Antioxidants protect materials from oxidative degradation caused by exposure to oxygen and heat, while antiozonants specifically shield rubber and polymers from damage induced by ozone exposure. Your choice depends on the type of environmental stress the material will most frequently encounter.
Table of Comparison
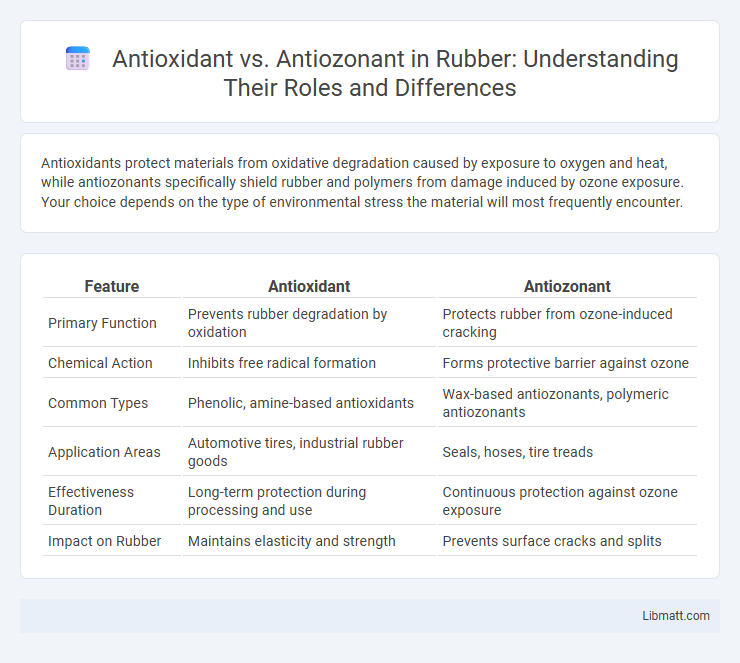
| Feature | Antioxidant | Antiozonant |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Prevents rubber degradation by oxidation | Protects rubber from ozone-induced cracking |
| Chemical Action | Inhibits free radical formation | Forms protective barrier against ozone |
| Common Types | Phenolic, amine-based antioxidants | Wax-based antiozonants, polymeric antiozonants |
| Application Areas | Automotive tires, industrial rubber goods | Seals, hoses, tire treads |
| Effectiveness Duration | Long-term protection during processing and use | Continuous protection against ozone exposure |
| Impact on Rubber | Maintains elasticity and strength | Prevents surface cracks and splits |
Introduction to Antioxidants and Antiozonants
Antioxidants protect materials from degradation caused by oxidation by neutralizing free radicals, a process crucial in preserving polymers, rubbers, and lubricants. Antiozonants specifically prevent ozone-induced damage to elastomers by reacting with ozone molecules, thus maintaining material elasticity and durability. Your choice between antioxidants and antiozonants depends on the environmental stressors affecting the material, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Understanding Oxidative Degradation
Oxidative degradation occurs when oxygen interacts with materials, causing deterioration and loss of performance. Antioxidants slow this process by neutralizing free radicals, while antiozonants specifically protect against ozone attacks that cause cracking in polymers. Understanding these differences helps you select the right additive to enhance the durability of rubber and plastic products in oxidative environments.
What Are Antioxidants?
Antioxidants are molecules that inhibit the oxidation process, preventing the formation of free radicals that can damage cells, oils, and polymers. Common antioxidants include vitamin E, BHT (butylated hydroxytoluene), and natural extracts like rosemary, which enhance the stability and lifespan of products by slowing down degradation. In contrast to antiozonants that specifically protect materials from ozone exposure, antioxidants primarily target oxidation reactions to preserve quality and functionality.
What Are Antiozonants?
Antiozonants are chemical additives used primarily in rubber and polymer industries to protect materials from ozone-induced cracking and degradation. While antioxidants prevent oxidation by neutralizing free radicals, antiozonants specifically shield your products from ozone attack by forming a protective barrier or reacting with ozone to prevent damage. Understanding the role of antiozonants is essential for enhancing the durability and lifespan of rubber components exposed to outdoor environments.
Key Differences Between Antioxidants and Antiozonants
Antioxidants protect materials by neutralizing free radicals generated through oxidation processes, while antiozonants specifically inhibit ozone-induced degradation in polymers like rubber. Your products benefit from antioxidants primarily by preventing oxidative aging, whereas antiozonants are essential for extending durability against environmental ozone exposure. Both play critical roles in enhancing the lifespan of materials but target different chemical threats.
Mechanisms of Action: How They Work
Antioxidants inhibit oxidation by neutralizing free radicals through electron donation, thereby preventing chain reactions that damage materials and biological cells. Antiozonants specifically protect polymers from ozone attack by reacting with ozone molecules before they can degrade the material, often forming stable, less reactive products. Your choice between antioxidant and antiozonant depends on the environmental stressor--oxidative or ozone exposure--to effectively enhance the longevity and performance of your products.
Industrial Applications of Antioxidants
Antioxidants play a crucial role in industrial applications by preventing the oxidation of materials such as polymers, fuels, and lubricants, thereby extending product life and maintaining performance. Their ability to inhibit free radical formation helps protect products from degradation caused by heat, light, and oxygen exposure during manufacturing and storage. You can enhance the durability and stability of industrial goods by selecting appropriate antioxidants tailored to specific environmental conditions and product requirements.
Industrial Applications of Antiozonants
Antiozonants are crucial in industrial applications for protecting rubber products such as tires, seals, and conveyor belts from ozone-induced cracking and degradation. These additives work by scavenging ozone molecules and preventing them from attacking the polymer chains, thereby extending the lifespan and performance of industrial materials. Your choice of antiozonants can significantly enhance durability in environments with high ozone exposure, ensuring product reliability and safety.
Importance in Rubber and Polymer Industries
Antioxidants and antiozonants play crucial roles in extending the life and performance of rubber and polymer products by preventing oxidative degradation and ozone-induced cracking. Antioxidants inhibit the chemical reactions caused by oxygen exposure, while antiozonants specifically protect against ozone attack by forming protective barriers or scavenging ozone molecules. Their combined use enhances durability, flexibility, and resistance to environmental stresses, making them indispensable in tire manufacturing, conveyor belts, seals, and automotive components.
Future Trends in Antioxidant and Antiozonant Technologies
Future trends in antioxidant and antiozonant technologies emphasize the development of bio-based and nanotechnology-enhanced compounds to improve polymer durability against oxidative and ozone-induced degradation. Innovations include multifunctional additives that combine antioxidant and antiozonant properties for extended service life in automotive and industrial applications. Advances in molecular design and sustainable sourcing are driving more effective, eco-friendly solutions in combating polymer aging and environmental stressors.
Antioxidant vs Antiozonant Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com