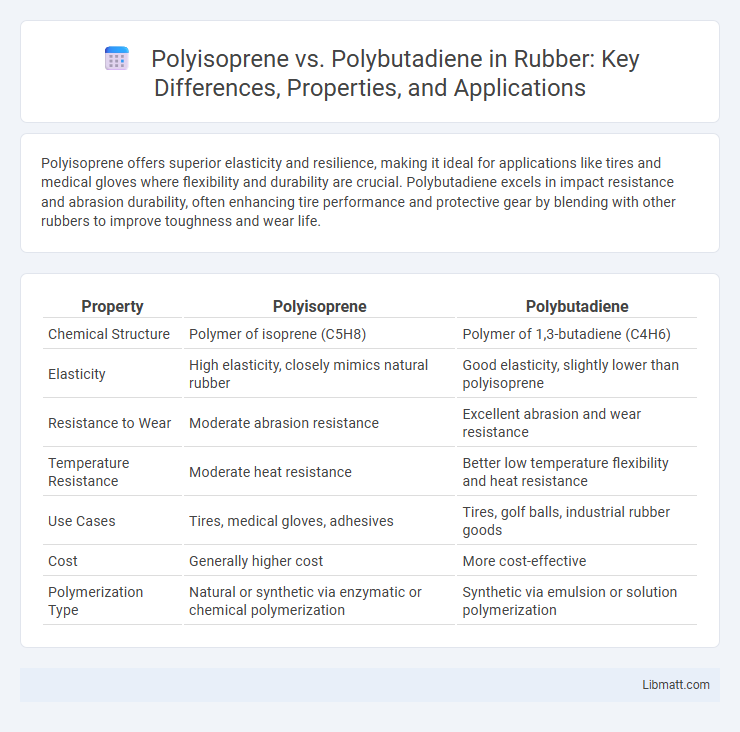
Polyisoprene offers superior elasticity and resilience, making it ideal for applications like tires and medical gloves where flexibility and durability are crucial. Polybutadiene excels in impact resistance and abrasion durability, often enhancing tire performance and protective gear by blending with other rubbers to improve toughness and wear life.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyisoprene | Polybutadiene |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Polymer of isoprene (C5H8) | Polymer of 1,3-butadiene (C4H6) |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, closely mimics natural rubber | Good elasticity, slightly lower than polyisoprene |
| Resistance to Wear | Moderate abrasion resistance | Excellent abrasion and wear resistance |
| Temperature Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | Better low temperature flexibility and heat resistance |
| Use Cases | Tires, medical gloves, adhesives | Tires, golf balls, industrial rubber goods |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | More cost-effective |
| Polymerization Type | Natural or synthetic via enzymatic or chemical polymerization | Synthetic via emulsion or solution polymerization |
Introduction to Polyisoprene and Polybutadiene
Polyisoprene and polybutadiene are synthetic elastomers widely used in tire manufacturing and industrial applications due to their excellent elasticity and resilience. Polyisoprene closely mimics natural rubber with high tensile strength and flexibility, making it ideal for medical gloves and adhesives. Polybutadiene offers superior abrasion resistance and low-temperature flexibility, commonly utilized in tire treads and golf balls to enhance durability and performance.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyisoprene and polybutadiene are synthetic elastomers distinguished by their chemical structures; polyisoprene consists of repeating isoprene units (C5H8) with a methyl group attached to the polymer backbone, giving it a configuration similar to natural rubber. Polybutadiene, composed of repeating butadiene units (C4H6), features a backbone with varying degrees of cis and trans double bonds, which affect its flexibility and resistance. Your choice between the two depends on specific application requirements such as elasticity, tensile strength, and wear resistance influenced by their molecular architecture.
Key Physical Properties
Polyisoprene exhibits high elasticity and tensile strength, closely resembling natural rubber with superior resilience and low hysteresis. Polybutadiene offers excellent abrasion resistance and impact toughness, making it ideal for tire treads and industrial applications requiring durability. Your choice depends on whether flexibility and natural rubber-like feel or enhanced wear resistance and toughness are prioritized.
Differences in Synthesis Methods
Polyisoprene is synthesized primarily through the polymerization of isoprene monomers, often using either synthetic or natural sources, resulting in materials that closely mimic natural rubber. Polybutadiene, on the other hand, is produced through the polymerization of 1,3-butadiene monomers, typically via anionic or coordination polymerization techniques that create a synthetic rubber with distinct microstructures. Your choice between polyisoprene and polybutadiene depends on the desired properties influenced by these differing synthesis pathways, which affect elasticity, strength, and temperature resistance.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Polyisoprene exhibits superior elasticity and flexibility due to its natural rubber-like structure, making it ideal for applications requiring high strain recovery. Polybutadiene offers enhanced mechanical strength and abrasion resistance, often used in tire manufacturing for durability under stress. Your choice depends on whether flexibility or toughness is the priority for the end-use application.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance
Polyisoprene offers excellent abrasion resistance due to its closely packed polymer chains and natural elasticity, making it ideal for applications requiring high wear durability. Polybutadiene exhibits superior wear resistance because of its high resilience and toughness, often used in tire manufacturing to enhance tread longevity. Both materials provide significant abrasion resistance, but polybutadiene generally outperforms polyisoprene in high-impact and high-wear environments.
Common Industrial Applications
Polyisoprene is widely used in manufacturing medical gloves, adhesives, and high-performance tires due to its excellent elasticity and resilience. Polybutadiene finds extensive application in the production of synthetic rubber for automobile tires, golf balls, and conveyor belts because of its high abrasion resistance and low heat buildup. Both polymers serve critical roles in the automotive and industrial sectors, with polybutadiene favored for durability and polyisoprene valued for its natural rubber-like properties.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Polyisoprene offers moderate cost efficiency with availability influenced by both natural rubber sources and synthetic production methods, often priced higher due to its close similarity to natural rubber. Polybutadiene is generally more cost-effective, benefiting from large-scale synthetic production and widespread industrial use, which ensures consistent availability and lower pricing. Manufacturers prioritize polybutadiene for applications requiring durability and cost efficiency, while polyisoprene is chosen for scenarios demanding elasticity and resilience despite its higher expense.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyisoprene exhibits superior environmental benefits due to its natural origins and biodegradability compared to synthetic polybutadiene, which relies heavily on petrochemicals and contributes to long-term environmental pollution. Polyisoprene production generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions and supports sustainable rubber harvesting practices, whereas polybutadiene involves energy-intensive processes and poses challenges in recycling and disposal. Preference for polyisoprene aligns with global sustainability goals by reducing ecological footprint and promoting renewable resource utilization.
Which Material is Better: Polyisoprene or Polybutadiene?
Polyisoprene offers superior elasticity and resilience, closely mimicking natural rubber, making it ideal for applications requiring high tensile strength and flexibility. Polybutadiene excels in wear resistance and impact strength, providing enhanced durability in tire manufacturing and industrial uses. Your choice between polyisoprene and polybutadiene depends on whether flexibility or toughness is the priority for your specific application.
Polyisoprene vs Polybutadiene Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com