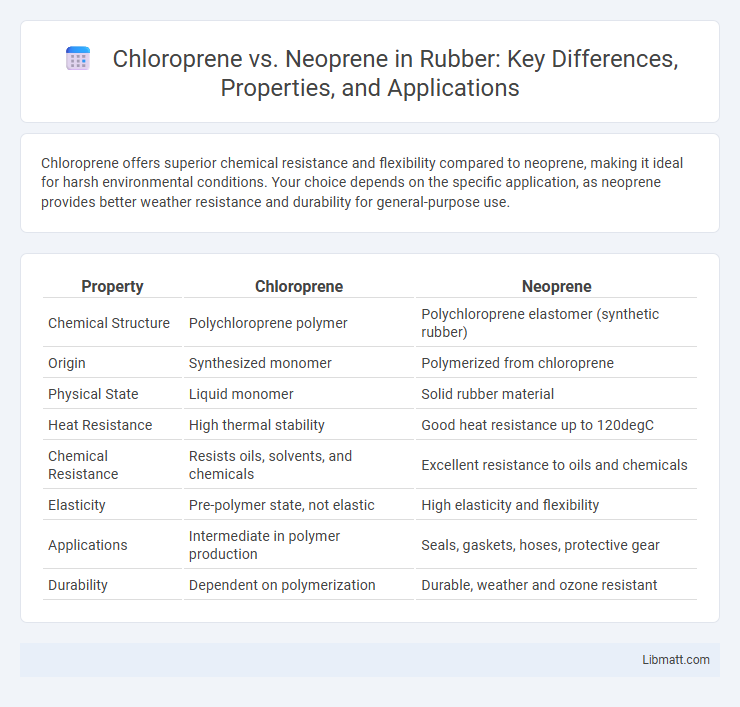
Chloroprene offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility compared to neoprene, making it ideal for harsh environmental conditions. Your choice depends on the specific application, as neoprene provides better weather resistance and durability for general-purpose use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chloroprene | Neoprene |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Polychloroprene polymer | Polychloroprene elastomer (synthetic rubber) |
| Origin | Synthesized monomer | Polymerized from chloroprene |
| Physical State | Liquid monomer | Solid rubber material |
| Heat Resistance | High thermal stability | Good heat resistance up to 120degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Resists oils, solvents, and chemicals | Excellent resistance to oils and chemicals |
| Elasticity | Pre-polymer state, not elastic | High elasticity and flexibility |
| Applications | Intermediate in polymer production | Seals, gaskets, hoses, protective gear |
| Durability | Dependent on polymerization | Durable, weather and ozone resistant |
Introduction to Chloroprene and Neoprene
Chloroprene is a synthetic rubber polymer primarily used in the production of neoprene, which is a versatile and durable material with excellent chemical stability and flexibility. Neoprene, derived from polymerized chloroprene, finds extensive applications in wetsuits, adhesives, and industrial coatings due to its resistance to oil, heat, and weathering. The molecular structure of chloroprene contributes to neoprene's strength and resilience, making it a popular choice in various commercial and industrial products.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Chloroprene and neoprene are closely related polymers, with chloroprene being the monomer and neoprene the synthetic rubber formed from its polymerization. Chloroprene's chemical structure features a vinyl group with chlorine substitution, which imparts unique properties during polymerization. Your understanding of this distinction helps explain neoprene's durability, chemical resistance, and elasticity derived from the specific arrangement of chloroprene units.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Chloroprene is primarily produced through the polymerization of chloroprene monomers, involving free radical or emulsion polymerization techniques to achieve desired molecular weight and properties. Neoprene, a synthetic rubber derived from chloroprene, undergoes vulcanization with sulfur or metal oxides to enhance its elasticity, chemical resistance, and durability. The key manufacturing difference lies in the initial polymer synthesis for chloroprene, while neoprene production emphasizes post-polymerization curing processes to tailor performance characteristics.
Key Physical Properties
Chloroprene and neoprene both exhibit excellent chemical stability and flexibility, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring durable elastomers. Chloroprene offers superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and flame compared to other rubbers, while neoprene boasts enhanced elasticity and tensile strength. Your selection between chloroprene and neoprene should consider factors like thermal stability, compressive strength, and resistance to oils and solvents for optimal performance.
Durability and Longevity
Chloroprene exhibits superior durability and longevity due to its enhanced resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering compared to neoprene. Neoprene maintains good flexibility and chemical resistance but tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to UV rays and harsh environmental conditions. Chloroprene's molecular structure provides greater tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for products requiring extended service life.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Chloroprene offers superior resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering compared to neoprene, making it ideal for outdoor applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Neoprene also resists oil and chemicals well but may degrade faster under prolonged sunlight and extreme temperatures. Your choice should consider the specific environmental factors your materials will face to ensure optimal durability and performance.
Applications and Common Uses
Chloroprene and neoprene are widely used in industrial applications due to their exceptional durability and chemical resistance. Chloroprene is commonly utilized in adhesives, coatings, and flexible molds, offering excellent resistance to oils and solvents. Neoprene finds extensive use in wetsuits, automotive parts, and gaskets, prized for its flexibility and weather-resistant properties.
Cost and Availability
Chloroprene generally costs more than neoprene due to its higher durability and superior chemical resistance, making it a premium choice for specialized applications. Neoprene is more widely available and affordable, commonly used in various industries for its versatility and cost-effectiveness. Your decision may depend on balancing budget constraints with the specific performance needs of your project.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Chloroprene and neoprene differ significantly in their environmental and health impacts, with neoprene generally considered safer due to advances in manufacturing that reduce toxic emissions and use less hazardous chemicals. Chloroprene production releases higher levels of toxic compounds such as dioxins and chlorinated hydrocarbons, posing greater risks to workers and surrounding ecosystems. Your choice between these materials should weigh neoprene's lower environmental footprint against performance needs in order to minimize health hazards and pollution.
Choosing Between Chloroprene and Neoprene
Choosing between chloroprene and neoprene depends on the specific application requirements such as chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability. Chloroprene offers superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for industrial and automotive uses. Neoprene provides enhanced flexibility and UV resistance, often favored in wetsuits and protective gear for water sports.
Chloroprene vs Neoprene Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com