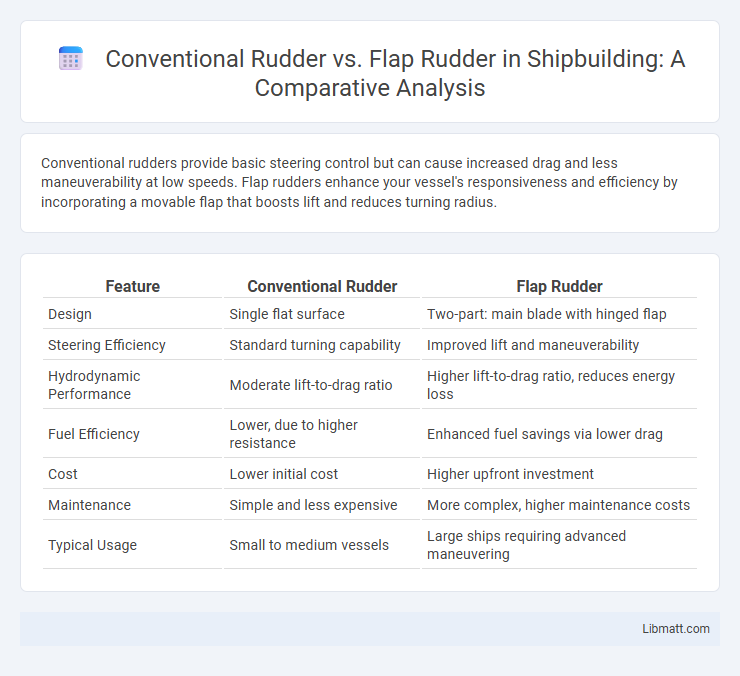
Conventional rudders provide basic steering control but can cause increased drag and less maneuverability at low speeds. Flap rudders enhance your vessel's responsiveness and efficiency by incorporating a movable flap that boosts lift and reduces turning radius.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Conventional Rudder | Flap Rudder |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Single flat surface | Two-part: main blade with hinged flap |
| Steering Efficiency | Standard turning capability | Improved lift and maneuverability |
| Hydrodynamic Performance | Moderate lift-to-drag ratio | Higher lift-to-drag ratio, reduces energy loss |
| Fuel Efficiency | Lower, due to higher resistance | Enhanced fuel savings via lower drag |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront investment |
| Maintenance | Simple and less expensive | More complex, higher maintenance costs |
| Typical Usage | Small to medium vessels | Large ships requiring advanced maneuvering |
Understanding Conventional Rudders
Conventional rudders are basic steering devices attached to the stern of a vessel, relying on a single flat surface to redirect water flow and change the ship's direction. They offer simplicity, durability, and lower maintenance costs compared to flap rudders, but generally provide less maneuverability and reduced efficiency at low speeds. Understanding the limitations and performance characteristics of conventional rudders helps optimize your vessel's handling under various operating conditions.
What Is a Flap Rudder?
A flap rudder is a type of marine rudder featuring an additional movable flap at its trailing edge, designed to enhance maneuverability and steering efficiency compared to conventional rudders. This advanced mechanism generates greater lift, allowing vessels to achieve sharper turns and improved control at lower speeds, particularly beneficial for large ships and maneuvering in tight spaces. By increasing hydrodynamic performance, flap rudders reduce steering effort and improve overall fuel efficiency during navigation.
Design Differences: Conventional vs Flap Rudders
Conventional rudders feature a single flat surface hinged to the sternpost, relying solely on the rudder's angle to steer, while flap rudders include an additional movable flap on the trailing edge to enhance lift and maneuverability. The flap section creates a variable camber effect, significantly improving hydrodynamic efficiency and reducing turning radius compared to conventional rudders. This design difference allows flap rudders to achieve higher steering forces at lower angles of deflection, making them ideal for vessels requiring precise handling and improved responsiveness.
Hydrodynamic Performance Comparison
Flap rudders offer superior hydrodynamic performance compared to conventional rudders by generating higher lift at lower angles of attack, improving maneuverability and reducing drag. Their adjustable flap allows for more efficient flow control and increased thrust, resulting in better turning response and fuel efficiency. Your vessel can achieve enhanced steering precision and reduced energy consumption with flap rudders, especially in demanding navigational conditions.
Maneuverability and Turning Efficiency
Flap rudders offer superior maneuverability and turning efficiency compared to conventional rudders due to their articulated design that allows for increased lift and reduced wake vortex. Conventional rudders rely solely on a single surface, limiting the angle and effectiveness during sharp turns, whereas flap rudders enhance hydrodynamic performance by adjusting the trailing edge angle independently. Your vessel will benefit from improved responsiveness and tighter turning radii with a flap rudder, especially in demanding navigation conditions.
Impact on Vessel Fuel Efficiency
Conventional rudders create more hydrodynamic drag due to their fixed surface area, leading to higher fuel consumption compared to flap rudders. Flap rudders enhance maneuverability by changing the flow direction more efficiently, reducing the vessel's resistance and improving fuel efficiency by up to 10%. Studies in marine propulsion highlight that vessels equipped with flap rudders achieve lower engine loads and reduced fuel costs during typical operational profiles.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Conventional rudders typically require less complex maintenance due to their simpler design, with fewer moving parts reducing the likelihood of mechanical failure and corrosion. Flap rudders, while offering superior maneuverability, involve additional hinges and actuators that demand regular inspection, lubrication, and potential replacement to maintain durability. Material choice and protective coatings play crucial roles in extending the operational lifespan of both rudder types in marine environments.
Suitability for Different Ship Types
Conventional rudders are widely suitable for various ship types, particularly smaller vessels and those with moderate maneuvering needs due to their simple design and reliable performance. Flap rudders offer enhanced maneuverability and steering efficiency, making them ideal for large ships, such as container ships, cruise liners, and tankers, where precision and reduced fuel consumption are critical. The choice between conventional and flap rudders depends on vessel size, operational requirements, and the need for maneuvering performance optimization.
Cost Implications and Installation
Conventional rudders typically incur lower initial costs and simpler installation processes due to their straightforward design and common use in smaller vessels. Flap rudders involve higher manufacturing and installation expenses, driven by their complex multi-part construction and the need for precise integration with hydraulic or electronic control systems. Maintenance costs for flap rudders can also be elevated because of their moving components, impacting long-term budgeting considerations.
Choosing the Right Rudder: Key Factors
Choosing the right rudder involves assessing maneuverability, efficiency, and vessel type, where flap rudders offer enhanced control and tighter turning radii compared to conventional rudders. Conventional rudders provide simplicity and lower maintenance costs, making them suitable for smaller vessels or applications with less demanding steering requirements. Consideration of hydrodynamic performance, operational environment, and fuel savings potential is critical in selecting between conventional and flap rudder systems.
Conventional rudder vs flap rudder Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com