Ozone resistance measures a material's ability to withstand degradation from ozone exposure, preventing cracking and brittleness, while UV resistance refers to how well it can endure ultraviolet light without fading, weakening, or breaking down. Your choice depends on the environment the material will face, especially if it will be exposed mainly to airborne pollutants or prolonged sunlight.
Table of Comparison
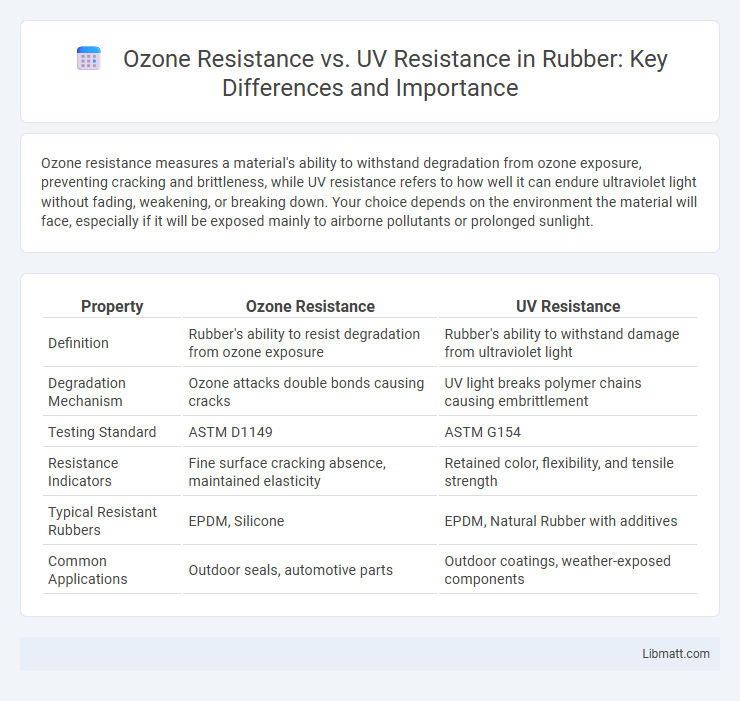
| Property | Ozone Resistance | UV Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rubber's ability to resist degradation from ozone exposure | Rubber's ability to withstand damage from ultraviolet light |
| Degradation Mechanism | Ozone attacks double bonds causing cracks | UV light breaks polymer chains causing embrittlement |
| Testing Standard | ASTM D1149 | ASTM G154 |
| Resistance Indicators | Fine surface cracking absence, maintained elasticity | Retained color, flexibility, and tensile strength |
| Typical Resistant Rubbers | EPDM, Silicone | EPDM, Natural Rubber with additives |
| Common Applications | Outdoor seals, automotive parts | Outdoor coatings, weather-exposed components |
Introduction to Ozone and UV Resistance
Ozone resistance refers to a material's ability to withstand degradation caused by ozone exposure, which breaks down chemical bonds in polymers, leading to cracks and loss of mechanical properties. UV resistance measures how well a material can resist damage from ultraviolet light exposure, preventing discoloration, weakening, and surface erosion. Both resistances are critical factors in the durability of outdoor materials, especially rubber and plastics used in automotive and construction industries.
Understanding Ozone Resistance in Materials
Ozone resistance in materials refers to their ability to withstand degradation caused by exposure to ozone, a highly reactive form of oxygen that can cause cracking and deterioration in polymers. Materials with high ozone resistance, such as EPDM rubber and certain synthetic elastomers, maintain flexibility and structural integrity even after prolonged ozone exposure. This property is critical for applications in automotive tires, seals, and outdoor equipment where ozone-induced wear can compromise performance and safety.
Basics of UV Resistance and Its Importance
UV resistance refers to a material's ability to withstand degradation caused by ultraviolet light exposure, which can lead to discoloration, brittleness, and loss of mechanical properties. This characteristic is crucial for products used outdoors, such as polymers, coatings, and automotive parts, as it ensures longevity and maintains performance under sunlight. Understanding UV resistance helps you select materials that protect against UV-induced damage, improving durability and reducing maintenance costs.
Key Differences: Ozone vs UV Resistance
Ozone resistance refers to a material's ability to withstand the deteriorating effects of ozone exposure, which typically causes cracking and degradation in rubber and elastomers. UV resistance measures how well materials endure ultraviolet radiation from sunlight, preventing discoloration, loss of strength, and surface breakdown. Key differences lie in the type of damage--ozone targets chemical bonds in elastomers causing cracks, while UV exposure causes photo-oxidative damage affecting polymers and coatings.
Mechanisms of Ozone Degradation
Ozone resistance involves materials' ability to withstand oxidative attacks from ozone molecules, which break down polymer chains through ozonolysis, leading to cracks and loss of elasticity. UV resistance, on the other hand, protects materials from photodegradation caused by ultraviolet radiation that disrupts chemical bonds and generates free radicals. Your choice of material should consider these mechanisms to ensure durability under specific environmental stresses such as ozone exposure or intense sunlight.
Effects of UV Exposure on Materials
UV exposure degrades polymers by breaking chemical bonds, leading to discoloration, surface cracking, and loss of mechanical strength. Materials with high UV resistance contain additives like UV stabilizers and absorbers that prevent photodegradation and extend service life. Ozone resistance primarily protects against oxidative damage from ozone molecules, which typically causes surface cracking but does not address UV-induced molecular breakdown.
Testing Methods for Ozone and UV Resistance
Testing methods for ozone resistance typically involve exposing materials to controlled ozone concentrations in an ozone chamber, simulating real-world environmental conditions to assess crack formation and degradation over time. UV resistance testing uses UV weathering chambers that emit specific wavelengths, measuring changes in color, tensile strength, and surface properties after prolonged exposure. Your choice of testing ensures materials can withstand environmental stressors, maintaining durability and performance in ozone-rich or sun-exposed applications.
Common Applications Requiring Resistance
Ozone resistance is crucial in automotive tires, rubber seals, and conveyor belts exposed to industrial pollutants, ensuring durability against ozone-induced cracking. UV resistance is vital for outdoor furniture, building facades, and agricultural films, protecting materials from degradation and color fading caused by ultraviolet radiation. Both resistances enhance the longevity and performance of materials utilized in harsh environmental conditions.
Enhancing Ozone and UV Protection in Products
Enhancing ozone and UV protection in products involves incorporating specialized additives such as anti-ozonants and UV stabilizers that prevent material degradation caused by ozone exposure and ultraviolet radiation. Selecting polymers with inherent ozone resistance like EPDM and using UV-absorbing coatings extend product lifespan by minimizing cracking and color fading. By optimizing these protective measures, your products maintain durability and performance in harsh environmental conditions.
Selecting the Right Material for Extreme Environments
Ozone resistance and UV resistance are critical factors when selecting materials for extreme environments, as ozone attacks rubber primarily through oxidative degradation causing cracks, while UV exposure breaks down polymer chains leading to surface deterioration. Materials like EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) excel in both ozone and UV resistance due to their saturated polymer backbone and stable bonding structure, making them ideal for outdoor applications with prolonged sunlight and ozone exposure. Selecting materials with balanced ozone and UV resistance ensures longevity, reduces maintenance costs, and maintains mechanical integrity under harsh environmental conditions.
Ozone Resistance vs UV Resistance Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com