Latex is a natural rubber made from the sap of rubber trees, offering excellent elasticity and biodegradability, while synthetic rubber is man-made from petroleum-based chemicals, providing enhanced resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize eco-friendliness and natural properties or durability and chemical resistance for specific applications.
Table of Comparison
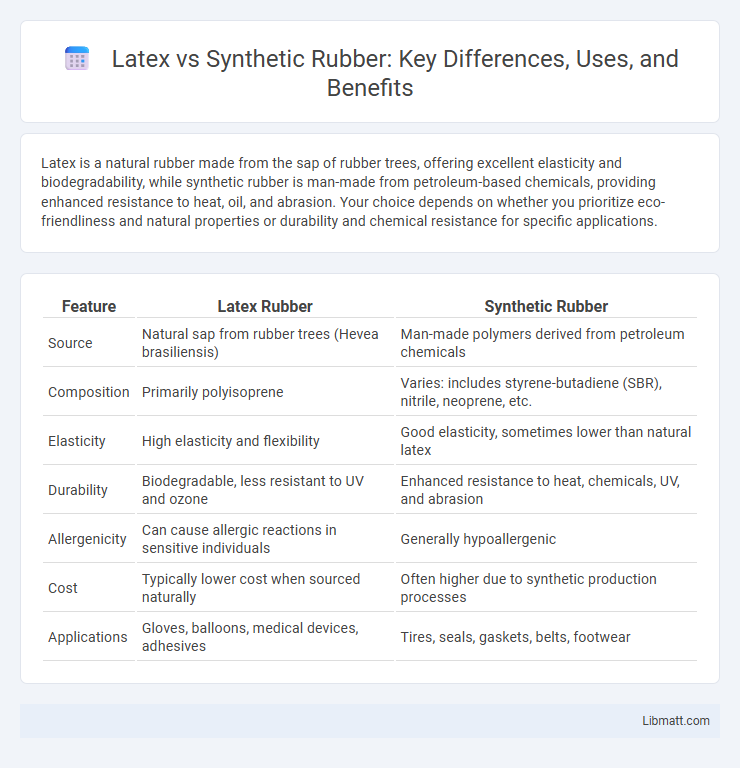
| Feature | Latex Rubber | Synthetic Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural sap from rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis) | Man-made polymers derived from petroleum chemicals |
| Composition | Primarily polyisoprene | Varies: includes styrene-butadiene (SBR), nitrile, neoprene, etc. |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and flexibility | Good elasticity, sometimes lower than natural latex |
| Durability | Biodegradable, less resistant to UV and ozone | Enhanced resistance to heat, chemicals, UV, and abrasion |
| Allergenicity | Can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals | Generally hypoallergenic |
| Cost | Typically lower cost when sourced naturally | Often higher due to synthetic production processes |
| Applications | Gloves, balloons, medical devices, adhesives | Tires, seals, gaskets, belts, footwear |
Introduction to Latex and Synthetic Rubber
Latex is a natural polymer harvested from the sap of rubber trees, prized for its elasticity, biodegradability, and hypoallergenic properties. Synthetic rubber, derived from petrochemical sources like styrene and butadiene, offers enhanced resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion compared to natural latex. Your choice between latex and synthetic rubber depends on the required durability, environmental impact, and specific application needs.
Key Differences Between Latex and Synthetic Rubber
Key differences between latex and synthetic rubber lie in their origin and properties; latex is a natural polymer harvested from rubber trees, while synthetic rubber is man-made through chemical processes using petroleum byproducts. Latex offers superior elasticity, biodegradability, and hypoallergenic qualities, whereas synthetic rubber provides enhanced resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion. Your choice between the two depends on the specific application requirements, such as environmental impact or durability.
Composition and Sources
Latex is a natural polymer primarily derived from the sap of rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis), consisting mainly of cis-1,4-polyisoprene suspended in water. Synthetic rubber is composed of various petrochemical-based monomers such as styrene, butadiene, and isoprene, produced through polymerization processes in industrial reactors. The primary source of latex is renewable plant-based material, while synthetic rubber originates from non-renewable fossil fuels.
Manufacturing Processes
Latex is produced primarily through the natural harvesting of sap from rubber trees, followed by coagulation, washing, and drying processes that maintain its elasticity and biodegradability. Synthetic rubber manufacturing involves polymerization techniques such as emulsion or solution polymerization, using petrochemical raw materials like styrene and butadiene to create specific rubber types tailored for durability and resistance. The distinct production methods impact material properties, with natural latex offering superior flexibility and synthetic rubber providing enhanced chemical and temperature resilience.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Latex, a natural polymer derived from rubber trees, exhibits high elasticity, tensile strength, and excellent biodegradability, while synthetic rubber, produced through polymerization of petrochemicals such as styrene and butadiene, offers superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion. Chemically, latex consists primarily of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, whereas synthetic rubber varies in composition depending on the monomers used, allowing customization for specific physical properties. Both materials differ significantly in molecular structure, impacting their durability, elasticity, and environmental degradation rates.
Applications and Uses
Latex is primarily used in medical gloves, balloons, and adhesives due to its excellent elasticity and biodegradability, making it ideal for sensitive skin applications and environmentally conscious products. Synthetic rubber, including types like neoprene and styrene-butadiene, finds extensive use in automotive tires, industrial hoses, and seals, offering superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion for demanding conditions. The choice between latex and synthetic rubber depends on the specific application requirements for performance, durability, and environmental factors.
Durability and Performance
Latex offers excellent elasticity and natural biodegradability but tends to wear out faster under constant friction and exposure to oils compared to synthetic rubber. Synthetic rubber, engineered for specific conditions, provides superior durability against abrasion, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, maintaining consistent performance in demanding environments. Your choice hinges on whether natural flexibility or enhanced resistance aligns better with your application needs.
Health and Environmental Impact
Latex, derived from natural rubber trees, is biodegradable and generally considered eco-friendly, but it can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals due to natural proteins. Synthetic rubber, made from petroleum-based polymers, poses environmental concerns during production and disposal because it is non-biodegradable and contributes to pollution. Your choice between latex and synthetic rubber should consider potential allergies and the environmental footprint associated with each material.
Cost Comparison and Market Trends
Latex generally incurs higher production costs due to its natural harvesting process, while synthetic rubber benefits from large-scale petrochemical manufacturing, making it more cost-effective for mass production. Market trends indicate increasing demand for synthetic rubber in automotive and industrial applications driven by its consistent quality and versatility, whereas latex remains preferred in medical and consumer products for its biodegradability. Price volatility in natural rubber markets due to climate dependency contrasts with the more stable pricing of synthetic rubber linked to petroleum market fluctuations.
Choosing the Right Material: Latex or Synthetic Rubber
Choosing between latex and synthetic rubber depends on your specific needs such as elasticity, durability, and allergen concerns. Latex offers superior flexibility and natural biodegradability, making it ideal for applications requiring comfort and environmental consideration, while synthetic rubber provides enhanced resistance to chemicals, heat, and aging, suitable for industrial or heavy-duty use. Assessing the intended application environment and potential allergies will help you determine the most effective material for your project.
Latex vs Synthetic rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com