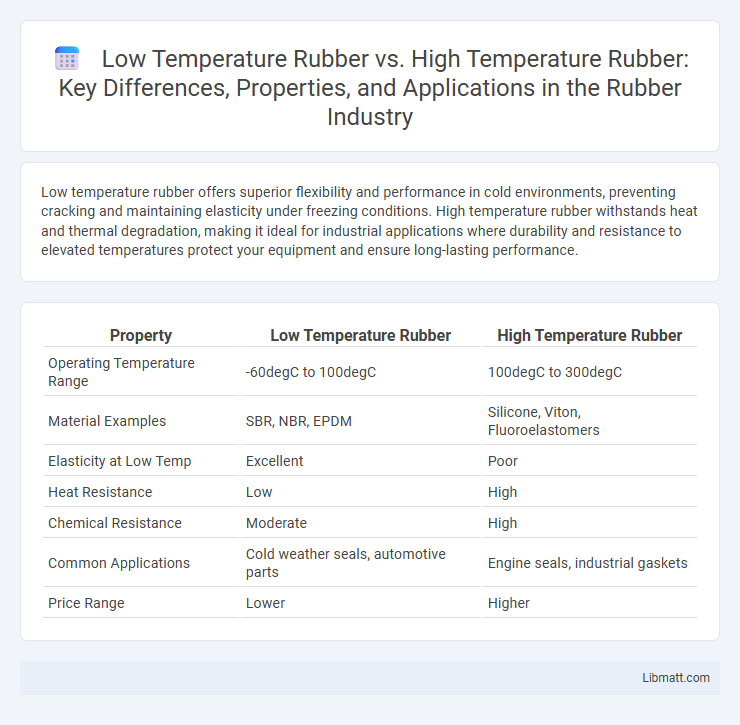
Low temperature rubber offers superior flexibility and performance in cold environments, preventing cracking and maintaining elasticity under freezing conditions. High temperature rubber withstands heat and thermal degradation, making it ideal for industrial applications where durability and resistance to elevated temperatures protect your equipment and ensure long-lasting performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Low Temperature Rubber | High Temperature Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature Range | -60degC to 100degC | 100degC to 300degC |
| Material Examples | SBR, NBR, EPDM | Silicone, Viton, Fluoroelastomers |
| Elasticity at Low Temp | Excellent | Poor |
| Heat Resistance | Low | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Common Applications | Cold weather seals, automotive parts | Engine seals, industrial gaskets |
| Price Range | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Low Temperature Rubber and High Temperature Rubber
Low Temperature Rubber maintains flexibility and resilience in extreme cold, making it ideal for applications in arctic conditions and refrigeration systems. High Temperature Rubber withstands elevated heat levels, providing durability and stability in environments exposed to continuous high temperatures, such as automotive engines and industrial machinery. Understanding the distinct thermal properties of these rubbers helps you select the right material for performance and longevity in specific temperature ranges.
Key Differences Between Low and High Temperature Rubbers
Low temperature rubber excels in flexibility and durability under subzero conditions, maintaining performance without becoming brittle. High temperature rubber withstands extreme heat, often exceeding 200degC, without degrading or losing elasticity. Your choice depends on the operating environment, with low temperature rubber suited for cold climates and high temperature rubber optimal for industrial applications involving heat exposure.
Material Composition and Chemical Structure
Low temperature rubber typically consists of polymers such as nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) and silicone rubber, characterized by flexible polymer chains and low glass transition temperatures (Tg) that maintain elasticity in cold environments. High temperature rubber often comprises fluoroelastomers (FKM) and perfluoroelastomers (FFKM), featuring highly fluorinated polymer backbones and cross-linked structures that provide stability and chemical resistance at elevated temperatures up to 300degC or higher. The distinct chemical composition and cross-link density in high temperature rubbers result in superior thermal degradation resistance compared to the more saturated, lower Tg elastomers used in low temperature applications.
Performance Under Extreme Temperatures
Low temperature rubber maintains flexibility and resists cracking in subzero conditions, making it ideal for cold climates and applications involving freezing temperatures. High temperature rubber withstands thermal degradation, preserving its elasticity and strength in environments exceeding 200degC, which is crucial for engines and industrial machinery. Your choice between these materials depends on the specific thermal demands of your application to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Common Applications and Industries
Low temperature rubber excels in cryogenic and cold storage industries, providing flexibility and resistance in applications like refrigerated transportation and cold climate seals. High temperature rubber is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors for engine gaskets, exhaust systems, and heat shields due to its ability to withstand extreme heat. Both materials serve critical roles in manufacturing, with low temperature rubber suited for cold environments and high temperature rubber optimized for thermal durability.
Advantages of Low Temperature Rubber
Low temperature rubber offers superior flexibility and elasticity in subzero environments, ensuring reliable performance where high temperature rubber may become brittle or crack. It excels in maintaining durability and sealing properties in cold climates, making it ideal for applications in refrigeration, cold storage, and arctic conditions. Your equipment benefits from reduced maintenance and longer service life when using low temperature rubber in such demanding environments.
Benefits of High Temperature Rubber
High temperature rubber offers superior resistance to heat, maintaining elasticity and structural integrity in extreme thermal environments up to 300degC. Its enhanced durability reduces wear and tear, providing longer service life in applications such as automotive engines, industrial machinery, and aerospace components. Compared to low temperature rubber, it effectively prevents deformation, oxidation, and aging, ensuring reliable performance under continuous exposure to elevated temperatures.
Durability, Flexibility, and Resilience Comparison
Low temperature rubber excels in flexibility and resilience when exposed to cold environments, maintaining performance without cracking or becoming brittle, while high temperature rubber offers superior durability under extreme heat and resists deformation over time. The resilience of low temperature rubber ensures elasticity at subzero conditions, whereas high temperature rubber withstands thermal aging and chemical exposure more effectively. Your choice depends on the operating temperature range, with low temperature rubber best for cold climates and high temperature rubber ideal for heat-intensive applications.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Low temperature rubber typically incurs higher costs due to specialized formulations designed to maintain flexibility in extreme cold, while high temperature rubber is often more readily available and cost-effective for general industrial use. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with performance needs, as low temperature variants may require more investment but ensure durability in frigid environments. Availability of high temperature rubber remains consistent across suppliers, whereas low temperature options can be limited and lead to longer lead times.
How to Choose the Right Rubber for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate rubber material depends on the operating temperature range and environmental conditions of your application. Low temperature rubber offers excellent flexibility and resistance to cracking in cold environments, making it ideal for subzero or cold climate uses. High temperature rubber withstands elevated heat without degrading, suitable for machinery or automotive parts exposed to continuous heat or flames, ensuring durability and safety.
Low Temperature Rubber vs High Temperature Rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com