Calendering produces smooth, glossy surfaces by passing materials through rollers, enhancing texture uniformity and thickness control. Embossing creates raised or recessed designs on your materials, adding decorative patterns or functional textures for visual and tactile effects.
Table of Comparison
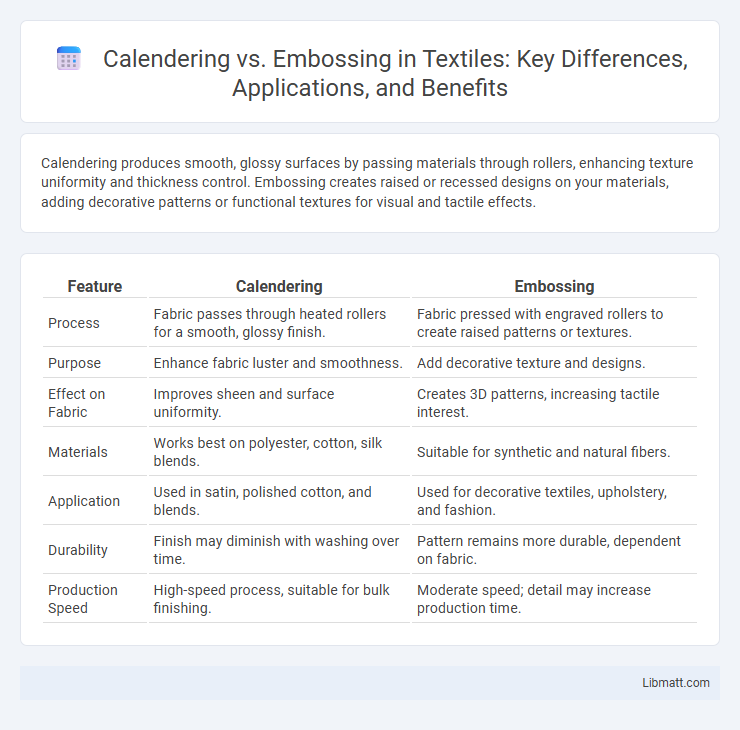
| Feature | Calendering | Embossing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Fabric passes through heated rollers for a smooth, glossy finish. | Fabric pressed with engraved rollers to create raised patterns or textures. |
| Purpose | Enhance fabric luster and smoothness. | Add decorative texture and designs. |
| Effect on Fabric | Improves sheen and surface uniformity. | Creates 3D patterns, increasing tactile interest. |
| Materials | Works best on polyester, cotton, silk blends. | Suitable for synthetic and natural fibers. |
| Application | Used in satin, polished cotton, and blends. | Used for decorative textiles, upholstery, and fashion. |
| Durability | Finish may diminish with washing over time. | Pattern remains more durable, dependent on fabric. |
| Production Speed | High-speed process, suitable for bulk finishing. | Moderate speed; detail may increase production time. |
Introduction to Calendering and Embossing
Calendering is a mechanical process that smooths and compresses materials, such as paper or textiles, by passing them through heated rollers to enhance surface finish and thickness uniformity. Embossing involves creating raised or recessed patterns on materials using patterned rollers or plates, adding texture and decorative effects to fabrics, paper, or metal sheets. Understanding the differences between calendering and embossing helps you select the right technique for achieving specific aesthetic or functional surface qualities in your products.
Understanding the Calendering Process
The calendering process involves passing materials like paper, textiles, or plastics through a series of heated rollers to achieve a smooth, glossy, or textured finish, enhancing surface uniformity and density. This technique improves product strength, appearance, and dimensional accuracy by applying pressure and heat simultaneously. In contrast to embossing, which creates raised patterns, calendering primarily focuses on surface smoothness and consistent thickness.
Exploring the Embossing Technique
Embossing is a technique used to create raised or recessed designs on materials such as paper, fabric, or leather by applying heat and pressure with engraved rollers or plates. This process enhances texture and visual appeal, often used for branding, decorative elements, and tactile effects in packaging and textiles. Unlike calendering, which smooths or compresses surfaces, embossing adds dimensionality and intricate patterns that improve product aesthetics and user experience.
Key Differences Between Calendering and Embossing
Calendering involves passing material through rollers to create a smooth, glossy, or textured surface, while embossing presses a pattern or design into the material to produce a raised or recessed effect. Calendering primarily modifies surface finish and thickness, whereas embossing enhances aesthetic appeal and adds tactile dimensionality. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate technique to achieve your desired visual and functional outcomes.
Materials Used in Calendering vs Embossing
Calendering primarily utilizes thermoplastic polymers like PVC, polyethylene, and polypropylene, which are softened by heat and pressure to form smooth, glossy surfaces. Embossing employs a wider range of materials such as paper, leather, metal foils, and plastic films, where patterns are impressed onto the surface using engraved rollers or plates. The choice of materials in calendering favors flexibility and heat tolerance, while embossing materials must have sufficient malleability to retain textured designs.
Industrial Applications of Calendering
Calendering is widely used in industrial applications to create smooth, uniform surfaces on materials like plastics, rubber, and textiles, enhancing their finish and functionality. This process is essential in manufacturing films, sheets, and coated fabrics where precise thickness and gloss are critical. Your production efficiency benefits from calendering's ability to ensure consistent product quality and improved material properties.
Common Uses of Embossing in Manufacturing
Embossing is widely used in manufacturing for creating textured surfaces on materials like paper, leather, and metal to enhance aesthetic appeal and tactile experience. Common applications include decorative packaging, branded stationery, automotive interior panels, and appliance covers where raised patterns improve both functionality and design. Your products can benefit from embossing techniques to add value and distinctiveness in competitive markets.
Advantages and Limitations of Calendering
Calendering offers precise control over material thickness and surface smoothness, making it ideal for producing consistent sheets and films in industries like textiles, plastics, and paper. Its advantages include high-speed production and the ability to create glossy finishes, but limitations involve potential material stress and reduced flexibility with complex textures. You should consider calendering when uniformity and surface quality are priorities, despite its constraints on embossing detailed patterns.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Embossing
Embossing enhances tactile appeal and visual depth, making your designs stand out with raised patterns that add luxury and sophistication to materials like paper, leather, and textiles. However, embossing can increase production time and costs due to specialized equipment and labor, and may not be suitable for all material thicknesses or intricate designs. Despite these drawbacks, the unique texture and premium feel created by embossing often justify its use for branding and decorative purposes.
Choosing Between Calendering and Embossing
Choosing between calendering and embossing depends on the desired surface texture and product functionality. Calendering produces smooth, glossy finishes by passing materials through rollers, ideal for films and synthetic textiles requiring uniform thickness and sheen. Embossing creates raised or recessed patterns to enhance tactile and visual appeal, often used for decorative paper, leather, and fabrics where texture and design are prioritized.
Calendering vs Embossing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com