the need for long-lasting performance against electrical conductivity requirements.
Cost Comparison and Economic Factors
Insulation rubber generally costs less than conductive rubber due to its simpler formulation and lower demand in specialized applications. Conductive rubber involves additives like carbon black or metal particles, increasing material costs and manufacturing complexity. Evaluating your project's budget, insulation rubber offers more economical solutions for standard uses, while conductive rubber justifies higher expenses through enhanced electrical performance.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate rubber type hinges on your application's electrical requirements; insulation rubber provides excellent resistance to electrical current, making it ideal for preventing electrical shocks and safeguarding sensitive components. Conductive rubber, embedded with conductive fillers like carbon or metal particles, facilitates the flow of electricity and is essential for applications requiring static discharge or electromagnetic shielding. Understanding these properties ensures you optimize performance, durability, and safety in your specific industrial or electronic projects.
Insulation Rubber vs Conductive Rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com