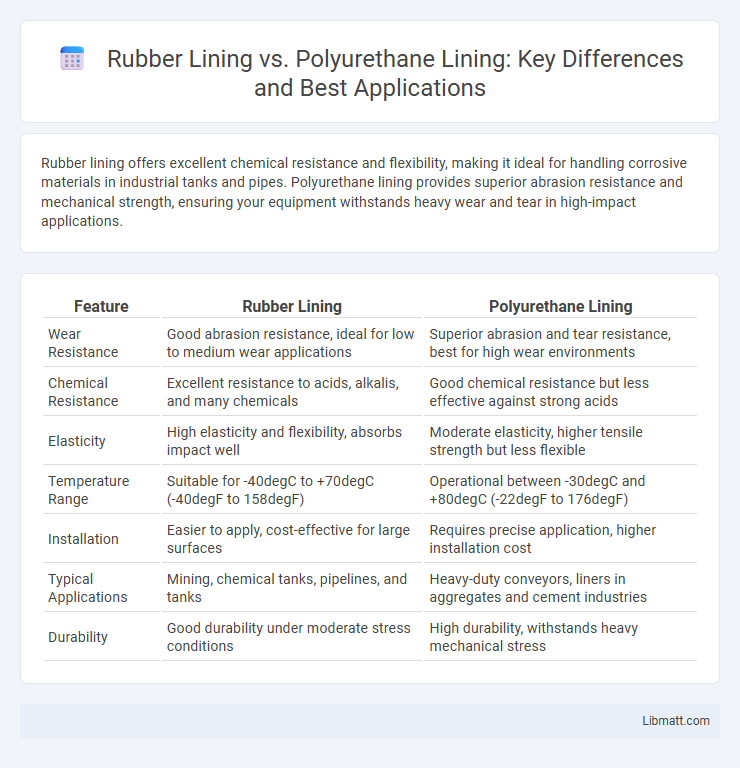
Rubber lining offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for handling corrosive materials in industrial tanks and pipes. Polyurethane lining provides superior abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, ensuring your equipment withstands heavy wear and tear in high-impact applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rubber Lining | Polyurethane Lining |
|---|---|---|
| Wear Resistance | Good abrasion resistance, ideal for low to medium wear applications | Superior abrasion and tear resistance, best for high wear environments |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and many chemicals | Good chemical resistance but less effective against strong acids |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and flexibility, absorbs impact well | Moderate elasticity, higher tensile strength but less flexible |
| Temperature Range | Suitable for -40degC to +70degC (-40degF to 158degF) | Operational between -30degC and +80degC (-22degF to 176degF) |
| Installation | Easier to apply, cost-effective for large surfaces | Requires precise application, higher installation cost |
| Typical Applications | Mining, chemical tanks, pipelines, and tanks | Heavy-duty conveyors, liners in aggregates and cement industries |
| Durability | Good durability under moderate stress conditions | High durability, withstands heavy mechanical stress |
Introduction to Rubber and Polyurethane Linings
Rubber linings provide excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making them ideal for protecting equipment from abrasion and corrosive substances in industries such as mining, chemical processing, and wastewater treatment. Polyurethane linings offer superior wear resistance, high tensile strength, and resistance to cuts and tears, which enhances their performance in heavy-duty applications like conveyor systems and material handling. Both linings serve as protective coatings that extend the lifespan of equipment by preventing wear and corrosion under harsh operating conditions.
Material Composition and Properties
Rubber lining consists primarily of natural or synthetic elastomers such as EPDM, neoprene, and nitrile, offering excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and impact absorption, ideal for corrosion protection and abrasion resistance in piping and tanks. Polyurethane lining is composed of thermoplastic polymers with high tensile strength, superior abrasion resistance, and remarkable durability against mechanical wear and chemical exposure, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications with high-impact and abrasive environments. The material properties of rubber provide greater elasticity and softness, while polyurethane offers enhanced hardness and resilience, influencing their selection based on operational demands and environmental factors.
Application Areas: Rubber vs Polyurethane
Rubber lining excels in chemical processing, mining, and wastewater treatment due to its superior resistance to acids, alkalis, and abrasion. Polyurethane lining is favored in industries like mining, pulp and paper, and steel manufacturing for its outstanding wear resistance and toughness under impact. Both materials protect equipment effectively, but your choice depends on the specific environmental conditions and mechanical stresses of your application.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Rubber lining offers excellent resistance to abrasion, impact, and chemical corrosion, making it highly durable in environments with moderate wear and exposure to harsh chemicals. Polyurethane lining surpasses rubber in wear resistance, particularly against abrasive materials and high-impact conditions, due to its superior tensile strength and toughness. Industries requiring extended service life with heavy abrasive wear favor polyurethane lining for its longer durability compared to traditional rubber lining.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Rubber lining offers superior resistance to highly acidic and alkaline substances, making it ideal for sulfuric acid and caustic soda environments. Polyurethane lining excels in resisting abrasion and hydrocarbon solvents but can degrade faster in strong acidic conditions compared to rubber. Selecting between rubber and polyurethane linings depends on specific chemical exposure, with rubber preferred for harsh chemicals and polyurethane for mechanical wear combined with moderate chemical contact.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Rubber lining generally offers a lower upfront cost compared to polyurethane lining, making it a cost-effective choice for abrasion and corrosion resistance in many industrial applications. Polyurethane lining, while more expensive initially, provides superior durability and longer lifespan, which can reduce maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Evaluating your specific operational conditions and budget will help determine which lining maximizes economic benefits and minimizes total cost of ownership.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Rubber lining installation requires precise surface preparation and seamless curing to ensure optimal adhesion and durability, whereas polyurethane lining involves a faster application process with minimal downtime due to its rapid curing properties. Maintenance of rubber linings typically involves routine inspections for tears or abrasions, as repairs can be more labor-intensive compared to polyurethane, which offers greater resistance to wear and chemical degradation, reducing overall maintenance frequency. Both materials demand specialized knowledge for proper installation, but polyurethane linings generally provide easier and more cost-effective upkeep in industrial environments.
Performance in Harsh Environments
Rubber lining offers superior resistance to abrasion, impact, and chemical corrosion, making it ideal for harsh environments such as mining, wastewater treatment, and chemical processing. Polyurethane lining provides exceptional wear resistance and tensile strength, excelling in applications involving high-impact and abrasive materials like sand, gravel, and slurry. Both materials enhance equipment durability, but rubber's flexibility and chemical resistance make it more suitable for acidic or highly corrosive conditions.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Rubber lining offers superior chemical resistance and recyclability, making it a sustainable choice for industries handling corrosive materials, while polyurethane lining is prized for its durability and abrasion resistance, extending the lifespan of equipment and reducing waste. Rubber's biodegradability and potential for reuse contribute to lower environmental impact compared to petroleum-based polyurethane, which may persist longer in landfills. Selecting between rubber and polyurethane lining depends on the specific application's environmental requirements and the lifecycle analysis of material durability and disposal.
Choosing the Right Lining for Your Application
Rubber lining offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for handling corrosive substances in mining and chemical industries, whereas polyurethane lining provides superior abrasion resistance and durability, suited for heavy-wear environments like slurry transport and material handling. Selecting the right lining depends on factors such as chemical exposure, impact resistance, temperature tolerance, and operational conditions, ensuring optimal performance and extended equipment life. Evaluating the specific application requirements and environmental conditions will guide the choice between rubber and polyurethane linings for maximum efficiency and protection.
Rubber Lining vs Polyurethane Lining Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com