NR (Non-Return) and IR (Immediate Return) represent different types of valve actuators, affecting how quickly the valve responds to control signals. Your choice between NR and IR influences system efficiency, with NR providing slower, energy-saving operation and IR enabling rapid valve adjustments for precise control.
Table of Comparison
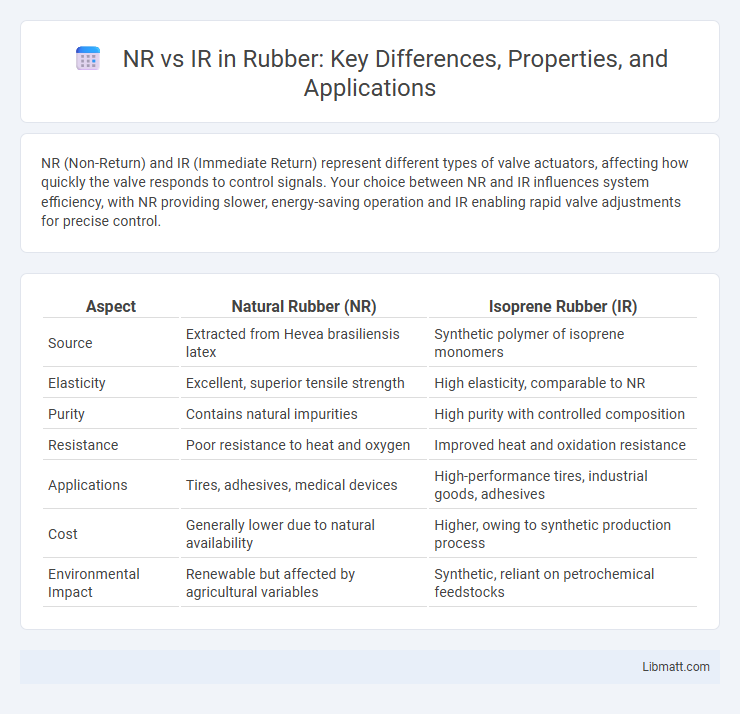
| Aspect | Natural Rubber (NR) | Isoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Extracted from Hevea brasiliensis latex | Synthetic polymer of isoprene monomers |
| Elasticity | Excellent, superior tensile strength | High elasticity, comparable to NR |
| Purity | Contains natural impurities | High purity with controlled composition |
| Resistance | Poor resistance to heat and oxygen | Improved heat and oxidation resistance |
| Applications | Tires, adhesives, medical devices | High-performance tires, industrial goods, adhesives |
| Cost | Generally lower due to natural availability | Higher, owing to synthetic production process |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable but affected by agricultural variables | Synthetic, reliant on petrochemical feedstocks |
Introduction to NR vs IR
New Radio (NR) represents the 5G wireless standard, designed to deliver enhanced mobile broadband, ultra-reliable low-latency communication, and massive machine-type communications. In contrast, Intermediate Representation (IR) refers to a programming language abstraction used in compiler design for optimization and code generation. NR targets next-generation wireless connectivity improvements, whereas IR focuses on software development processes and efficient code compilation.
Definitions: What are NR and IR?
NR (New Radio) is the global standard for 5G wireless technology developed by 3GPP, designed to support enhanced mobile broadband, ultra-reliable low latency communication, and massive machine-type communication. IR (Infrared) refers to the wireless communication technology that uses infrared light waves to transmit data over short distances, often employed in remote controls and niche data transfer applications. NR focuses on high-speed, high-capacity cellular networks, while IR is primarily used for line-of-sight, short-range, and low-data-rate communication scenarios.
Key Differences Between NR and IR
NR (New Radio) is the 5G wireless access technology designed to offer higher data rates, lower latency, and improved capacity compared to IR (Infrared) communication, which uses light waves for short-range data transmission. NR operates on a broader spectrum, including sub-6 GHz and millimeter-wave frequencies, enabling enhanced mobile broadband and massive IoT support, whereas IR is limited to line-of-sight and close proximity applications. The key differences lie in NR's scalability and network integration capabilities versus IR's simplicity and constrained range, making NR suitable for large-scale wireless networks and IR for niche, secure, or indoor communication scenarios.
Applications of NR and IR Technologies
NR (Near-Field Communication) technology revolutionizes contactless payments, access control, and smart device pairing by enabling secure short-range data exchange. IR (Infrared) technology excels in remote control systems, data transmission between devices without network connectivity, and environmental sensing applications. Your choice between NR and IR depends on the required communication range, security level, and device compatibility in specific use cases.
Advantages of NR Over IR
NR (New Radio) offers significant advantages over IR (Infrared) technology, including faster data transfer rates and enhanced mobility due to its wireless radio frequency-based communication. NR supports broader coverage and higher capacity, enabling seamless connectivity for 5G networks, whereas IR is limited by line-of-sight and short-range constraints. Your network performance will improve with NR's low latency and greater reliability, making it ideal for modern applications in IoT, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities.
Limitations of IR Compared to NR
Infrared (IR) technology has limitations compared to Near-Infrared (NR) in terms of penetration depth and resolution, resulting in reduced effectiveness for high-precision imaging and analysis. IR signals are more susceptible to atmospheric interference and offer lower spatial resolution, which impacts applications requiring detailed data capture. Your choice between NR and IR should consider these constraints to optimize performance in imaging or sensing tasks.
Performance Comparison: NR vs IR
5G New Radio (NR) significantly outperforms LTE's Initial Release (IR) by offering enhanced spectral efficiency and ultra-low latency, enabling peak data rates up to 20 Gbps. NR's advanced modulation schemes, flexible numerology, and massive MIMO technology improve throughput and reliability compared to IR's fixed bandwidth and lower-order modulation. The adaptive frame structure of NR also supports dynamic resource allocation, delivering superior performance in diverse network conditions relative to IR.
Real-World Use Cases for NR and IR
NR (New Radio) enhances 5G connectivity in smart cities by enabling ultra-reliable low-latency communication for autonomous vehicles and IoT devices, improving traffic management and public safety. IR (Infrared) technology excels in secure, short-range communication applications such as remote controls, medical sensors, and data transfer between devices without radio interference. Your choice between NR and IR depends on whether you require wide-area high-speed connectivity or specialized, localized communication solutions.
NR and IR in Emerging Technologies
NR (New Radio) and IR (Infrared) play crucial roles in emerging technologies, with NR enabling high-speed 5G connectivity to support IoT, smart cities, and autonomous systems. IR technology is integral in short-range communication, especially in secure data transmission and gesture recognition in wearables and augmented reality devices. Your innovative projects benefit from leveraging NR's expansive coverage and IR's precision for enhanced performance and user experience.
Future Trends in NR and IR
Future trends in NR (New Radio) emphasize enhanced 5G capabilities such as ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), massive machine-type communication (mMTC), and network slicing to support diverse use cases including IoT and immersive AR/VR applications. Industrial Reality (IR) technologies are evolving with advancements in real-time data processing, AI-driven analytics, and edge computing integration, enabling more precise digital twins and augmented human-machine collaboration. Your business can leverage the convergence of NR and IR innovations to unlock smarter, faster, and more adaptive wireless and immersive environments.
NR vs IR Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com