Oiling enhances wood's natural grain and moisture resistance by penetrating the surface, while sizing creates a protective layer that reduces absorbency and improves paint or finish adhesion. Understanding the difference helps you choose the right treatment to preserve and beautify your wood projects.
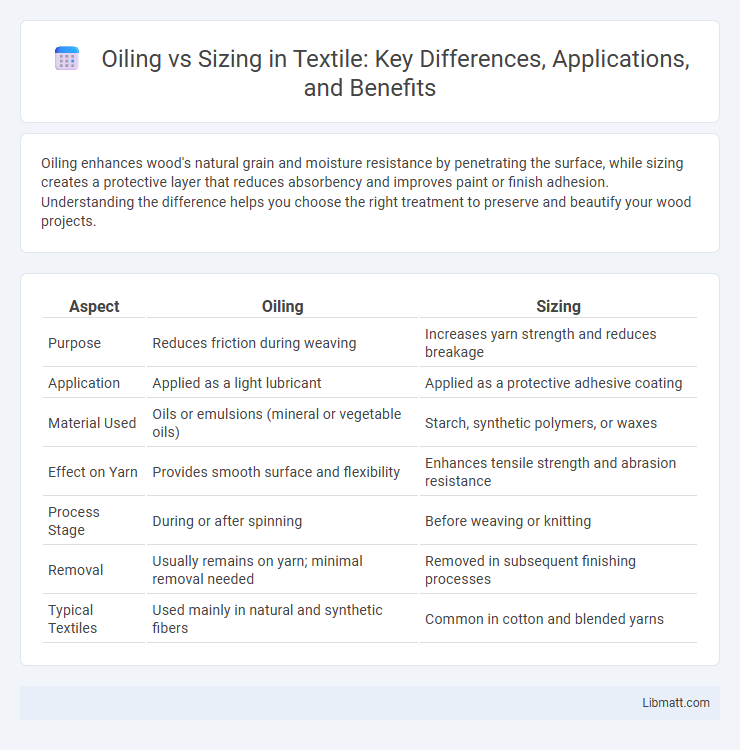
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Oiling | Sizing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces friction during weaving | Increases yarn strength and reduces breakage |
| Application | Applied as a light lubricant | Applied as a protective adhesive coating |
| Material Used | Oils or emulsions (mineral or vegetable oils) | Starch, synthetic polymers, or waxes |
| Effect on Yarn | Provides smooth surface and flexibility | Enhances tensile strength and abrasion resistance |
| Process Stage | During or after spinning | Before weaving or knitting |
| Removal | Usually remains on yarn; minimal removal needed | Removed in subsequent finishing processes |
| Typical Textiles | Used mainly in natural and synthetic fibers | Common in cotton and blended yarns |
Understanding Oiling and Sizing: Definitions and Applications
Oiling and sizing are crucial processes in textile manufacturing that significantly impact fabric performance and quality. Oiling involves applying lubricants to fibers or yarns to reduce friction during weaving or knitting, enhancing smoothness and preventing breakage. Sizing adds a protective adhesive coating, increasing yarn strength and stability, which is essential for efficient weaving and improving the durability of your final fabric.
Key Differences Between Oiling and Sizing
Oiling involves applying a lubricant to fibers or filaments to reduce friction during processing, enhancing flexibility and preventing breakage, whereas sizing applies a protective coating to yarns or fabrics to increase strength and abrasion resistance during weaving. Oiling primarily targets improving machine performance by reducing static and friction, while sizing focuses on reinforcing the material's structural integrity. Both processes serve distinct roles in textile manufacturing, optimizing different aspects of fiber treatment for efficient production.
Benefits of Oiling in Textile Processing
Oiling in textile processing enhances fiber flexibility and reduces friction, leading to smoother weaving and less breakage. It improves dye uptake uniformity, resulting in richer and more consistent fabric colors. The application of oil also protects fibers against static electricity and environmental damage, extending the durability of the textiles.
Advantages of Sizing for Fabric Quality
Sizing enhances fabric quality by improving yarn strength and abrasion resistance, resulting in more durable and less prone-to-breakage textiles. It creates a protective film over yarns, reducing hairiness and increasing weaving efficiency, which leads to smoother, higher-quality fabric surfaces. The controlled application of sizing agents also minimizes fabric defects and enhances dimensional stability during processing, contributing to superior fabric performance.
Common Materials Used for Oiling and Sizing
Common materials used for oiling include mineral oils, synthetic oils, and vegetable oils, which provide lubrication and reduce friction on various surfaces. Sizing commonly involves starches, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and acrylic polymers, aimed at improving fabric strength and surface smoothness. Both processes utilize water-based solutions to ensure even application and enhance performance qualities in textiles and paper products.
Impact of Oiling vs Sizing on Fabric Performance
Oiling enhances fabric flexibility and water resistance by coating fibers with lubricants, reducing friction during weaving and improving durability. Sizing strengthens yarns by applying a starch-based coating that increases tensile strength and reduces breakage, leading to smoother weaving and improved fabric uniformity. Understanding the impact of oiling versus sizing on your fabric performance helps optimize production efficiency and final product quality.
Oiling vs Sizing: Environmental Considerations
Oiling and sizing treatments impact environmental sustainability differently, with oiling often involving natural or plant-based oils that can be biodegradable and less toxic to aquatic ecosystems. Sizing agents, typically synthetic polymers, may persist in the environment and contribute to pollution if not managed properly. Your choice between oiling and sizing should consider the ecological footprint, especially regarding biodegradability and potential water contamination.
Choosing the Right Method: Factors to Consider
Choosing between oiling and sizing depends on factors such as the material type, desired finish, and end-use application. Oiling enhances flexibility and natural texture, making it ideal for leather goods requiring softness, while sizing improves stiffness and surface strength, better suited for fabrics needing crispness. Consider environmental conditions, cost-effectiveness, and long-term durability when selecting the appropriate method.
Innovations and Trends in Oiling and Sizing Technologies
Innovations in oiling and sizing technologies have advanced significantly with the integration of bio-based and nanomaterials, enhancing fabric performance and environmental sustainability. Sizing formulations now incorporate smart polymers that improve yarn strength and fabric resilience while enabling easier removal during washing, minimizing chemical residues. These trends reflect a growing emphasis on eco-friendly solutions and functional enhancements, driving the textile industry toward more efficient and sustainable production processes.
Frequently Asked Questions: Oiling vs Sizing
Oiling and sizing serve distinct purposes in fabric treatment, with oiling enhancing lubrication and flexibility, while sizing improves fabric strength and resistance to abrasion during weaving. Frequently asked questions focus on differences in application methods, impact on fabric texture, and suitability for various fiber types. Understanding these distinctions helps manufacturers choose the right process to optimize textile performance and durability.
Oiling vs Sizing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com