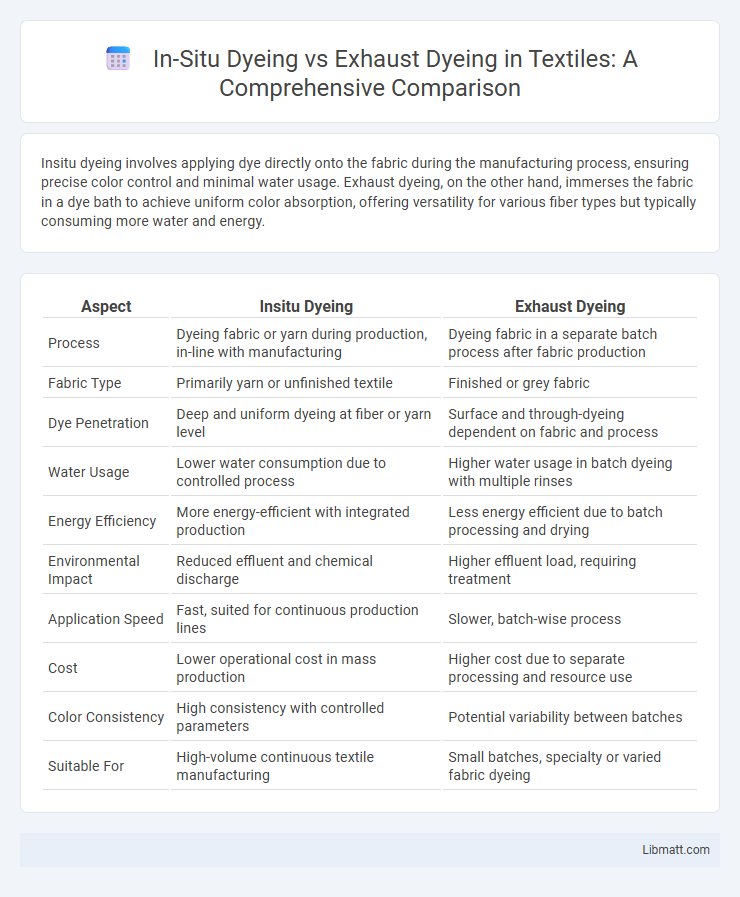
Insitu dyeing involves applying dye directly onto the fabric during the manufacturing process, ensuring precise color control and minimal water usage. Exhaust dyeing, on the other hand, immerses the fabric in a dye bath to achieve uniform color absorption, offering versatility for various fiber types but typically consuming more water and energy.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Insitu Dyeing | Exhaust Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Dyeing fabric or yarn during production, in-line with manufacturing | Dyeing fabric in a separate batch process after fabric production |
| Fabric Type | Primarily yarn or unfinished textile | Finished or grey fabric |
| Dye Penetration | Deep and uniform dyeing at fiber or yarn level | Surface and through-dyeing dependent on fabric and process |
| Water Usage | Lower water consumption due to controlled process | Higher water usage in batch dyeing with multiple rinses |
| Energy Efficiency | More energy-efficient with integrated production | Less energy efficient due to batch processing and drying |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced effluent and chemical discharge | Higher effluent load, requiring treatment |
| Application Speed | Fast, suited for continuous production lines | Slower, batch-wise process |
| Cost | Lower operational cost in mass production | Higher cost due to separate processing and resource use |
| Color Consistency | High consistency with controlled parameters | Potential variability between batches |
| Suitable For | High-volume continuous textile manufacturing | Small batches, specialty or varied fabric dyeing |
Introduction to Insitu Dyeing and Exhaust Dyeing
Insitu dyeing involves applying color directly onto fabrics or fibers during the manufacturing process, ensuring deep penetration and uniform distribution of dyes. Exhaust dyeing, a traditional method, submerges textiles in a dye bath where dye molecules gradually transfer from the liquor to the fabric until equilibrium is reached. Your choice between insitu and exhaust dyeing impacts colorfastness, resource consumption, and environmental footprint.
