Sponge rubber offers superior cushioning and flexibility due to its cellular structure, making it ideal for applications requiring shock absorption and insulation. Solid rubber provides greater durability and resistance to wear, making it suitable for heavy-duty uses where strength and longevity are essential for your projects.
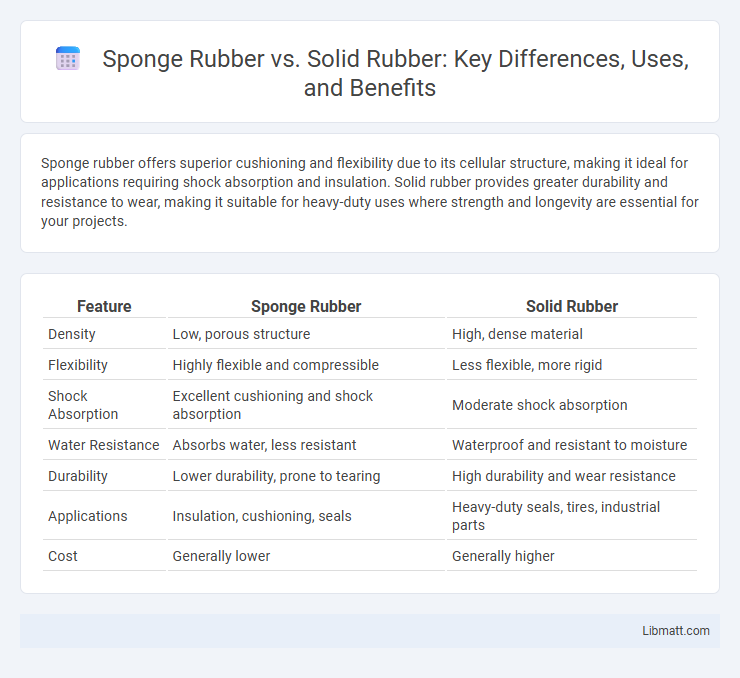
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sponge Rubber | Solid Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low, porous structure | High, dense material |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and compressible | Less flexible, more rigid |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent cushioning and shock absorption | Moderate shock absorption |
| Water Resistance | Absorbs water, less resistant | Waterproof and resistant to moisture |
| Durability | Lower durability, prone to tearing | High durability and wear resistance |
| Applications | Insulation, cushioning, seals | Heavy-duty seals, tires, industrial parts |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
Introduction to Sponge Rubber and Solid Rubber
Sponge rubber is a lightweight, flexible material characterized by its porous structure, offering excellent cushioning and thermal insulation properties in numerous applications. Solid rubber, on the other hand, is dense and durable, providing superior resistance to abrasion, compression, and environmental factors for heavy-duty uses. Understanding the differences between sponge rubber and solid rubber helps you select the ideal type based on your specific needs, such as shock absorption or structural strength.
Key Differences Between Sponge Rubber and Solid Rubber
Sponge rubber features a porous structure that provides superior cushioning, flexibility, and excellent insulation against sound and vibration, making it ideal for sealing and padding applications. Solid rubber, characterized by its dense, non-porous composition, offers higher durability, tensile strength, and resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and weathering, suitable for heavy-duty industrial uses. The key differences lie in their density, resilience, and application suitability, with sponge rubber prioritizing softness and compression recovery and solid rubber ensuring structural integrity and longevity.
Physical Properties Comparison
Sponge rubber features a cellular structure that provides excellent cushioning, flexibility, and sound absorption, while solid rubber offers superior durability, tensile strength, and resistance to abrasion and impact. The closed-cell nature of sponge rubber results in lower density and enhanced compressibility, making it ideal for sealing and insulation applications where lightweight materials are needed. Your choice depends on whether cushioning and flexibility or toughness and load-bearing capability are the primary physical property requirements.
Manufacturing Processes
Sponge rubber is created through a vulcanization process that introduces gas bubbles into the rubber matrix, resulting in a lightweight, porous material ideal for cushioning and insulation. Solid rubber undergoes a different manufacturing method where the rubber is compounded, molded, and vulcanized without gas expansion, producing a dense, durable product for heavy-duty applications. Understanding these distinct manufacturing processes helps you select the right rubber type tailored to your performance and durability requirements.
Applications of Sponge Rubber
Sponge rubber is extensively used in automotive seals, gaskets, and sound insulation due to its lightweight, cushioning, and thermal insulation properties. Its closed-cell structure offers excellent resistance to water, oil, and chemicals, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications. This material is also favored in footwear and packaging industries for shock absorption and protective padding.
Applications of Solid Rubber
Solid rubber is primarily used in heavy-duty applications requiring high durability and resistance to abrasion, such as industrial gaskets, seals, and automotive tires. Its dense structure provides excellent load-bearing capacity and resistance to oil, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. Solid rubber is also preferred for conveyor belts, vibration dampening components, and heavy machinery mounts due to its robustness and longevity.
Durability and Lifespan
Sponge rubber offers excellent cushioning and flexibility but typically has a shorter lifespan due to its porous structure, which can degrade faster under abrasive conditions. Solid rubber boasts superior durability, resisting wear, tears, and environmental factors, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring long-lasting performance. The dense composition of solid rubber ensures prolonged lifespan compared to sponge rubber in demanding industrial or outdoor environments.
Cost Considerations
Sponge rubber typically costs less than solid rubber due to its lower material density and easier manufacturing process, making it a budget-friendly option for applications requiring cushioning or insulation. Solid rubber, while more expensive, offers superior durability and resistance to wear, ideal for heavy-duty uses where longevity is critical. Understanding your project's cost constraints and performance needs helps determine whether sponge or solid rubber provides the best value.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sponge rubber, characterized by its cellular structure, typically uses less raw material per volume compared to solid rubber, potentially reducing resource extraction and carbon footprint during production. Solid rubber, while denser and more durable, often has a higher environmental impact due to greater material usage and energy consumption in manufacturing. Recycling options for sponge rubber are limited because of its porous nature, whereas solid rubber can be more effectively reclaimed and repurposed, enhancing its sustainability profile.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Needs
Sponge rubber offers excellent cushioning and shock absorption, making it ideal for sealing, insulation, and noise reduction in applications requiring flexibility and compressibility. Solid rubber provides superior durability, resistance to wear, and load-bearing capacity, suitable for heavy-duty industrial use, abrasion resistance, and outdoor conditions. Selecting between sponge and solid rubber depends on specific requirements such as cushioning needs, environmental exposure, and mechanical stress tolerance.
Sponge Rubber vs Solid Rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com