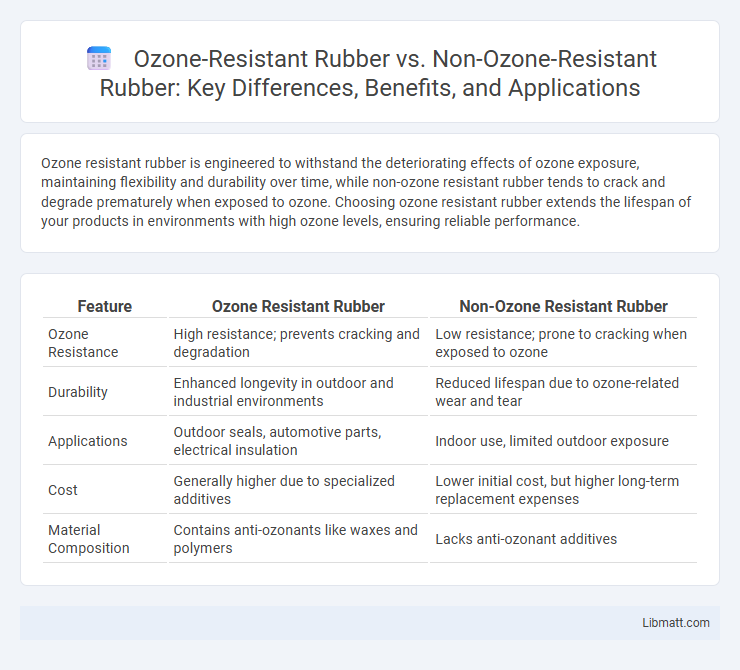
Ozone resistant rubber is engineered to withstand the deteriorating effects of ozone exposure, maintaining flexibility and durability over time, while non-ozone resistant rubber tends to crack and degrade prematurely when exposed to ozone. Choosing ozone resistant rubber extends the lifespan of your products in environments with high ozone levels, ensuring reliable performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ozone Resistant Rubber | Non-Ozone Resistant Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Ozone Resistance | High resistance; prevents cracking and degradation | Low resistance; prone to cracking when exposed to ozone |
| Durability | Enhanced longevity in outdoor and industrial environments | Reduced lifespan due to ozone-related wear and tear |
| Applications | Outdoor seals, automotive parts, electrical insulation | Indoor use, limited outdoor exposure |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized additives | Lower initial cost, but higher long-term replacement expenses |
| Material Composition | Contains anti-ozonants like waxes and polymers | Lacks anti-ozonant additives |
Introduction to Ozone Resistance in Rubber
Ozone-resistant rubber is formulated with additives or specific polymers that inhibit ozone degradation, significantly enhancing the material's durability in environments exposed to ozone and atmospheric pollutants. Non-ozone resistant rubber lacks these protective features and is more prone to cracking, embrittlement, and surface deterioration when exposed to ozone, leading to reduced lifespan and performance. Understanding the chemical composition and resistance mechanisms is essential for selecting rubber materials in industrial applications requiring long-term ozone exposure resilience.
What Is Ozone Resistant Rubber?
Ozone resistant rubber is a specialized elastomer designed to withstand the deteriorating effects of ozone exposure, which can cause cracking and material failure over time. Unlike non-ozone resistant rubber, this type contains additives that enhance its durability against ozone-induced degradation, making it ideal for outdoor applications or environments with high ozone concentrations. Your choice of ozone resistant rubber ensures longer-lasting performance and reduced maintenance in products exposed to harsh atmospheric conditions.
Understanding Non-Ozone Resistant Rubber
Non-ozone resistant rubber degrades quickly when exposed to ozone, causing cracks and surface deterioration that reduce its durability and lifespan. This type of rubber lacks the chemical additives that protect against ozone-induced oxidation, making it unsuitable for outdoor applications or environments with high ozone levels. Understanding your use case is essential to choose rubber that withstands environmental stressors and maintains performance over time.
Key Differences Between Ozone Resistant and Non-Ozone Resistant Rubber
Ozone resistant rubber contains specific additives such as antiozonants and stabilizers that protect its polymer chains from degradation caused by ozone exposure, whereas non-ozone resistant rubber lacks these protective compounds, leading to surface cracking and reduced durability. The molecular structure of ozone resistant rubber is designed to withstand molecular attacks by ozone, maintaining flexibility and elasticity over time, while non-resistant varieties often experience embrittlement and premature failure in ozone-rich environments. These differences are crucial for applications involving outdoor exposure or high ozone concentrations, where ozone resistant rubber significantly extends component lifespan and performance.
Chemical Composition and Ozone Degradation
Ozone resistant rubber typically contains synthetic polymers such as EPDM or silicone, formulated with stabilizers like anti-ozonants that prevent ozone molecule attack on double bonds. Non-ozone resistant rubber commonly consists of natural rubber or unsaturated elastomers, which lack protective additives and have more double bonds prone to ozonolysis, leading to chain scission and cracks. The chemical composition difference directly impacts resistance, where ozone resistant rubber maintains molecular integrity and mechanical properties despite ozone exposure, while non-ozone resistant rubber degrades rapidly through surface cracking and brittleness.
Performance in Harsh Environments
Ozone resistant rubber exhibits superior durability and maintains elasticity when exposed to harsh environments, including UV radiation, ozone, and extreme weather conditions, preventing cracking and surface degradation. Non-ozone resistant rubber tends to crack, harden, and degrade quickly under similar conditions, leading to premature failure and reduced service life. Performance metrics such as tensile strength retention and resistance to surface checking highlight the significant advantage of ozone resistant rubber in maintaining integrity and functionality in demanding applications.
Applications of Ozone Resistant Rubber
Ozone resistant rubber is essential in industries where exposure to ozone and UV radiation can cause material degradation, such as automotive tires, seals, gaskets, and outdoor electrical insulations. Its ability to withstand cracking and deterioration extends the lifespan of products used in harsh environmental conditions, including transportation and construction. Choosing ozone resistant rubber for your applications ensures durability and reliability in ozone-prone environments.
Common Uses of Non-Ozone Resistant Rubber
Non-ozone resistant rubber is commonly used in applications where exposure to ozone, UV radiation, and harsh environmental conditions is minimal, such as indoor seals, gaskets, and certain types of hoses. It is suitable for general-purpose products like automotive door seals, flooring, and electrical insulation where resistance to ozone degradation is not critical. Your choice of non-ozone resistant rubber is ideal for cost-effective, short-term uses where ozone exposure is unlikely to compromise performance.
Cost Implications and Longevity Comparison
Ozone resistant rubber typically costs more upfront than non-ozone resistant varieties due to its specialized additives and manufacturing process, but this investment extends the material's lifespan significantly in environments exposed to ozone and UV radiation. Non-ozone resistant rubber may be cheaper initially, but it tends to degrade faster, leading to frequent replacements and higher long-term expenses. Choosing ozone resistant rubber ensures your products maintain elasticity and durability, ultimately providing better value through reduced maintenance and replacement costs.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Needs
Ozone resistant rubber is formulated with additives like anti-ozonants that prevent cracking and degradation when exposed to ozone, making it ideal for outdoor applications and environments with high ozone levels. Non-ozone resistant rubber lacks these protective additives, resulting in reduced durability and premature failure under ozone exposure, but may be suitable for indoor or low-ozone conditions. Choosing the right rubber for your needs depends on the environmental exposure and longevity requirements of your application.
Ozone Resistant Rubber vs Non-Ozone Resistant Rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com