NR Block technology offers advanced connectivity for 5G networks by enabling efficient resource allocation and better signal management, while RSS (Received Signal Strength) measures the power level of the received signal and helps optimize network performance. Your choice between NR Block scheduling and monitoring RSS can impact the quality and reliability of wireless communications in modern cellular systems.
Table of Comparison
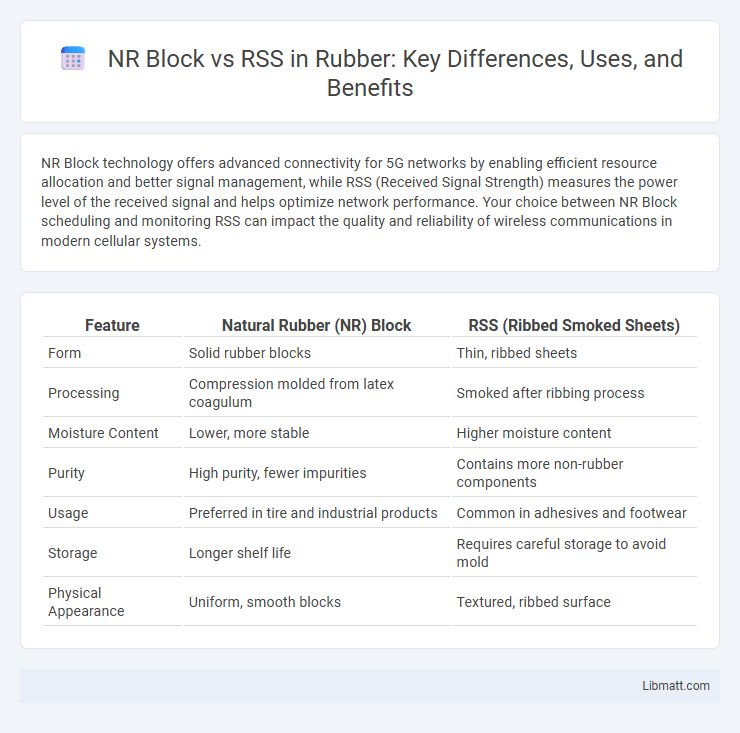
| Feature | Natural Rubber (NR) Block | RSS (Ribbed Smoked Sheets) |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Solid rubber blocks | Thin, ribbed sheets |
| Processing | Compression molded from latex coagulum | Smoked after ribbing process |
| Moisture Content | Lower, more stable | Higher moisture content |
| Purity | High purity, fewer impurities | Contains more non-rubber components |
| Usage | Preferred in tire and industrial products | Common in adhesives and footwear |
| Storage | Longer shelf life | Requires careful storage to avoid mold |
| Physical Appearance | Uniform, smooth blocks | Textured, ribbed surface |
Introduction to NR Block and RSS
NR Block (New Radio Block) defines a specific unit of resource allocation in 5G NR networks, crucial for managing radio frequency spectrum efficiently. RSS (Received Signal Strength) measures the power level of a received signal, providing essential data for optimizing network performance and coverage. Understanding NR Block allocation alongside RSS values helps improve your network's capacity and signal quality in 5G deployments.
What is NR Block?
NR Block, or New Radio Block, is a fundamental unit of resource allocation in 5G NR (New Radio) technology, representing a contiguous set of subcarriers within a specific frequency range. It plays a crucial role in defining the bandwidth and spectral efficiency for data transmission in 5G networks. NR Block allocation enables flexible and dynamic spectrum usage, enhancing network capacity and performance compared to traditional RSS (Reference Signal System).
What is RSS in Wireless Communications?
RSS, or Received Signal Strength, measures the power level of a wireless signal received by a device, crucial for assessing link quality and network performance in wireless communications. It provides real-time data on signal attenuation and interference, influencing handover decisions and resource allocation in cellular networks like 5G NR (New Radio). Accurate RSS measurement helps optimize coverage, enhance connectivity, and improve user experience in dynamic radio environments.
Key Differences Between NR Block and RSS
NR Block refers to a specific resource allocation unit in 5G New Radio (NR) technology used for transmitting data, while RSS (Received Signal Strength) measures the power level of a received radio signal. Key differences include their functions: NR Block is a structural element in data transmission and resource allocation, whereas RSS indicates signal quality and helps in assessing link reliability. NR Block deals with spectral resources within a network, whereas RSS serves as an indicator for network optimization and handover decisions.
Role of NR Block in 5G Networks
NR Block plays a critical role in 5G networks by managing the control and synchronization signals necessary for efficient communication between user equipment and the network. It ensures that resource allocation, beamforming, and mobility management are optimized for high-speed data transfer and low latency. Your 5G experience benefits from NR Block's precise handling of radio signals, resulting in improved connection reliability and network performance.
Importance of RSS in Signal Quality
RSS (Received Signal Strength) plays a critical role in determining the signal quality in NR (New Radio) networks by providing a direct measurement of the power level received by the user equipment from the base station. Higher RSS values typically correlate with better signal quality, leading to improved data throughput and reduced error rates in 5G communication. Monitoring RSS enables dynamic adjustment of NR block resource allocation to optimize network performance and maintain robust connectivity.
Advantages of Using NR Block
NR Block technology offers superior spectral efficiency and reduced interference compared to RSS, enabling higher data throughput and improved network capacity. Its dynamic allocation capabilities optimize resource management in real-time, enhancing overall system performance and user experience. Enhanced scalability and support for massive connectivity make NR Block ideal for next-generation 5G networks and beyond.
Limitations of RSS Measurements
RSS measurements often suffer from inaccuracies due to multipath propagation and signal shadowing, which can distort the received signal strength values. These limitations impact your ability to precisely evaluate network quality and coverage in NR Block deployments, as RSS cannot fully capture interference or dynamic network conditions. Advanced metrics like SINR or CQI provide more reliable insights for optimizing NR Block performance beyond basic RSS assessments.
NR Block vs RSS in Network Optimization
NR Block and RSS play crucial roles in network optimization by managing radio resources and improving signal quality. NR Block refers to the configuration of numerical resource blocks in 5G NR technology, directly impacting throughput and spectral efficiency. RSS (Received Signal Strength) measures the power level of a received signal, helping you optimize coverage and handover decisions for enhanced network performance.
Conclusion: NR Block or RSS for Modern Networks?
NR Block and RSS both enhance signal processing in modern networks, but NR Block offers advanced beamforming and lower latency suited for 5G deployments. RSS, while simpler and effective in traditional systems, lacks the scalability and adaptability required for dynamic, high-frequency environments. Your choice depends on network complexity, with NR Block favored for future-ready, high-performance connectivity.
NR Block vs RSS Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com