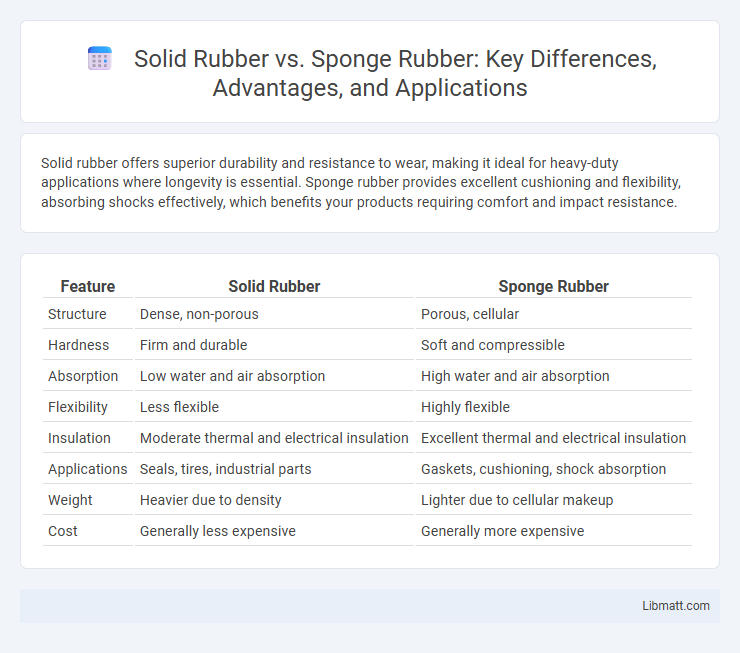
Solid rubber offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications where longevity is essential. Sponge rubber provides excellent cushioning and flexibility, absorbing shocks effectively, which benefits your products requiring comfort and impact resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solid Rubber | Sponge Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Dense, non-porous | Porous, cellular |
| Hardness | Firm and durable | Soft and compressible |
| Absorption | Low water and air absorption | High water and air absorption |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | Highly flexible |
| Insulation | Moderate thermal and electrical insulation | Excellent thermal and electrical insulation |
| Applications | Seals, tires, industrial parts | Gaskets, cushioning, shock absorption |
| Weight | Heavier due to density | Lighter due to cellular makeup |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Generally more expensive |
Introduction to Solid Rubber and Sponge Rubber
Solid rubber offers high durability, excellent resistance to abrasion, and is commonly used in heavy-duty applications requiring long-lasting performance. Sponge rubber features a cellular structure with air pockets, providing superior cushioning, flexibility, and shock absorption ideal for sealing and insulation purposes. Understanding these distinct properties helps you select the best material for your specific industrial or commercial needs.
Key Properties of Solid Rubber
Solid rubber exhibits superior durability, high tensile strength, and excellent resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting performance. It offers better load-bearing capacity and is less compressible compared to sponge rubber, which enhances its structural stability. Its impermeable nature ensures resistance to water, oils, and chemicals, contributing to its widespread use in industrial seals and heavy-duty tires.
Key Properties of Sponge Rubber
Sponge rubber is characterized by its lightweight, compressible structure with excellent shock absorption and insulation properties, making it highly effective for cushioning and sealing applications. Its porous composition provides enhanced flexibility and resistance to water, oils, and chemicals, distinguishing it from solid rubber which is denser and less pliable. These key properties enable sponge rubber to excel in uses requiring softness, resilience, and airtight seals, particularly in automotive, industrial, and sealing industries.
Differences in Material Structure
Solid rubber consists of a dense, homogeneous material that provides durability and high resistance to wear, while sponge rubber features a cellular, porous structure that offers cushioning and flexibility. The closed-cell composition of solid rubber ensures minimal water absorption, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications, whereas the open-cell or semi-open-cell configuration of sponge rubber allows for compressibility and shock absorption. These structural differences directly impact their performance characteristics in industries such as automotive, sealing, and footwear.
Comparative Durability and Resilience
Solid rubber outperforms sponge rubber in durability due to its dense molecular structure, offering higher resistance to abrasion, cuts, and deformation under heavy loads. Sponge rubber exhibits superior resilience with enhanced shock absorption and flexibility, making it ideal for cushioning applications but more prone to wear and tear over time. The choice between solid and sponge rubber depends on the required balance between long-term durability and elastic performance in specific industrial or consumer uses.
Performance in Sealing Applications
Solid rubber offers superior durability and resistance to compression, making it ideal for high-pressure sealing applications where long-term performance is critical. Sponge rubber provides excellent flexibility and cushioning, ensuring effective seals in dynamic environments with frequent movement or vibrations. Your choice depends on sealing requirements, balancing the need for resilience with flexibility and adaptability.
Flexibility and Compression Characteristics
Solid rubber offers high durability with limited flexibility and resists compression deformation, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring firm support. Sponge rubber provides superior flexibility and cushioning due to its air-filled cellular structure, allowing greater compression and rebound, which enhances comfort and shock absorption. When selecting material, your choice depends on whether flexibility or compression resilience is the priority for the specific use case.
Environmental Resistance and Longevity
Solid rubber exhibits superior environmental resistance, including excellent durability against ozone, UV rays, and abrasion, making it ideal for harsh outdoor conditions. Sponge rubber, while offering better cushioning and flexibility, generally has lower resistance to environmental factors and tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to heat and chemicals. The longevity of solid rubber outperforms sponge rubber in demanding applications, ensuring extended service life and reduced maintenance costs.
Typical Uses of Solid vs. Sponge Rubber
Solid rubber is commonly used in applications requiring high durability and resistance to abrasion, such as industrial gaskets, tires, and heavy-duty seals. Sponge rubber, characterized by its lightweight and cushioning properties, finds typical uses in packaging, cushioning pads, and shock-absorbing seals. Industries like automotive, electronics, and construction rely on solid rubber for structural components, whereas sponge rubber is preferred for insulation and padding due to its compressible nature.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Application
Solid rubber offers superior durability and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications and environments requiring high resistance to wear and tear. Sponge rubber provides excellent cushioning, flexibility, and sound absorption, perfect for sealing, vibration dampening, and comfort-focused uses. Understanding your application's needs for resilience versus softness helps you select the right material to optimize performance and longevity.
Solid rubber vs Sponge rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com