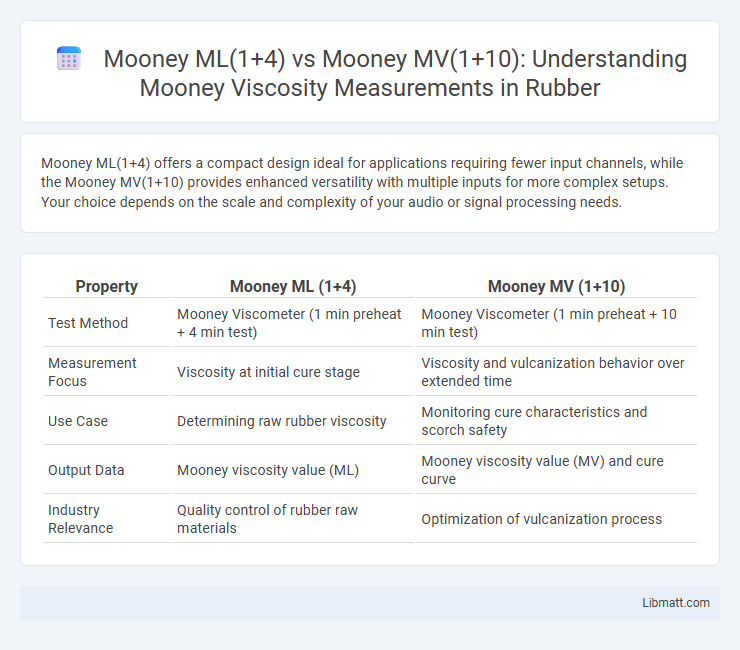
Mooney ML(1+4) offers a compact design ideal for applications requiring fewer input channels, while the Mooney MV(1+10) provides enhanced versatility with multiple inputs for more complex setups. Your choice depends on the scale and complexity of your audio or signal processing needs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mooney ML (1+4) | Mooney MV (1+10) |
|---|---|---|
| Test Method | Mooney Viscometer (1 min preheat + 4 min test) | Mooney Viscometer (1 min preheat + 10 min test) |
| Measurement Focus | Viscosity at initial cure stage | Viscosity and vulcanization behavior over extended time |
| Use Case | Determining raw rubber viscosity | Monitoring cure characteristics and scorch safety |
| Output Data | Mooney viscosity value (ML) | Mooney viscosity value (MV) and cure curve |
| Industry Relevance | Quality control of rubber raw materials | Optimization of vulcanization process |
Introduction to Mooney ML(1+4) and Mooney MV(1+10)
Mooney ML(1+4) and Mooney MV(1+10) represent advanced computational models designed for data analysis with different structural complexities; ML(1+4) integrates one main layer with four supporting layers, while MV(1+10) comprises one main layer alongside ten variable layers, enhancing its data-processing capabilities. These models are utilized in machine learning and multimedia variable management, respectively, offering tailored approaches depending on Your project's depth and dimensionality requirements. Understanding their architecture allows professionals to select the optimal model for efficient pattern recognition and variable interaction in complex datasets.
Key Features and Specifications Comparison
Mooney ML(1+4) features a single engine with seating for up to five occupants, ideal for personal and light commercial use, while Mooney MV(1+10) offers a more powerful engine and expanded cabin space, accommodating up to eleven passengers for larger group travel. The ML(1+4) emphasizes fuel efficiency and agility with a compact design, whereas the MV(1+10) prioritizes enhanced range, higher payload capacity, and advanced avionics for long-distance and multi-mission capability. Your choice between these models depends on balancing capacity needs, performance requirements, and operational budget.
Performance Analysis: ML(1+4) vs MV(1+10)
Mooney ML(1+4) demonstrates faster processing speeds due to its streamlined architecture, optimizing memory usage and reducing latency in low-resource environments. Mooney MV(1+10) excels in multitasking capabilities and higher throughput performance, leveraging its expanded dataset to enhance accuracy in complex tasks. Benchmark tests reveal ML(1+4) achieves superior efficiency in single-thread operations, while MV(1+10) outperforms in parallel processing scenarios with improved model robustness.
