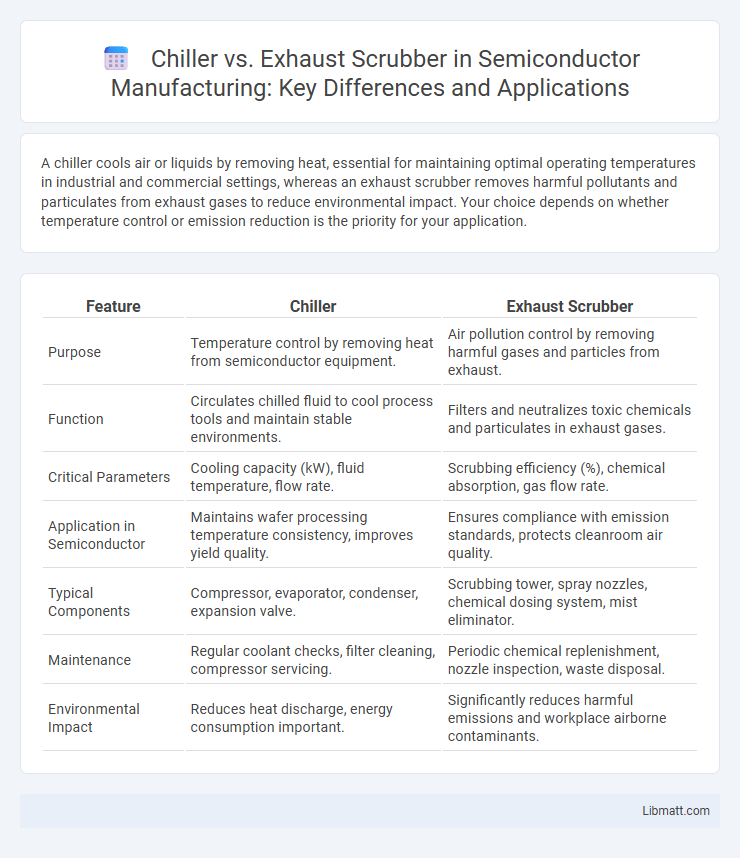
A chiller cools air or liquids by removing heat, essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures in industrial and commercial settings, whereas an exhaust scrubber removes harmful pollutants and particulates from exhaust gases to reduce environmental impact. Your choice depends on whether temperature control or emission reduction is the priority for your application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Chiller | Exhaust Scrubber |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Temperature control by removing heat from semiconductor equipment. | Air pollution control by removing harmful gases and particles from exhaust. |
| Function | Circulates chilled fluid to cool process tools and maintain stable environments. | Filters and neutralizes toxic chemicals and particulates in exhaust gases. |
| Critical Parameters | Cooling capacity (kW), fluid temperature, flow rate. | Scrubbing efficiency (%), chemical absorption, gas flow rate. |
| Application in Semiconductor | Maintains wafer processing temperature consistency, improves yield quality. | Ensures compliance with emission standards, protects cleanroom air quality. |
| Typical Components | Compressor, evaporator, condenser, expansion valve. | Scrubbing tower, spray nozzles, chemical dosing system, mist eliminator. |
| Maintenance | Regular coolant checks, filter cleaning, compressor servicing. | Periodic chemical replenishment, nozzle inspection, waste disposal. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces heat discharge, energy consumption important. | Significantly reduces harmful emissions and workplace airborne contaminants. |
Introduction to Chillers and Exhaust Scrubbers
Chillers are mechanical devices that remove heat from liquids or air to provide cooling in industrial and commercial applications. Exhaust scrubbers are pollution control systems designed to remove harmful gases and particulates from industrial exhaust streams, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Both technologies play crucial roles in process optimization and environmental sustainability across various industries.
How Chillers Work
Chillers operate by removing heat from a liquid through a vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycle, which then circulates the cooled liquid to absorb heat from equipment or processes. This cooled liquid effectively lowers temperatures in industrial or commercial settings, enhancing operational efficiency. Your choice of cooling system depends on the specific heat removal needs, where chillers provide precise temperature control compared to exhaust scrubbers.
How Exhaust Scrubbers Operate
Exhaust scrubbers operate by channeling exhaust gases through a scrubbing medium, typically water or a chemical solution, which absorbs and neutralizes harmful pollutants such as sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter. The process involves spraying or bubbling the scrubbing liquid to maximize contact with the exhaust, enabling chemical reactions or physical capture of contaminants. This technology significantly reduces emissions from industrial equipment and marine engines, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Applications in Industrial Settings
Chillers are widely used in industrial settings to provide precise temperature control for processes such as plastic molding, chemical reactions, and HVAC systems, ensuring equipment operates within optimal thermal limits. Exhaust scrubbers serve a critical role in pollution control by removing harmful gases, particulates, and volatile organic compounds from industrial emissions, particularly in factories, power plants, and chemical processing facilities. Both systems contribute to regulatory compliance and environmental sustainability by enhancing operational efficiency and minimizing industrial pollution.
Key Differences Between Chillers and Exhaust Scrubbers
Chillers and exhaust scrubbers serve distinct industrial functions, with chillers primarily designed to remove heat from liquids or air through refrigeration cycles, while exhaust scrubbers focus on filtering and neutralizing harmful gases and particulates from industrial emissions. Chillers typically use compressors, condensers, and evaporators to regulate temperature, enhancing process efficiency and equipment lifespan. Exhaust scrubbers often employ chemical sprays, filters, or electrostatic precipitators to reduce pollutants like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Chillers and exhaust scrubbers differ significantly in energy efficiency based on their operational mechanisms; chillers consume considerable power to remove heat via refrigeration cycles, while exhaust scrubbers primarily use chemical or physical processes with relatively lower energy input. Your choice should consider the specific energy consumption rates, where chillers often have higher kilowatt-hour usage per ton of cooling compared to scrubbers that focus on pollutant removal rather than thermal management. Evaluating the energy efficiency ratio (EER) for chillers versus the operational power needs of scrubbers helps optimize your system's overall energy usage and sustainability goals.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chillers consume significant energy to cool industrial processes, often relying on refrigerants with high global warming potential (GWP), which poses environmental challenges. Exhaust scrubbers reduce harmful emissions by filtering pollutants and can operate with less energy, promoting cleaner air and supporting sustainability goals. Choosing the right system impacts Your facility's carbon footprint and compliance with environmental regulations.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Chiller systems generally require higher upfront capital investment due to complex installation and energy consumption, whereas exhaust scrubbers often involve moderate initial costs but can incur ongoing expenses related to chemical use and maintenance. Your budget should account for long-term operational costs, including electricity for chillers and reagent replenishment for scrubbers. Analyzing total lifecycle expenses and return on investment helps determine the more cost-effective solution for your specific environmental control needs.
Maintenance and Operational Requirements
Chillers require regular maintenance including refrigerant level checks, compressor servicing, and coil cleaning to ensure efficient cooling performance. Exhaust scrubbers demand frequent inspection of nozzles, pump operation, and chemical dosing systems to maintain effective pollutant removal and avoid clogging. Your choice should consider the operational demands and maintenance expertise available to optimize system longevity and performance.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Facility
Selecting between a chiller and an exhaust scrubber depends on your facility's needs for temperature control and air quality management. Chillers efficiently regulate cooling by removing heat from fluids, ideal for maintaining optimal operating temperatures in industrial processes. Exhaust scrubbers are essential for filtering and neutralizing pollutants from emissions, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and improving air quality.
Chiller vs Exhaust Scrubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com