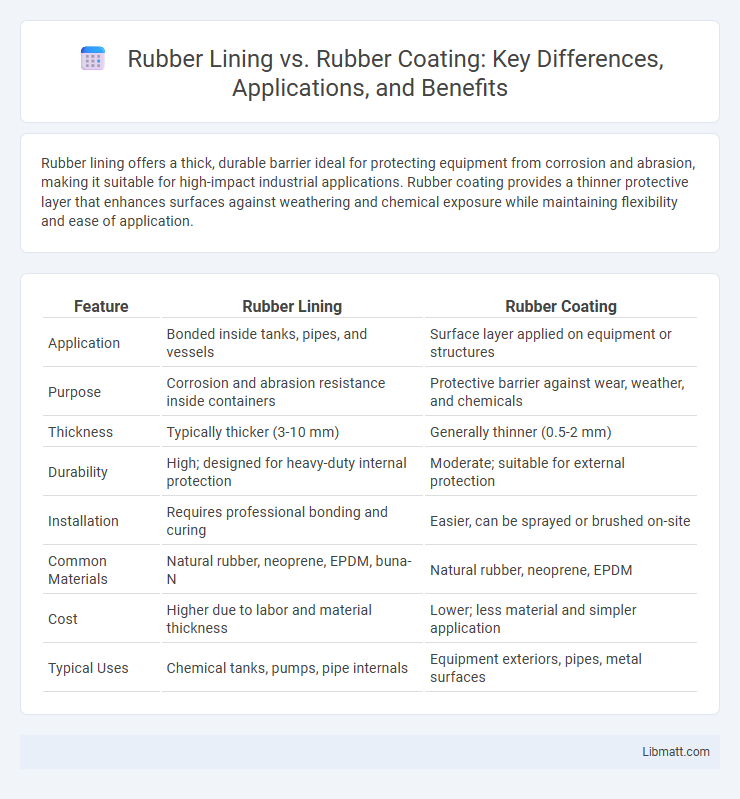
Rubber lining offers a thick, durable barrier ideal for protecting equipment from corrosion and abrasion, making it suitable for high-impact industrial applications. Rubber coating provides a thinner protective layer that enhances surfaces against weathering and chemical exposure while maintaining flexibility and ease of application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rubber Lining | Rubber Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Bonded inside tanks, pipes, and vessels | Surface layer applied on equipment or structures |
| Purpose | Corrosion and abrasion resistance inside containers | Protective barrier against wear, weather, and chemicals |
| Thickness | Typically thicker (3-10 mm) | Generally thinner (0.5-2 mm) |
| Durability | High; designed for heavy-duty internal protection | Moderate; suitable for external protection |
| Installation | Requires professional bonding and curing | Easier, can be sprayed or brushed on-site |
| Common Materials | Natural rubber, neoprene, EPDM, buna-N | Natural rubber, neoprene, EPDM |
| Cost | Higher due to labor and material thickness | Lower; less material and simpler application |
| Typical Uses | Chemical tanks, pumps, pipe internals | Equipment exteriors, pipes, metal surfaces |
Introduction to Rubber Lining and Rubber Coating
Rubber lining involves applying a thick, durable layer of natural or synthetic rubber onto surfaces to provide erosion, corrosion, and chemical resistance in industrial equipment like tanks and pipes. Rubber coating typically refers to spraying or brushing a thinner rubber layer on surfaces, offering flexible protection and waterproofing mainly for automotive and construction applications. Both methods enhance material longevity, but rubber lining is preferred for heavy-duty environments while rubber coating suits lighter, protective uses.
Key Differences Between Rubber Lining and Rubber Coating
Rubber lining involves applying a thick, durable sheet of rubber to protect surfaces from corrosion, abrasion, and chemical damage, commonly used in industrial tanks and pipes. Rubber coating is a thinner, sprayable layer designed to provide waterproofing, weather resistance, and surface protection for structures like roofs and metal frameworks. The key differences lie in application methods, thickness, and primary functions: rubber lining offers heavy-duty protection and chemical resistance, while rubber coating focuses on surface sealing and environmental protection.
Material Composition and Application Methods
Rubber lining consists of thick sheets or slabs of natural or synthetic rubber bonded to surfaces, providing durable chemical resistance and abrasion protection primarily in industrial pipelines and tanks. Rubber coating involves applying a thin, liquid rubber compound through spraying, brushing, or dipping, creating a flexible, waterproof barrier suited for surfaces like metal, concrete, or wood. You should choose rubber lining for heavy-duty wear resistance and rubber coating for versatile, ease-of-application surface protection.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Rubber lining offers superior abrasion resistance and chemical protection, making it ideal for industrial applications exposed to harsh environments and corrosive substances. Rubber coating provides a thinner, flexible protective layer that enhances surface durability but is less resistant to heavy wear and impact compared to lining. In terms of longevity, rubber lining generally delivers extended service life under extreme conditions, while rubber coating suits applications requiring moderate protection with easier reapplication.
Chemical Resistance: Lining vs Coating
Rubber lining offers superior chemical resistance by creating a thick, seamless barrier that protects surfaces from corrosive substances, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. Rubber coating provides a protective layer but is typically thinner and less resistant to aggressive chemicals, suitable for less demanding applications. Your choice between lining and coating should depend on the specific chemical exposure and durability requirements of your equipment.
Common Industrial Applications
Rubber lining is commonly used in industries such as chemical processing, mining, and wastewater treatment to provide corrosion resistance and protection against abrasive materials inside pipes and tanks. Rubber coating, on the other hand, is preferred for external surfaces requiring waterproofing and impact resistance, often seen in marine, automotive, and construction applications. Understanding the specific needs of your industrial environment will help determine whether rubber lining or rubber coating offers the most effective solution.
Cost Considerations and Budget Planning
Rubber lining typically involves higher initial costs due to precise application processes and the need for skilled labor, making it a longer-term investment with excellent durability and resistance to corrosion. Rubber coating tends to be more budget-friendly upfront, offering quicker application and easier maintenance but may require more frequent reapplications to maintain protection. When planning your budget, consider the total lifecycle costs and the specific operational demands to determine which rubber protection method provides the best value for your project.
Maintenance and Repair Requirements
Rubber lining offers superior durability with minimal maintenance, as it resists corrosion, abrasion, and chemical damage more effectively than rubber coatings. Rubber coatings often require more frequent inspections and repairs due to potential wear and peeling under harsh conditions. Your choice between rubber lining and coating significantly impacts long-term maintenance costs and repair frequency, making rubber lining preferable for demanding industrial applications.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Rubber lining provides superior chemical resistance, significantly reducing hazardous leaks and environmental contamination compared to rubber coating, which has a thinner application and higher wear risk. The dense, seamless nature of rubber lining enhances workplace safety by preventing exposure to harmful substances and ensuring durable corrosion protection in industrial settings. Both methods contribute to sustainability, but rubber lining's longer lifespan and reduced maintenance lower overall environmental impact through decreased resource consumption.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Rubber lining offers a durable protective layer bonded to metal surfaces, ideal for corrosion resistance in chemical processing and mining industries. Rubber coating provides a thinner, flexible layer suited for surface protection and aesthetic enhancement in automotive and industrial applications. Selecting the right solution depends on factors such as environmental exposure, abrasion resistance, and application requirements.
Rubber Lining vs Rubber Coating Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com