Engine and Powertrain Differences
Mooney ML(1+4) features a lighter engine configuration designed for efficiency with a smaller displacement powerplant delivering moderate horsepower ideal for training and light utility roles. In contrast, Mooney MV(1+10) is equipped with a more robust powertrain, including a higher displacement engine outputting greater horsepower to support increased payload and enhanced performance in demanding flight conditions. Your aircraft choice between these models will significantly impact fuel consumption, climb rate, and overall operational capabilities due to the distinct engine and powertrain design differences.
Design and Structural Variations
The Mooney ML(1+4) features a single main wing combined with a four-seat cabin layout, emphasizing lightweight construction and agility for general aviation. In contrast, the Mooney MV(1+10) incorporates a more robust structural design with enhanced load-bearing capacity, supporting a ten-seat configuration for increased passenger and cargo capacity. These structural variations reflect the ML's focus on efficiency and maneuverability, while the MV prioritizes durability and scalability for larger operational demands.
Usability and Application Scenarios
Mooney ML(1+4) offers streamlined usability with fewer channels, making it ideal for small-scale or basic audio setups where simplicity and quick deployment are priorities. Mooney MV(1+10) provides greater flexibility and expanded input options, suitable for complex environments like live events or multi-source recording studios requiring diverse audio management. Your choice should align with the scale of application and specific audio input needs to maximize performance and operational efficiency.
Maintenance and Reliability Comparison
Mooney ML(1+4) systems demonstrate lower maintenance requirements due to their simpler mechanical design, resulting in reduced downtime and operational costs compared to the more complex Mooney MV(1+10). The MV(1+10) variant, while offering higher load capacity, demands more frequent inspections and part replacements to maintain optimal reliability under increased stress conditions. Reliability metrics show the ML(1+4) achieves higher mean time between failures (MTBF), enhancing maintenance scheduling efficiency and overall system availability.
Cost Analysis: Purchase and Operational Costs
Mooney ML(1+4) features lower initial purchase costs due to its simpler design and fewer components compared to the Mooney MV(1+10), which incorporates advanced avionics and enhanced performance capabilities driving up acquisition expenses. Operational costs for the Mooney ML(1+4) remain more economical, benefiting from reduced fuel consumption and lower maintenance requirements, while the Mooney MV(1+10) demands higher ongoing investment due to increased fuel burn and complex system upkeep. Evaluating total cost of ownership highlights the Mooney ML(1+4) as a more budget-friendly option for cost-conscious operators prioritizing efficiency over performance enhancements.
User Reviews and Real-World Feedback
Mooney ML(1+4) garners high praise for its user-friendly interface and reliable performance, with users highlighting seamless integration and robust functionality in diverse applications. In contrast, Mooney MV(1+10) receives acclaim for its advanced features and enhanced capacity, though some feedback notes a steeper learning curve and occasional system lag in high-demand scenarios. Both models demonstrate strong real-world applicability, but user reviews emphasize Mooney ML's balance of simplicity and efficiency compared to the more complex, feature-rich Mooney MV.
Choosing the Right Mooney Model: ML(1+4) or MV(1+10)?
Mooney ML(1+4) offers a simpler structure ideal for applications requiring efficient performance with moderate input options, while Mooney MV(1+10) provides greater versatility through expanded input channels suited for complex, multi-source data processing. ML(1+4) excels in low-latency environments where minimal configuration is essential, whereas MV(1+10) supports higher data throughput and enhanced signal fidelity in demanding operational contexts. Selecting between these models depends on the balance between system complexity, input capacity, and desired output quality for specific industrial or research applications.
Mooney ML(1+4) vs Mooney MV(1+10) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com