Buna N and Nitrile are essentially the same material, referring to a synthetic rubber known for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and other chemicals. If your application involves exposure to petroleum-based fluids, Buna N provides durable performance and reliable sealing properties.
Table of Comparison
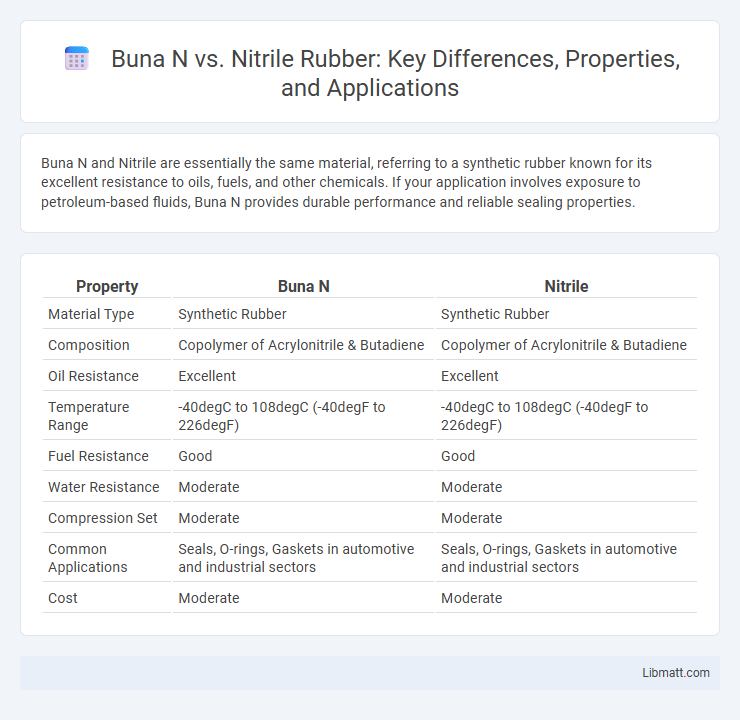
| Property | Buna N | Nitrile |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Rubber | Synthetic Rubber |
| Composition | Copolymer of Acrylonitrile & Butadiene | Copolymer of Acrylonitrile & Butadiene |
| Oil Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 108degC (-40degF to 226degF) | -40degC to 108degC (-40degF to 226degF) |
| Fuel Resistance | Good | Good |
| Water Resistance | Moderate | Moderate |
| Compression Set | Moderate | Moderate |
| Common Applications | Seals, O-rings, Gaskets in automotive and industrial sectors | Seals, O-rings, Gaskets in automotive and industrial sectors |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate |
Introduction to Buna N and Nitrile
Buna N, also known as Nitrile, is a synthetic rubber widely used for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and other chemicals, making it ideal for seals and gaskets in automotive and industrial applications. This copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene offers variations in acrylonitrile content, influencing its flexibility and temperature resistance. Your choice between Buna N and Nitrile commonly refers to the same material, emphasizing durability and performance in harsh environments.
Chemical Composition: Buna N vs Nitrile
Buna N and Nitrile are essentially the same synthetic rubber, composed primarily of acrylonitrile and butadiene polymers. The key difference lies in the acrylonitrile content, which typically ranges from 18% to 50% in Nitrile, affecting oil resistance and flexibility, while Buna N often refers to the same copolymer with standard acrylonitrile ratios. Understanding this chemical composition allows you to select the optimal material for applications requiring resistance to oils, fuels, and other chemicals.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Buna N, also known as Nitrile rubber, is produced through the copolymerization of acrylonitrile and butadiene using emulsion polymerization techniques, offering controlled molecular structure and properties. Manufacturing of Nitrile variants involves adjusting acrylonitrile content to tailor resistance to oils and chemicals, typically via emulsion or mass polymerization methods. Both processes emphasize temperature control and catalyst selection to optimize polymer chain length and cross-link density, critical for the elastomer's durability and performance in industrial applications.
Key Physical Properties
Buna N and Nitrile are essentially the same synthetic rubber, known for their excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, with a typical tensile strength ranging from 15 to 25 MPa and elongation at break between 300% to 500%. The material exhibits a temperature range of approximately -40degC to 120degC, making it suitable for various industrial applications including seals, gaskets, and hoses. Buna N/Nitrile also offers good abrasion resistance and low gas permeability, further contributing to its versatility in harsh environments.
Performance in Different Environments
Buna N and Nitrile, often used interchangeably, offer excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making them suitable for automotive and industrial applications. Buna N performs well in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 108degC, while some Nitrile variants can withstand up to 120degC, providing better heat resistance. Your choice between these elastomers depends on specific operational environments, especially exposure to heat, oils, and flexing demands.
Chemical Resistance: Similarities and Differences
Buna N and Nitrile are essentially the same material, both known as acrylonitrile butadiene rubber, offering excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and other hydrocarbons. Their chemical resistance shows strong performance against aliphatic hydrocarbons and many common chemicals but reduced stability when exposed to ketones, esters, and strong acids. Variations in acrylonitrile content affect resistance properties, with higher acrylonitrile levels improving resistance to oils but decreasing flexibility at low temperatures.
Common Applications for Buna N and Nitrile
Buna N and Nitrile are widely used in automotive and industrial applications due to their excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals. Common applications include gaskets, seals, O-rings, and fuel system components where durability and oil resistance are critical. Your machinery benefits from Buna N and Nitrile materials by ensuring reliable performance in environments exposed to petroleum-based fluids.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Buna N and Nitrile are essentially the same synthetic rubber, often used interchangeably in industrial applications, with Nitrile commonly referring to the copolymer form. Cost-wise, Buna N is generally more affordable due to its widespread production and varied applications in fuel and oil-resistant products, making it budget-friendly for manufacturers and suppliers. Availability is high for both Buna N and Nitrile globally, but specific grades tailored for specialized uses may influence price and supply, affecting your sourcing decisions in sectors such as automotive and aerospace.
Choosing Between Buna N and Nitrile
Choosing between Buna N and nitrile requires understanding that Buna N is a specific type of nitrile rubber commonly used in seals, gaskets, and fuel hoses due to its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and other chemicals. Nitrile, or NBR (nitrile butadiene rubber), offers various formulations to balance properties like hardness, temperature resistance, and elasticity, making it versatile for automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. Selecting the right material depends on the specific environmental conditions and chemical exposure, with Buna N typically favored for its cost-effective durability in mid-temperature ranges.
Summary: Which Material to Use?
Buna N and Nitrile are essentially the same material, with Buna N being a specific brand name for Nitrile rubber known for its exceptional resistance to oils, fuels, and other chemicals. Choose Buna N/Nitrile for applications requiring strong durability and resistance to petroleum-based fluids in automotive, industrial, and aerospace industries. For environments involving extreme temperatures or exposure to specific solvents, alternative elastomers like Viton or EPDM may be more suitable.
Buna N vs Nitrile Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com