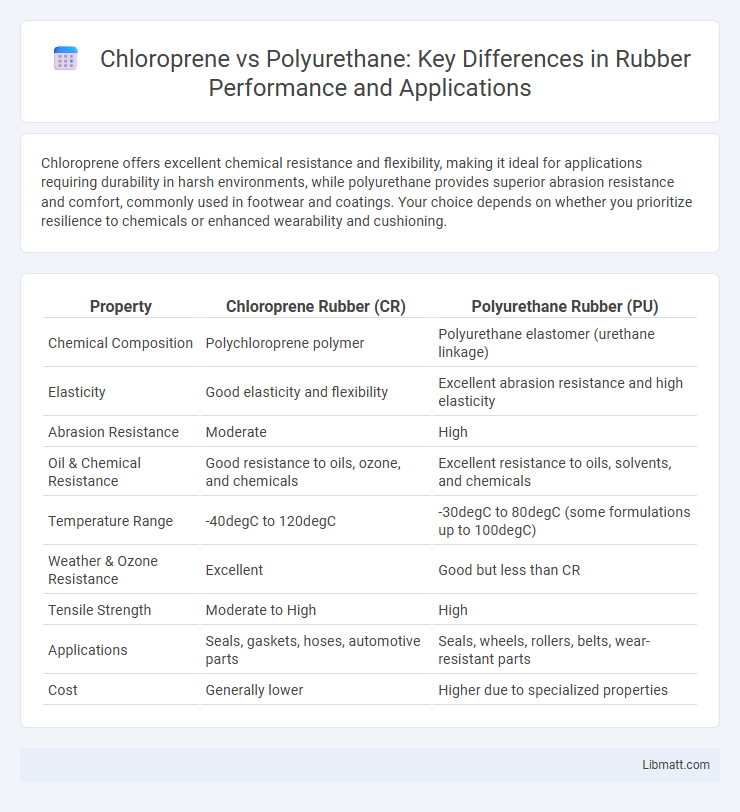
Chloroprene offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring durability in harsh environments, while polyurethane provides superior abrasion resistance and comfort, commonly used in footwear and coatings. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize resilience to chemicals or enhanced wearability and cushioning.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Polychloroprene polymer | Polyurethane elastomer (urethane linkage) |
| Elasticity | Good elasticity and flexibility | Excellent abrasion resistance and high elasticity |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Oil & Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils, ozone, and chemicals | Excellent resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 80degC (some formulations up to 100degC) |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Good but less than CR |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate to High | High |
| Applications | Seals, gaskets, hoses, automotive parts | Seals, wheels, rollers, belts, wear-resistant parts |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to specialized properties |
Introduction to Chloroprene and Polyurethane
Chloroprene and polyurethane are versatile synthetic materials widely used in diverse industrial applications due to their unique chemical structures and properties. Chloroprene, a neoprene-based synthetic rubber, offers excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for protective gear and seals. Polyurethane exhibits remarkable flexibility, abrasion resistance, and durability, allowing it to be tailored for coatings, foams, and elastomers that enhance your product's performance and longevity.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Chloroprene is a synthetic rubber derived from chloroprene monomers, featuring a polymer chain with alternating single and double bonds that provide excellent elasticity and chemical resistance. Polyurethane consists of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links, forming a versatile polymer network with varying rigidity depending on the ratio of soft and hard segments in its structure. Understanding these chemical compositions helps you select the right material based on desired durability, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Chloroprene exhibits excellent elasticity, chemical resistance, and moderate tensile strength, making it ideal for flexible applications such as wetsuits and adhesives. Polyurethane stands out for its superior abrasion resistance, higher tensile strength, and excellent toughness, commonly used in foam cushioning, coatings, and sealants. When choosing between them, your decision should weigh Chloroprene's flexibility against Polyurethane's durability and mechanical strength for optimal performance in specific environments.
Durability and Lifespan Differences
Chloroprene offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals, ensuring a longer lifespan in harsh environments compared to polyurethane, which is more prone to degradation under UV exposure and abrasion. Polyurethane, while less durable in extreme conditions, provides superior flexibility and resistance to oil and grease, making it suitable for applications requiring frequent movement. The durability of chloroprene typically results in extended service life for industrial seals and wetsuits, whereas polyurethane's lifespan is shorter but optimized for wear-intensive components like rollers and wheels.
Flexibility and Comfort Analysis
Chloroprene offers excellent flexibility with its inherent elastic properties, making it ideal for applications requiring stretch and adaptability such as wetsuits and gloves. Polyurethane provides superior comfort through its cushioning and abrasion resistance, commonly used in footwear and upholstery to enhance wearability. Both materials balance flexibility and comfort, but chloroprene excels in stretchability, while polyurethane delivers enhanced softness and durability.
Resistance to Water and Chemicals
Chloroprene offers excellent resistance to water, oils, and moderate chemical exposure, making it durable in environments involving moisture and certain solvents. Polyurethane provides superior chemical resistance, especially against oils, fuels, and abrasion, but can degrade when exposed to strong solvents or prolonged water immersion. Selecting between chloroprene and polyurethane depends on the specific water and chemical resistance requirements of the application.
Common Applications in Industries
Chloroprene is widely used in industries such as automotive manufacturing, electronics, and construction due to its excellent resistance to weathering, oils, and chemicals. Polyurethane finds common applications in furniture, footwear, insulation, and adhesives, prized for its flexibility, durability, and cushioning properties. Understanding these materials helps you select the right polymer for your industry's specific performance requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chloroprene production involves significant emissions of hazardous chemicals such as HCl and VOCs, contributing to air and water pollution, whereas polyurethane manufacturing typically emits fewer toxic byproducts but relies heavily on fossil fuel-based raw materials. Polyurethane offers better potential for recycling and can incorporate bio-based polyols, enhancing its sustainability compared to chloroprene rubber, which has limited recyclability and biodegradability. Your choice between chloroprene and polyurethane should consider the environmental footprint of production, end-of-life disposal, and the availability of greener alternatives like bio-based polyurethanes.
Cost and Availability Overview
Chloroprene generally costs more than polyurethane due to its specialized chemical properties and limited production sources. Polyurethane is widely available and produced in large quantities, making it more cost-effective for various industrial applications. Your choice between chloroprene and polyurethane should consider both the budget constraints and the accessibility of these materials in your local market.
Choosing Between Chloroprene and Polyurethane
Choosing between chloroprene and polyurethane depends on application requirements such as chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability. Chloroprene is highly resistant to oils and weathering, making it ideal for automotive and industrial uses. Polyurethane offers superior abrasion resistance and elasticity, preferred in footwear and coatings where mechanical stress is frequent.
Chloroprene vs Polyurethane Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com