Latex offers superior elasticity and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring high stretch and comfort, while solid rubber provides enhanced durability and resistance to wear under heavy use. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize softness and responsiveness or long-lasting toughness.
Table of Comparison
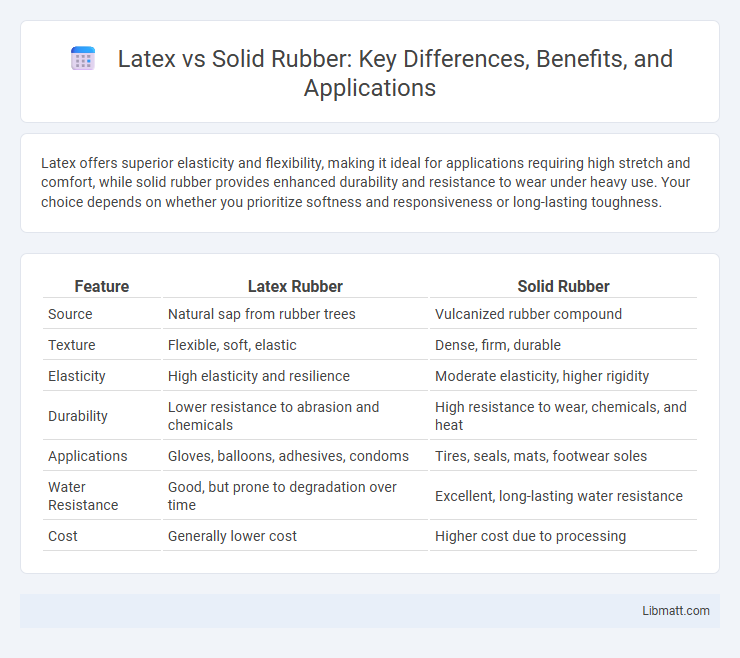
| Feature | Latex Rubber | Solid Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural sap from rubber trees | Vulcanized rubber compound |
| Texture | Flexible, soft, elastic | Dense, firm, durable |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and resilience | Moderate elasticity, higher rigidity |
| Durability | Lower resistance to abrasion and chemicals | High resistance to wear, chemicals, and heat |
| Applications | Gloves, balloons, adhesives, condoms | Tires, seals, mats, footwear soles |
| Water Resistance | Good, but prone to degradation over time | Excellent, long-lasting water resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to processing |
Introduction to Latex and Solid Rubber
Latex is a natural material derived from the sap of rubber trees, known for its elasticity, durability, and hypoallergenic properties. Solid rubber, made from synthetic or natural rubber compounds, offers enhanced resilience, abrasion resistance, and versatility for various industrial applications. Understanding the differences between latex and solid rubber helps you select the right material based on flexibility, strength, and environmental conditions.
Material Composition and Properties
Latex is a natural polymer derived from rubber tree sap, known for its elasticity, flexibility, and ability to return to its original shape after stretching. Solid rubber, often made from synthetic or natural rubber compounds, features higher density and durability, offering superior resistance to abrasion and wear. Your choice between latex and solid rubber depends on the need for softness and stretchability versus robustness and long-lasting performance.
Manufacturing Processes
Latex products are typically manufactured using a dipping process, where liquid latex is poured or dipped onto molds and then vulcanized through heating to create flexible, lightweight items. Solid rubber manufacturing involves mixing raw rubber with additives, followed by shaping through compression or injection molding and curing under heat and pressure to achieve a durable, dense material. Your choice between latex and solid rubber hinges on the specific application requirements and the manufacturing techniques that best suit the desired material properties.
Durability and Longevity
Latex offers excellent flexibility but tends to deteriorate faster with exposure to sunlight and ozone, reducing its overall durability compared to solid rubber. Solid rubber is highly resistant to wear, abrasions, and environmental conditions, ensuring longer-lasting performance in demanding applications. Your choice should prioritize solid rubber for maximum longevity and consistent durability in harsh environments.
Comfort and Flexibility
Latex offers superior comfort and flexibility due to its natural elasticity, contouring easily to body shapes and providing excellent support with a responsive bounce. Solid rubber, while durable, tends to be firmer and less adaptable to pressure, resulting in reduced cushioning and limited movement freedom. For applications requiring enhanced comfort and flexibility, latex is typically the preferred material over solid rubber.
Applications and Use Cases
Latex is widely used in flexible, lightweight products such as gloves, balloons, and adhesive materials due to its excellent elasticity and comfort. Solid rubber finds extensive applications in heavy-duty products like tires, seals, and vibration dampening components because of its durability and resistance to deformation. Industries such as healthcare rely on latex for disposable items, while automotive and industrial sectors prioritize solid rubber for long-lasting performance under mechanical stress.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Latex is a biodegradable material derived from natural rubber trees, making it more environmentally sustainable compared to solid rubber, which is often synthetic and petroleum-based. The production of latex involves less energy consumption and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions than synthetic solid rubber manufacturing. Disposal of latex products results in lower environmental pollution due to its natural decomposition process, whereas solid rubber can persist in landfills for decades, contributing to long-term waste problems.
Cost Comparison
Latex materials typically cost more than solid rubber due to their natural sourcing and manufacturing processes, which involve harvesting sap from rubber trees and complex treatment methods. Solid rubber offers a more affordable option as it is often produced synthetically with simpler production techniques, making it budget-friendly for large-scale or industrial applications. If you prioritize durability and elasticity within a reasonable budget, understanding the cost differences between latex and solid rubber can help optimize your purchasing decisions.
Maintenance and Care
Latex requires gentle cleaning with mild soap and lukewarm water, avoiding exposure to oils and direct sunlight to prevent material degradation. Solid rubber is more resilient, tolerating harsher cleaning agents and less sensitive to environmental factors, making maintenance easier and less frequent. Proper storage for both materials involves keeping them in cool, dry places away from sharp objects to extend their lifespan.
Choosing the Right Material: Latex or Solid Rubber
Latex offers superior flexibility and elasticity, making it ideal for applications requiring stretchability and comfort, such as gloves and balloons. Solid rubber provides enhanced durability, resistance to abrasion, and structural support, making it suitable for heavy-duty products like tires and industrial seals. Selecting between latex and solid rubber depends on prioritizing elasticity and tactile sensitivity versus strength and long-lasting resilience.
Latex vs Solid Rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com