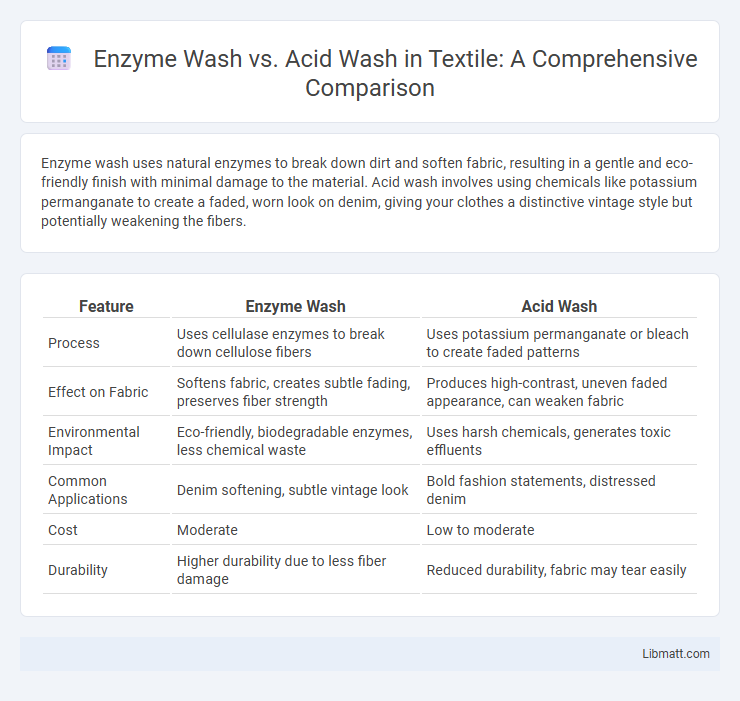
Enzyme wash uses natural enzymes to break down dirt and soften fabric, resulting in a gentle and eco-friendly finish with minimal damage to the material. Acid wash involves using chemicals like potassium permanganate to create a faded, worn look on denim, giving your clothes a distinctive vintage style but potentially weakening the fibers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Enzyme Wash | Acid Wash |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Uses cellulase enzymes to break down cellulose fibers | Uses potassium permanganate or bleach to create faded patterns |
| Effect on Fabric | Softens fabric, creates subtle fading, preserves fiber strength | Produces high-contrast, uneven faded appearance, can weaken fabric |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable enzymes, less chemical waste | Uses harsh chemicals, generates toxic effluents |
| Common Applications | Denim softening, subtle vintage look | Bold fashion statements, distressed denim |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Durability | Higher durability due to less fiber damage | Reduced durability, fabric may tear easily |
Introduction to Enzyme Wash and Acid Wash
Enzyme wash utilizes natural enzymes to break down cellulose fibers in denim, resulting in a softer texture and improved fabric durability without harsh chemicals. Acid wash involves treating fabric with pumice stones soaked in chlorine or bleaching agents, creating a distinctive faded, marbled appearance ideal for vintage-style denim. Both techniques enhance denim's aesthetic and tactile properties but differ significantly in chemical process and environmental impact.
What is Enzyme Wash?
Enzyme wash is a textile finishing process that uses natural enzymes to break down the fibers on the fabric surface, resulting in a softer texture and a worn-in appearance without damaging the material. This eco-friendly technique is commonly used in denim production to achieve a faded, distressed look while maintaining fabric strength and reducing chemical usage. Enzyme wash enhances fabric softness, color fading, and overall garment durability compared to traditional washing methods.
What is Acid Wash?
Acid wash is a garment treatment process that uses pumice stones soaked in a chlorine or acidic solution to create a faded, marbled effect on denim or other fabrics. This technique breaks down the dye on the fabric's surface, producing a distinctive worn-out look with high contrast and random patterns. Your clothing treated with acid wash gains a vintage-inspired appearance while maintaining the fabric's flexibility and texture.
Key Differences Between Enzyme and Acid Wash
Enzyme wash uses biological catalysts to gently break down fabric fibers, resulting in softer textures and less environmental impact, while acid wash involves chlorine or potassium permanganate to create faded, vintage looks with more aggressive fiber alteration. The enzyme wash is ideal for preserving fabric strength and achieving subtle color changes, whereas acid wash delivers high-contrast patterns but can weaken material over time. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right wash technique based on desired fabric feel and garment durability.
Benefits of Enzyme Wash
Enzyme wash offers superior fabric softness and reduced fiber damage by using natural enzymes to gently break down cellulose fibers, enhancing garment comfort and durability. It improves color retention and reduces pilling, making it ideal for maintaining the quality of denim and other cotton fabrics. This eco-friendly process minimizes water and chemical use, promoting sustainable textile manufacturing.
Advantages of Acid Wash
Acid wash offers significant advantages in garment finishing by providing a unique, vintage appearance with enhanced color fading and texture that enzyme washes cannot achieve. This method improves fabric softness and breathability while maintaining durability, making it ideal for denim and tough fabrics. Acid wash also helps remove surface impurities and create eye-catching contrasts, giving textiles a distinct, trendy look favored in fashion industries.
Environmental Impact: Enzyme Wash vs Acid Wash
Enzyme wash utilizes biodegradable enzymes that break down fabric fibers naturally, resulting in significantly lower water pollution and reduced chemical runoff compared to traditional acid wash processes. Acid wash involves strong acids like potassium permanganate, which can produce hazardous waste requiring careful disposal to prevent soil and water contamination. Enzyme wash is considered more eco-friendly due to its milder chemicals, decreased energy consumption, and minimal environmental footprint.
Cost Comparison: Enzyme vs Acid Treatment
Enzyme wash typically costs more due to the complex biological processes involved, while acid wash is generally cheaper because it uses readily available chemicals and faster procedures. Your choice may affect overall expenses, with enzyme treatments offering eco-friendly benefits that could offset higher initial costs in some markets. Acid wash remains favored for budget-conscious projects but might require more safety measures, potentially influencing total expenditure.
Applications in Textile and Denim Industry
Enzyme wash utilizes cellulase enzymes to selectively break down cellulose fibers, creating a softer texture and faded appearance in denim and other textiles without harsh chemicals. Acid wash involves pumice stones soaked in chlorine or potassium permanganate, generating a high-contrast, marbled effect primarily used in denim fashion for a vintage look. Both techniques enhance fabric aesthetics and hand feel, with enzyme wash favored for sustainable, gentle fading, while acid wash achieves bold, dramatic visual patterns in denim production.
Choosing the Right Wash: Factors to Consider
Choosing between enzyme wash and acid wash depends on desired fabric texture, color retention, and environmental impact. Enzyme wash offers a softer fabric feel and enhanced biodegradability due to natural enzymes breaking down cellulose fibers, making it suitable for sustainable fashion. Acid wash delivers a distinct faded, worn look but involves harsher chemicals that may affect fabric longevity and generate more environmental waste.
Enzyme wash vs Acid wash Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com