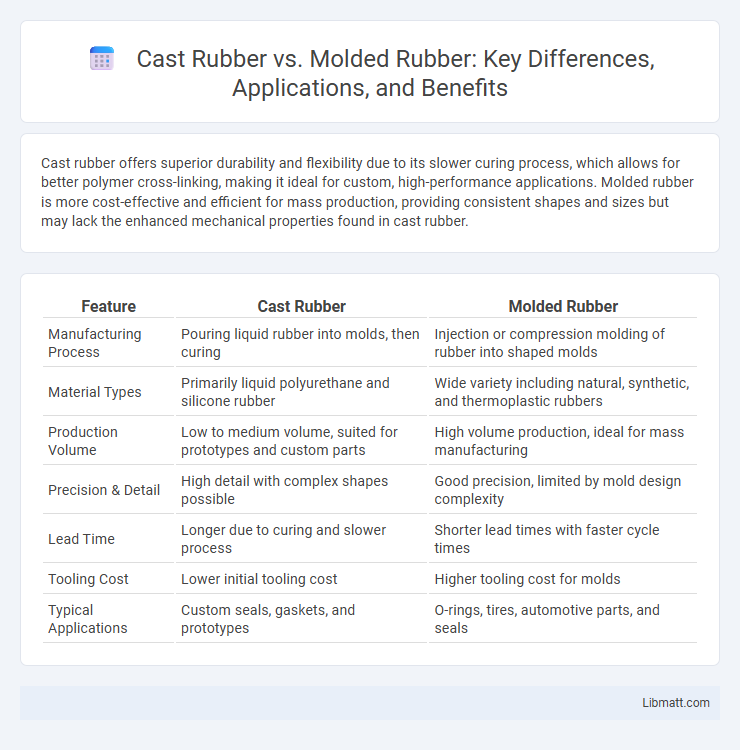
Cast rubber offers superior durability and flexibility due to its slower curing process, which allows for better polymer cross-linking, making it ideal for custom, high-performance applications. Molded rubber is more cost-effective and efficient for mass production, providing consistent shapes and sizes but may lack the enhanced mechanical properties found in cast rubber.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cast Rubber | Molded Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Pouring liquid rubber into molds, then curing | Injection or compression molding of rubber into shaped molds |
| Material Types | Primarily liquid polyurethane and silicone rubber | Wide variety including natural, synthetic, and thermoplastic rubbers |
| Production Volume | Low to medium volume, suited for prototypes and custom parts | High volume production, ideal for mass manufacturing |
| Precision & Detail | High detail with complex shapes possible | Good precision, limited by mold design complexity |
| Lead Time | Longer due to curing and slower process | Shorter lead times with faster cycle times |
| Tooling Cost | Lower initial tooling cost | Higher tooling cost for molds |
| Typical Applications | Custom seals, gaskets, and prototypes | O-rings, tires, automotive parts, and seals |
Introduction to Cast Rubber and Molded Rubber
Cast rubber is a versatile material created by pouring liquid rubber compounds into molds, allowing complex shapes and precise details with excellent mechanical properties. Molded rubber, produced by compressing or injecting rubber into pre-designed molds under heat and pressure, offers high efficiency for mass production and consistent quality. Understanding the differences between cast rubber and molded rubber can help you choose the ideal process for your application requirements.
Understanding Cast Rubber: Process and Characteristics
Cast rubber involves pouring liquid rubber compounds into a mold where it cures and solidifies, allowing for complex shapes with uniform density and smooth surface finishes. This process provides excellent dimensional accuracy, reduced internal stresses, and enhanced mechanical properties, making cast rubber ideal for custom parts and intricate designs. Compared to molded rubber, cast rubber offers greater flexibility in material formulations and improved resistance to harsh environmental conditions.
Molded Rubber: Production Methods and Features
Molded rubber is produced using compression, transfer, or injection molding processes, which allow precise control over shape and dimensions through pre-designed molds. This method enhances production efficiency and consistency, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing of complex and uniform rubber components. Molded rubber parts exhibit excellent surface finish, uniform mechanical properties, and reduced material waste compared to cast rubber alternatives.
Material Composition Differences
Cast rubber is created by liquefying raw rubber compounds and pouring them into molds, resulting in a homogenous material with excellent strength and flexibility. Molded rubber, on the other hand, involves shaping rubber using heat and pressure, often combining various additives that enhance specific properties like durability or chemical resistance. Your choice between cast and molded rubber should consider these material composition differences to meet performance and application requirements.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Cast rubber offers superior performance in applications requiring complex shapes and high precision, as it provides excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability. Molded rubber excels in mass production with consistent quality and faster cycle times but may have slightly lower resistance to mechanical stress compared to cast rubber. Durability in cast rubber is enhanced by its uniform structure, which reduces the risk of weaknesses, whereas molded rubber may experience variability due to the molding process.
Cost Factors: Cast Rubber vs Molded Rubber
Cast rubber typically incurs higher production costs due to longer curing times and labor-intensive processes, making it suitable for low to medium volume runs. Molded rubber benefits from faster cycle times and automation, leading to lower per-unit costs in high-volume manufacturing. Tooling expenses are generally higher for molded rubber but amortized over large production runs, whereas cast rubber requires minimal initial tooling investment.
Typical Applications in Various Industries
Cast rubber excels in applications requiring complex shapes and high chemical resistance, making it ideal for automotive seals, aerospace components, and industrial gaskets. Molded rubber is preferred for mass production of standardized parts such as O-rings, automotive tires, and footwear soles due to its efficient manufacturing process. Your choice depends on whether you need customization and durability or fast, cost-effective production for high-volume needs.
Design Flexibility and Customization
Cast rubber offers superior design flexibility and customization due to its ability to form complex shapes, intricate details, and varying thicknesses without the constraints of molds. Molded rubber relies on pre-made molds, which limits customization to the mold design, making it less adaptable for unique or intricate configurations. Your choice between cast and molded rubber should consider the complexity and specificity of the design requirements for optimal performance and functionality.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cast rubber offers enhanced environmental benefits due to its lower energy consumption during production and reduced waste generation compared to molded rubber, which often involves higher heat and pressure processes. Molded rubber typically produces more scrap material and emissions, making cast rubber a more sustainable option for eco-conscious manufacturing. You can choose cast rubber components to support greener practices and reduce your environmental footprint.
Choosing the Right Rubber Solution for Your Needs
Cast rubber offers superior customization with intricate shapes and consistent thickness, ideal for complex designs and low-volume production. Molded rubber provides faster manufacturing and cost efficiency, perfect for high-volume runs and standardized parts. Evaluating production scale, design complexity, and budget will help determine the optimal rubber solution.
Cast rubber vs Molded rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com