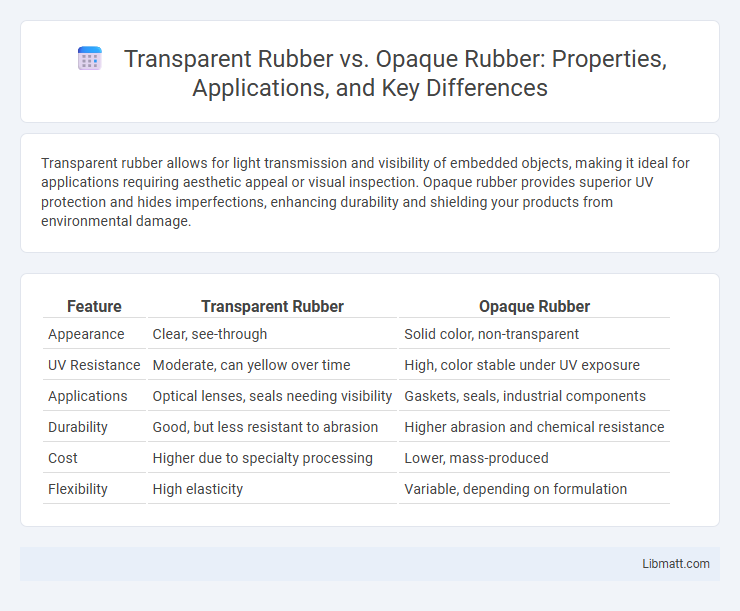
Transparent rubber allows for light transmission and visibility of embedded objects, making it ideal for applications requiring aesthetic appeal or visual inspection. Opaque rubber provides superior UV protection and hides imperfections, enhancing durability and shielding your products from environmental damage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transparent Rubber | Opaque Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear, see-through | Solid color, non-transparent |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, can yellow over time | High, color stable under UV exposure |
| Applications | Optical lenses, seals needing visibility | Gaskets, seals, industrial components |
| Durability | Good, but less resistant to abrasion | Higher abrasion and chemical resistance |
| Cost | Higher due to specialty processing | Lower, mass-produced |
| Flexibility | High elasticity | Variable, depending on formulation |
Introduction to Transparent and Opaque Rubber
Transparent rubber offers clear visibility and light transmission, making it ideal for applications requiring aesthetic appeal and optical clarity, such as seals and gaskets in medical devices or electronic displays. Opaque rubber, with its solid color and density, provides superior UV resistance and durability, commonly used in automotive parts, industrial machinery, and heavy-duty seals. Both materials vary significantly in chemical composition and curing processes, influencing their mechanical properties and environmental resistance.
Material Composition Comparison
Transparent rubber typically consists of polyisoprene or silicone-based materials with fewer fillers, resulting in clarity and flexibility, while opaque rubber often incorporates carbon black or other pigments that enhance durability and UV resistance but reduce transparency. The molecular structure of transparent rubber is designed for minimal light scattering, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility through the material, whereas opaque rubber's composition prioritizes strength and resistance to environmental factors. Understanding the material composition helps you choose the right type of rubber based on your specific requirements for transparency and performance.
Manufacturing Processes
Transparent rubber is produced using specialized manufacturing processes that incorporate clear polymers and additives to maintain clarity and flexibility, often requiring precise temperature control and mixing to prevent discoloration or cloudiness. Opaque rubber manufacturing typically involves blending carbon black or other pigments into the base polymer, resulting in a durable material that masks impurities but lacks transparency. Understanding these manufacturing differences can help you select the right rubber type for applications where visual appearance and material properties are critical.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Transparent rubber offers superior clarity and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility and elasticity, while opaque rubber typically provides enhanced UV resistance and durability due to its pigment content. The mechanical properties of transparent rubber include a lower tensile strength and hardness compared to opaque rubber, which often exhibits greater abrasion resistance and stiffness. Your choice between transparent and opaque rubber should consider the balance between optical properties and mechanical performance for specific application needs.
Optical Characteristics: Transparency vs. Opacity
Transparent rubber offers high optical clarity, allowing light to pass through with minimal scattering, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility or light transmission. Opaque rubber blocks light completely, providing a solid, non-transparent surface that enhances privacy and hides internal components. Differences in polymer structure and fillers determine their optical performance, with transparent variants using purified materials to maintain clarity, while opaque rubbers incorporate pigments or additives to achieve opacity.
Common Applications of Transparent Rubber
Transparent rubber is frequently used in applications requiring visual clarity combined with flexibility, such as flexible displays, touchscreens, and medical devices like catheters and flexible tubing. Its optical transparency and durability make it ideal for sealing windows, lenses, and protective covers where visibility and protection are both crucial. Additionally, transparent rubber finds use in consumer products like watch straps and wearable devices, where aesthetic appeal and comfort are important.
Typical Uses for Opaque Rubber
Opaque rubber is commonly used in automotive parts, seals, gaskets, and industrial applications where durability and resistance to environmental factors like UV light and chemicals are crucial. Its non-transparent nature makes it ideal for products requiring color stability and masking of internal components. You will find opaque rubber extensively in manufacturing where consistent performance and longevity are essential.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Transparent rubber typically offers moderate durability but may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure due to its chemical composition, leading to yellowing and brittleness. Opaque rubber, often reinforced with carbon black or other additives, exhibits superior weather resistance and enhanced durability, maintaining structural integrity in harsh environmental conditions like extreme temperatures and moisture. The choice between transparent and opaque rubber hinges on balancing aesthetic clarity with long-term performance and resilience in outdoor applications.
Cost Factors and Availability
Transparent rubber generally costs more than opaque rubber due to the specialized materials and processing techniques required to maintain clarity and resist discoloration. Opaque rubber is widely available and produced in larger quantities, making it a cost-effective option for most industrial and consumer applications. Cost factors for transparent rubber include premium raw materials like silicone or polyurethane, while opaque rubber benefits from abundant natural and synthetic rubber sources.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Application
Transparent rubber offers excellent visibility for applications requiring clear or aesthetic qualities, while opaque rubber provides superior UV resistance and durability for outdoor or heavy-duty uses. Your choice depends on factors like environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and visual requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Selecting the right rubber type enhances product functionality and meets specific industry standards effectively.
Transparent Rubber vs Opaque Rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com