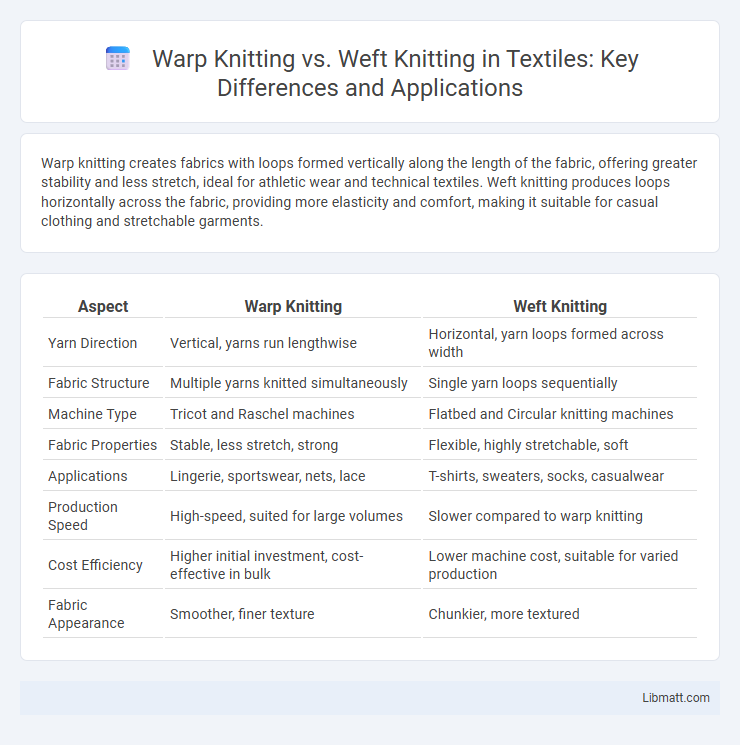
Warp knitting creates fabrics with loops formed vertically along the length of the fabric, offering greater stability and less stretch, ideal for athletic wear and technical textiles. Weft knitting produces loops horizontally across the fabric, providing more elasticity and comfort, making it suitable for casual clothing and stretchable garments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Warp Knitting | Weft Knitting |
|---|---|---|
| Yarn Direction | Vertical, yarns run lengthwise | Horizontal, yarn loops formed across width |
| Fabric Structure | Multiple yarns knitted simultaneously | Single yarn loops sequentially |
| Machine Type | Tricot and Raschel machines | Flatbed and Circular knitting machines |
| Fabric Properties | Stable, less stretch, strong | Flexible, highly stretchable, soft |
| Applications | Lingerie, sportswear, nets, lace | T-shirts, sweaters, socks, casualwear |
| Production Speed | High-speed, suited for large volumes | Slower compared to warp knitting |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial investment, cost-effective in bulk | Lower machine cost, suitable for varied production |
| Fabric Appearance | Smoother, finer texture | Chunkier, more textured |
Introduction to Warp Knitting and Weft Knitting
Warp knitting involves yarns running vertically, creating fabrics with high dimensional stability and resistance to runs, commonly used in technical textiles and sportswear. Weft knitting consists of yarns interlaced horizontally, yielding stretchable and flexible fabrics ideal for apparel like sweaters and t-shirts. Differences in machine types, fabric structure, and performance characteristics distinguish warp knitting from weft knitting in textile manufacturing.
Fundamental Differences Between Warp and Weft Knitting
Warp knitting produces fabric by interlocking loops vertically along the length of the fabric, creating high stability and resistance to runs, while weft knitting forms loops horizontally across the width, offering greater elasticity and comfort. Warp knit fabrics are typically used for technical applications like sportswear and industrial textiles due to their durability, whereas weft knit fabrics dominate in apparel because of their stretch and softness. The distinct loop formation and yarn orientation in warp and weft knitting fundamentally affect fabric texture, strength, and application suitability.
Yarn Orientation in Warp vs Weft Knitting
Warp knitting features yarns running vertically and parallel to the selvage, creating loops along the fabric's length, which enhances stability and reduces stretch. In contrast, weft knitting has yarns oriented horizontally across the width, forming loops that interlock from side to side, offering greater flexibility and elasticity. Understanding these yarn orientations helps you select the right knit type for durability or comfort in your textile projects.
Machinery Used in Warp and Weft Knitting
Warp knitting machinery includes tricot and raschel machines, which operate with multiple yarns fed parallel to the fabric's length, enabling fast production of stable and non-runner fabrics. Weft knitting machines, such as circular and flat-bed knitting machines, knit yarns crosswise in loops, creating stretchable and flexible fabrics ideal for garments like T-shirts and sweaters. The technological design of warp knitting machines supports intricate mesh and lace structures, while weft knitting machines excel in producing knitwear with varying textures and patterns.
Fabric Properties and Texture Comparison
Warp knitting produces fabrics with higher dimensional stability, less stretch, and a more structured texture, making them ideal for technical applications and durable garments. Weft knitting yields softer, more elastic fabrics with pronounced stretch and a smoother texture, enhancing comfort and flexibility in everyday wear. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize resilience and shape retention or softness and stretchability in the fabric.
Applications of Warp Knitted Fabrics
Warp knitted fabrics are widely used in technical textiles due to their high dimensional stability, strength, and resistance to runs, making them ideal for automotive upholstery, sportswear, and industrial filters. Their open and lace-like structures offer breathability and elasticity, which enhances comfort in swimwear, lingerie, and activewear. In comparison to weft knitting, warp knitting provides superior durability and shape retention, critical for applications like medical textiles and geotextiles.
Applications of Weft Knitted Fabrics
Weft knitted fabrics find extensive applications in apparel manufacturing due to their stretchability and comfort, making them ideal for t-shirts, sweaters, and activewear. Their ability to conform to body shapes and provide ventilation suits sportswear and casual clothing perfectly. You can also find weft knits in home textiles such as upholstery and blankets, emphasizing versatility across industries.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Warp vs Weft Knitting
Warp knitting offers advantages such as faster production rates, greater fabric stability, and enhanced resistance to runs or ladders, making it ideal for technical and industrial textiles. Weft knitting provides superior elasticity, comfort, and ease of garment shaping but tends to have lower dimensional stability and is more prone to laddering or snagging. Each method's suitability depends on the end-use requirements, with warp knitting excelling in durability and strength, while weft knitting prioritizes flexibility and softness.
Quality Control in Warp and Weft Knitting Processes
Quality control in warp knitting emphasizes maintaining uniform tension and yarn alignment to prevent defects such as loose loops or holes, ensuring consistent fabric strength and appearance. Weft knitting quality control focuses on monitoring stitch formation and loop density to avoid issues like dropped stitches or uneven fabric edges, which can affect elasticity and fit. Both processes require precise machine calibration and continuous inspection to uphold fabric durability and performance standards.
Choosing the Right Knitting Technique for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate knitting technique depends on the project's desired fabric characteristics and application. Warp knitting produces stable, less stretchy fabrics ideal for sportswear, lingerie, and technical textiles, while weft knitting offers greater elasticity and comfort, making it suitable for casual clothing and sweaters. Understanding factors like durability, stretch, and production speed ensures optimal results for your specific textile requirements.
Warp knitting vs Weft knitting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com