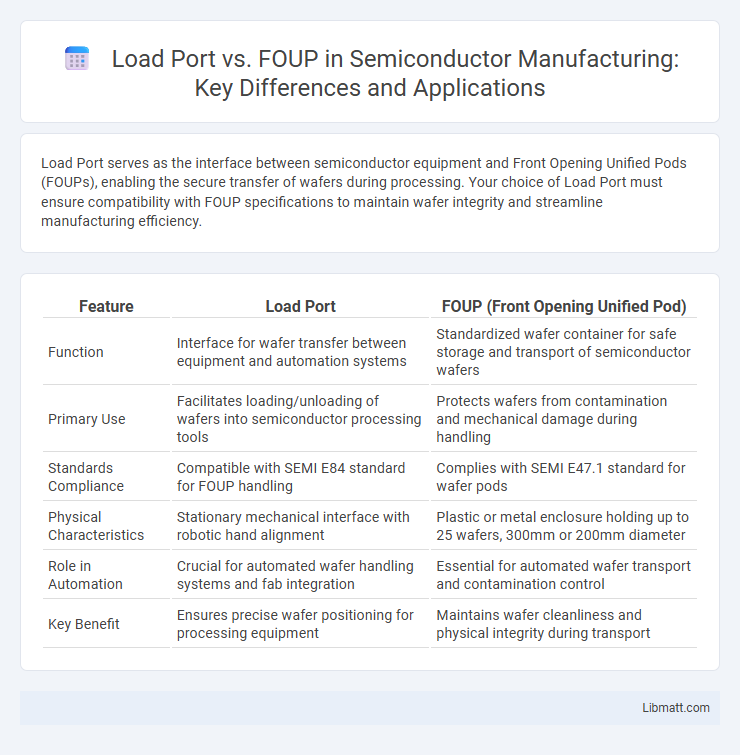
Load Port serves as the interface between semiconductor equipment and Front Opening Unified Pods (FOUPs), enabling the secure transfer of wafers during processing. Your choice of Load Port must ensure compatibility with FOUP specifications to maintain wafer integrity and streamline manufacturing efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Load Port | FOUP (Front Opening Unified Pod) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Interface for wafer transfer between equipment and automation systems | Standardized wafer container for safe storage and transport of semiconductor wafers |
| Primary Use | Facilitates loading/unloading of wafers into semiconductor processing tools | Protects wafers from contamination and mechanical damage during handling |
| Standards Compliance | Compatible with SEMI E84 standard for FOUP handling | Complies with SEMI E47.1 standard for wafer pods |
| Physical Characteristics | Stationary mechanical interface with robotic hand alignment | Plastic or metal enclosure holding up to 25 wafers, 300mm or 200mm diameter |
| Role in Automation | Crucial for automated wafer handling systems and fab integration | Essential for automated wafer transport and contamination control |
| Key Benefit | Ensures precise wafer positioning for processing equipment | Maintains wafer cleanliness and physical integrity during transport |
Introduction to Load Port and FOUP
Load Ports serve as the critical interface between semiconductor manufacturing equipment and Front Opening Unified Pods (FOUPs), enabling the secure transfer of silicon wafers. FOUPs are specialized containers designed to hold and protect wafers during transportation and processing, maintaining contamination-free environments. Understanding the distinct roles of Load Ports and FOUPs helps optimize your wafer handling and equipment integration processes.
Defining Load Port: Functions and Features
A load port is a critical interface in semiconductor manufacturing equipment designed for the precise transfer of FOUPs (Front Opening Unified Pods) containing silicon wafers. It facilitates automated loading and unloading, maintaining a controlled environment to prevent contamination while aligning FOUPs accurately for seamless integration with processing tools. Key features include robotic compatibility, vacuum sealing, and sensors for position verification, ensuring efficient wafer handling and protection throughout the manufacturing process.
Understanding FOUP: Purpose and Design
A FOUP (Front Opening Unified Pod) is a specialized container designed for safely transporting and storing semiconductor wafers within cleanroom environments. Its purpose is to protect wafers from contamination and mechanical damage during automated processing, featuring airtight seals and electrostatic discharge protection. The load port interfaces with FOUPs by providing a standardized access point for loading and unloading wafers into semiconductor equipment, ensuring precise alignment and contamination control.
Key Differences Between Load Port and FOUP
Load Port is a mechanical interface on semiconductor manufacturing equipment designed for the precise alignment and transfer of silicon wafers, whereas FOUP (Front Opening Unified Pod) is a specialized container that securely houses and protects wafers during transportation and storage. Load Ports facilitate automated wafer handling by providing mechanical, electrical, and pneumatic connectivity, while FOUPs maintain wafer cleanliness and prevent contamination with controlled environments. The key difference lies in Load Port's role as an equipment interface versus FOUP's function as a protective carrier in semiconductor fabrication processes.
Integration of Load Port and FOUP in Semiconductor Manufacturing
Integration of Load Ports and FOUPs in semiconductor manufacturing streamlines wafer handling by enabling automated transfer between equipment and storage, reducing contamination risk and improving throughput. Load Ports serve as the interface for FOUPs to be loaded onto processing tools, ensuring precise alignment and secure sealing to maintain wafer integrity. Your facility benefits from enhanced process efficiency and minimized human intervention through this coordinated interaction.
Advantages of Load Port Systems
Load port systems provide high precision alignment and automated wafer transfer, significantly reducing contamination risks and mechanical damages. Integrated load ports enhance throughput by enabling parallel processing and minimizing downtime during wafer loading and unloading. These systems also improve compatibility with FOUP carriers, ensuring secure handling and maintaining semiconductor production standards.
Benefits of Using FOUP
FOUPs (Front Opening Unified Pods) provide enhanced contamination control and protect semiconductor wafers during transport and processing, significantly reducing particle generation compared to load ports. Using FOUPs ensures better wafer handling precision and minimizes the risk of damage or loss, leading to higher yields in semiconductor manufacturing. Your cleanroom environment benefits from the standardized design of FOUPs, which enables seamless integration with automated equipment and improves overall production efficiency.
Compatibility and Interoperability Considerations
Load ports and FOUPs must be compatible to ensure seamless wafer transfer in semiconductor manufacturing, focusing on standardized interfaces and mechanical tolerances. Interoperability considerations include alignment accuracy, communication protocols, and environmental control features that prevent contamination and damage. Your equipment's efficiency depends on verifying these compatibility factors to optimize throughput and maintain process integrity.
Industry Trends: Load Port and FOUP Evolution
Industry trends highlight the rapid evolution of Load Ports and FOUPs as semiconductor manufacturing demands greater precision and automation. Advanced Load Ports now integrate smart sensors and robotics to enhance wafer transfer efficiency, while FOUPs have evolved with improved materials and contamination control features to protect delicate wafers during transport. Streamlining your fab's automation system with these innovations ensures higher throughput and minimized defect rates in wafer handling processes.
Choosing Between Load Port and FOUP: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a Load Port and FOUP depends on factors such as automation requirements, compatibility with semiconductor manufacturing equipment, and contamination control needs. Load Ports serve as interfaces for wafer handling systems, ensuring precise wafer transfer, while FOUPs (Front Opening Unified Pods) provide secure wafer storage and transport. Evaluating your production throughput, cleanroom standards, and wafer protection will help determine the most suitable option for your semiconductor fabrication process.
Load Port vs FOUP Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com