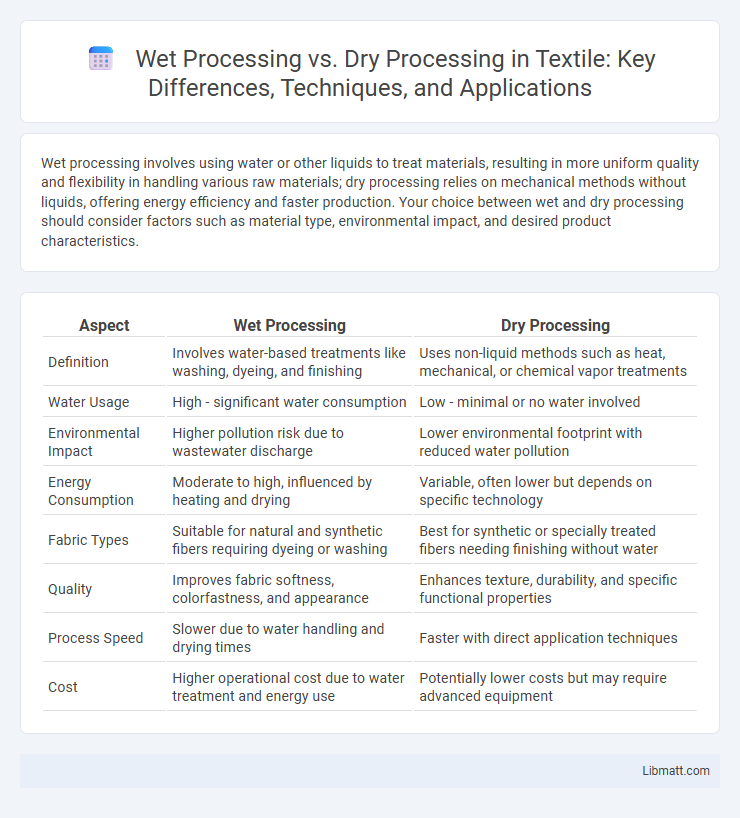
Wet processing involves using water or other liquids to treat materials, resulting in more uniform quality and flexibility in handling various raw materials; dry processing relies on mechanical methods without liquids, offering energy efficiency and faster production. Your choice between wet and dry processing should consider factors such as material type, environmental impact, and desired product characteristics.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Wet Processing | Dry Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Involves water-based treatments like washing, dyeing, and finishing | Uses non-liquid methods such as heat, mechanical, or chemical vapor treatments |
| Water Usage | High - significant water consumption | Low - minimal or no water involved |
| Environmental Impact | Higher pollution risk due to wastewater discharge | Lower environmental footprint with reduced water pollution |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate to high, influenced by heating and drying | Variable, often lower but depends on specific technology |
| Fabric Types | Suitable for natural and synthetic fibers requiring dyeing or washing | Best for synthetic or specially treated fibers needing finishing without water |
| Quality | Improves fabric softness, colorfastness, and appearance | Enhances texture, durability, and specific functional properties |
| Process Speed | Slower due to water handling and drying times | Faster with direct application techniques |
| Cost | Higher operational cost due to water treatment and energy use | Potentially lower costs but may require advanced equipment |
Introduction to Wet and Dry Processing
Wet processing involves treating coffee beans with water to remove the fruit's outer layers, resulting in a cleaner and brighter flavor profile. Dry processing, also known as natural processing, dries the whole coffee cherries under the sun, which often produces a fruitier and more complex taste. Your choice between wet and dry processing directly influences the coffee's acidity, body, and overall flavor characteristics.
Key Differences Between Wet and Dry Processing
Wet processing involves the use of water or other liquids to extract material, resulting in cleaner and more refined products often favored in textile and food industries. Dry processing relies on mechanical or thermal methods without liquids, leading to faster processing times and reduced water consumption, commonly used in mineral extraction and grain milling. The key differences lie in environmental impact, product quality, and operational costs, with wet processing generally having higher water usage and energy consumption, while dry processing emphasizes efficiency and minimal waste generation.
Applications of Wet Processing
Wet processing is extensively applied in textile manufacturing for dyeing, washing, bleaching, and finishing fabrics to enhance color fastness, texture, and durability. It is crucial in producing high-quality garments and technical textiles, ensuring uniform dye absorption and impurity removal. This method is preferred for cotton, wool, and synthetic fibers requiring precise color treatments and surface modifications.
Applications of Dry Processing
Dry processing techniques are widely applied in industries such as mineral extraction, ceramics manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals for separating valuable materials without the use of water. This method is especially advantageous for processing materials that are sensitive to moisture or when water conservation is critical. Applications include gravity separation, magnetic separation, and electrostatic separation, which efficiently isolate and refine minerals and powders in an environmentally friendly manner.
Advantages of Wet Processing
Wet processing offers superior cleaning and washing capabilities, effectively removing impurities from raw materials and enhancing product quality. This method is ideal for delicate beans or fruits, preserving their flavor profiles and ensuring consistent taste in the final product. By using water to separate desirable characteristics, wet processing improves uniformity and reduces defects that could affect Your product's market value.
Advantages of Dry Processing
Dry processing offers significant water conservation benefits by eliminating the need for large volumes of water, making it environmentally sustainable and cost-effective in arid regions. This method reduces energy consumption and operational costs by avoiding water treatment and drying phases typical of wet processing. Additionally, dry processing minimizes wastewater discharge, lowering environmental pollution and simplifying compliance with environmental regulations.
Limitations of Wet vs Dry Processing
Wet processing requires large amounts of water and energy, leading to environmental concerns and higher operational costs, while dry processing uses less water but can result in lower quality output and increased dust pollution. Wet processing is limited by waste treatment challenges, whereas dry processing struggles with less efficient contaminant removal and difficulty handling certain material types. Your choice between these methods depends on balancing environmental impact, material characteristics, and cost considerations.
Equipment Used in Wet and Dry Processing
Wet processing primarily utilizes equipment such as drum washers, hydro-extractors, and vacuum dryers to remove impurities and moisture from raw materials. Dry processing relies on machinery like air classifiers, magnetic separators, and rotary kilns to sort and treat materials without the use of water. The choice between wet and dry processing equipment impacts operational efficiency, environmental considerations, and final product quality.
Environmental Impact: Wet vs Dry Processing
Wet processing in textiles consumes significantly more water and energy compared to dry processing, resulting in higher wastewater generation with chemical pollutants. Dry processing techniques, such as air dyeing and digital printing, reduce water usage and lower emissions, making them more environmentally sustainable. The shift towards dry processing helps mitigate water scarcity and decreases the ecological footprint of textile manufacturing industries.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Application
Selecting between wet processing and dry processing depends on the specific requirements and desired outcomes of your application. Wet processing excels in applications needing enhanced precision, consistent results, and thorough cleaning or coating, such as in textile finishing or semiconductor manufacturing. Dry processing suits tasks where speed, cost-effectiveness, and minimal environmental impact are priorities, commonly found in powder metallurgy or additive manufacturing.
Wet processing vs Dry processing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com