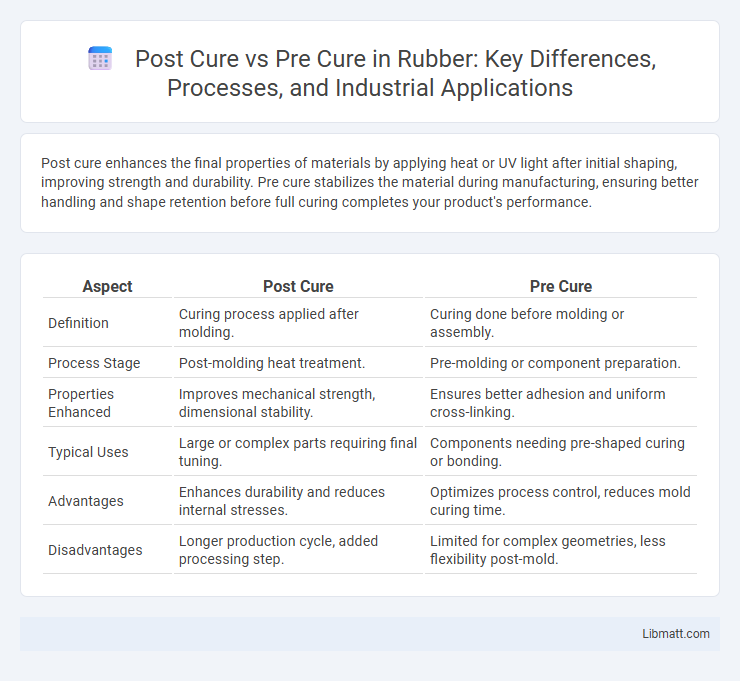
Post cure enhances the final properties of materials by applying heat or UV light after initial shaping, improving strength and durability. Pre cure stabilizes the material during manufacturing, ensuring better handling and shape retention before full curing completes your product's performance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Post Cure | Pre Cure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Curing process applied after molding. | Curing done before molding or assembly. |
| Process Stage | Post-molding heat treatment. | Pre-molding or component preparation. |
| Properties Enhanced | Improves mechanical strength, dimensional stability. | Ensures better adhesion and uniform cross-linking. |
| Typical Uses | Large or complex parts requiring final tuning. | Components needing pre-shaped curing or bonding. |
| Advantages | Enhances durability and reduces internal stresses. | Optimizes process control, reduces mold curing time. |
| Disadvantages | Longer production cycle, added processing step. | Limited for complex geometries, less flexibility post-mold. |
Introduction to Post Cure and Pre Cure
Post Cure and Pre Cure are critical processes in materials science, particularly in polymer and composite manufacturing, aimed at enhancing mechanical properties and chemical stability. Pre Cure refers to the initial partial curing stage that stabilizes the shape and structure of a material before final processing, while Post Cure involves subjecting the material to additional heat or radiation after initial curing to improve cross-linking and durability. Efficient control of both stages significantly influences the final product's strength, thermal resistance, and overall performance.
Defining Post Cure: What Does It Mean?
Post cure refers to the process of further hardening and stabilizing a 3D printed resin object after the initial print is complete, typically using UV light or heat. This step enhances the material's mechanical properties, improves durability, and ensures optimal dimensional accuracy. Understanding post cure is essential for achieving the best performance and longevity in your 3D printed parts.
Explaining Pre Cure: Key Concepts
Pre Cure refers to the initial curing stage of a material, typically in resin or composite manufacturing, where partial polymerization occurs to stabilize the shape before final processing. This phase enhances the material's handling properties and prevents deformation during subsequent steps. Understanding Pre Cure is crucial for optimizing manufacturing workflows and ensuring Your product attains the desired mechanical strength and dimensional accuracy after the final cure.
Main Differences Between Post Cure and Pre Cure
Post cure involves applying heat or UV light after initial 3D printing to enhance the material's mechanical properties and ensure complete polymerization, while pre cure refers to treating raw resin before printing to improve consistency and reduce print defects. The main differences lie in timing and purpose: pre cure conditions the material for optimal printing, whereas post cure finalizes strength and stability of the printed object. Understanding these stages helps you optimize print quality and durability depending on your project requirements.
Applications of Post Cure in Industry
Post cure processes enhance the final properties of 3D printed parts by improving material strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance, which are critical in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. Industries use post cure to ensure parts meet stringent regulatory standards, enabling durable prototypes and functional components. Your products benefit from increased performance and longevity when post cure methods are applied after initial printing.
Applications of Pre Cure in Manufacturing
Pre cure processes are essential in composite manufacturing, particularly in aerospace and automotive industries, where partial curing of resin matrix enhances handling and moldability before final curing. This step improves dimensional stability and reduces defects such as warping or sink marks, ensuring higher quality in carbon fiber and fiberglass components. Pre cure materials are also widely applied in electronic encapsulation and tooling, optimizing performance by balancing material flow and mechanical properties before full cure.
Advantages and Limitations of Post Cure
Post cure enhances polymer material properties such as strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability by completing the cross-linking process after initial curing, making it ideal for applications requiring high-performance durability. Limitations of post cure include increased production time and energy consumption, as well as potential thermal stress that may cause warping or degradation in temperature-sensitive materials. This process ensures superior mechanical properties but requires careful temperature control to avoid compromising component integrity.
Advantages and Limitations of Pre Cure
Pre Cure offers advantages such as improved dimensional stability and reduced residual stresses, resulting in enhanced mechanical properties of the final product. It enables easier handling and machining between curing stages, increasing production flexibility and efficiency. However, limitations include longer overall processing times and the requirement for precise control of temperature and timing to avoid incomplete curing or defects.
Comparing Performance: Post Cure vs Pre Cure
Post Cure enhances material properties by completing polymerization after the initial shaping, resulting in superior mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and dimensional stability compared to Pre Cure processes. Pre Cure partially polymerizes materials to a firm state, facilitating easier handling but often leading to lower final performance metrics. Your choice between Post Cure and Pre Cure directly impacts the durability and functionality of the finished product, with Post Cure typically providing more reliable and consistent results.
Choosing Between Post Cure and Pre Cure: Factors to Consider
Choosing between post cure and pre cure processes depends on factors such as the type of material, the desired mechanical properties, and the final application of the product. Post cure enhances polymer cross-linking after initial shaping, improving strength and thermal resistance, whereas pre cure stabilizes the material before further processing, ensuring dimensional accuracy and reduced defects. Your decision should weigh processing time, equipment availability, and the critical performance requirements of the end product.
Post Cure vs Pre Cure Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com