Defining Insitu Dyeing
Insitu dyeing is a textile coloration method where dye synthesis and fiber dyeing occur simultaneously within the fabric or fiber matrix, enabling precise color formation directly on the substrate. This technique contrasts with exhaust dyeing, where dyes are applied from a dye bath and absorbed by fibers during a separate process. Advantages of insitu dyeing include enhanced colorfastness, reduced water consumption, and minimized environmental impact due to localized dye generation.
Overview of Exhaust Dyeing
Exhaust dyeing is a traditional textile dyeing process where fabric or yarn is immersed in a dye bath, allowing the dye molecules to gradually transfer and fix onto the fibers through controlled temperature and time. This method offers uniform color penetration and excellent reproducibility for large-scale production of cotton, polyester, and blended fabrics. Compared to insitu dyeing, exhaust dyeing provides higher dye uptake efficiency and better color fastness, making it a preferred choice in mass dyeing applications.
Key Differences Between Insitu and Exhaust Dyeing
Insitu dyeing applies color directly onto fabric during the production process, ensuring precise pattern placement and reduced water usage, while exhaust dyeing immerses fabric in a dye bath for uniform color absorption, often leading to longer processing times and higher water consumption. Insitu dyeing excels in efficiency for complex patterns and digital textile printing, whereas exhaust dyeing is preferred for bulk dyeing of uniform solid colors. Understanding these key differences helps optimize your choice for specific fabric types and environmental considerations.
Process Steps in Insitu Dyeing
Insitu dyeing involves the direct application of dye onto fibers or fabrics during the formation process, where the dye molecules penetrate fibers in real-time, ensuring uniform color distribution and reduced water usage. Key process steps include fiber preparation, simultaneous dye application during fiber formation or fabric production, and controlled fixation to lock in the pigment without extensive post-treatment. This method differs from traditional exhaust dyeing by minimizing environmental impact and improving dyeing efficiency through integrated, continuous processing.
Process Workflow of Exhaust Dyeing
Exhaust dyeing involves immersing the fabric in a large dye bath where the dye gradually transfers from the liquor to the textile material through diffusion and adsorption, ensuring uniform color distribution. The process workflow includes fabric preparation, dye bath formulation, dyeing under controlled temperature and pH conditions, rinsing, and drying. This method is ideal for dyeing large volumes of fabric with consistent color quality and excellent depth.
Environmental Impact: Insitu vs Exhaust Dyeing
Insitu dyeing significantly reduces water and energy consumption by applying dyes directly to textiles without requiring large water baths, unlike exhaust dyeing that relies on extensive water use and generates higher volumes of wastewater. Your choice of insitu dyeing lowers chemical discharge and minimizes ecological footprints compared to traditional exhaust dyeing processes. Insitu dyeing's precise application techniques enhance sustainability by reducing pollution and conserving natural resources.
Efficiency and Cost Comparison
Insitu dyeing offers higher efficiency by minimizing water and energy consumption through targeted fabric treatment, reducing waste and processing time. Exhaust dyeing, while more flexible for large batch processing, typically incurs higher operational costs due to extended dyeing cycles and greater resource usage. Your choice between these methods should consider ongoing production scale and cost-effectiveness in water and energy management.
Quality and Performance Analysis
Insitu dyeing produces fabric with superior color uniformity and enhanced fastness properties by directly applying dye during fiber formation, resulting in reduced dye wastage and environmental impact. Exhaust dyeing offers better depth of shade and is suitable for a wider range of fibers, but may exhibit variations in color consistency and requires larger water usage. You can achieve optimal textile quality and performance by selecting the dyeing method matching fiber type and production scale.
Choosing the Right Dyeing Technique
Choosing the right dyeing technique depends on factors like fabric type, production scale, and desired colorfastness. Insitu dyeing offers precise color application and is ideal for small batch, design-focused projects, while exhaust dyeing ensures uniform color penetration suitable for large-scale manufacturing. Understanding your fabric's compatibility and production goals ensures optimal results and efficient resource use.
Insitu Dyeing vs Exhaust Dyeing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com