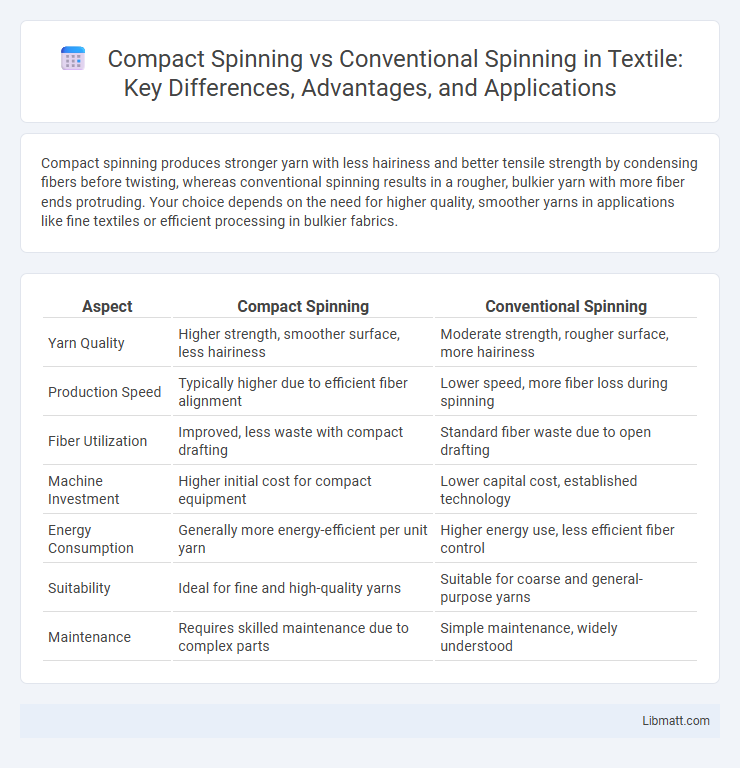
Compact spinning produces stronger yarn with less hairiness and better tensile strength by condensing fibers before twisting, whereas conventional spinning results in a rougher, bulkier yarn with more fiber ends protruding. Your choice depends on the need for higher quality, smoother yarns in applications like fine textiles or efficient processing in bulkier fabrics.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Compact Spinning | Conventional Spinning |
|---|---|---|
| Yarn Quality | Higher strength, smoother surface, less hairiness | Moderate strength, rougher surface, more hairiness |
| Production Speed | Typically higher due to efficient fiber alignment | Lower speed, more fiber loss during spinning |
| Fiber Utilization | Improved, less waste with compact drafting | Standard fiber waste due to open drafting |
| Machine Investment | Higher initial cost for compact equipment | Lower capital cost, established technology |
| Energy Consumption | Generally more energy-efficient per unit yarn | Higher energy use, less efficient fiber control |
| Suitability | Ideal for fine and high-quality yarns | Suitable for coarse and general-purpose yarns |
| Maintenance | Requires skilled maintenance due to complex parts | Simple maintenance, widely understood |
Introduction to Spinning Technologies
Compact spinning technology enhances yarn strength and reduces hairiness by condensing fibers before twist insertion, leading to improved fabric quality compared to conventional ring spinning. Conventional spinning involves drafting fibers into a strand and inserting twist directly, which can result in higher hairiness and lower yarn uniformity. The adoption of compact spinning addresses common drawbacks of conventional methods, boosting productivity and fabric performance in textile manufacturing.
What is Compact Spinning?
Compact spinning is an advanced yarn production technology that enhances fiber alignment by condensing the fiber strand during the draw frame process, resulting in stronger and smoother yarns. Unlike conventional spinning, which leaves more air between fibers, compact spinning reduces hairiness and improves yarn uniformity, leading to higher fabric quality and durability. Your textile manufacturing can benefit significantly from compact spinning through improved productivity and enhanced fabric performance.
What is Conventional Spinning?
Conventional spinning is a traditional yarn production method where fibers are drawn out and twisted to form yarn with a spinning frame or ring spinning machine. This process results in yarns that may have higher hairiness and lower strength compared to advanced methods. It is widely used due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness but often requires additional finishing processes to improve yarn quality.
Key Differences between Compact and Conventional Spinning
Compact spinning reduces hair fly and increases yarn strength by using a fiber-condensing zone, unlike conventional spinning which relies on a standard drafting system. The compact process yields finer, smoother yarn with less hairiness and improved uniformity, enhancing fabric quality. Productivity is higher in compact spinning due to reduced yarn breakage and improved machine efficiency compared to conventional spinning.
Yarn Structure and Quality Comparison
Compact spinning produces yarns with a more uniform fiber arrangement, resulting in higher yarn strength, reduced hairiness, and improved smoothness compared to conventional spinning. The compacted fiber strand in compact spinning minimizes fiber fly and produces yarns with better tensile properties and enhanced evenness. Conventional spinning, while versatile, often results in yarns with higher hairiness and lower tenacity due to less fiber alignment.
Production Efficiency and Cost Analysis
Compact spinning enhances production efficiency by significantly reducing yarn hairiness and breakage rates, leading to higher machine speeds and improved yarn quality compared to conventional spinning. The increased productivity often results in lower overall production costs despite a higher initial investment due to energy savings and reduced material waste. Cost analysis indicates that compact spinning delivers better yarn strength and uniformity, minimizing downstream processing expenses and boosting profitability in textile manufacturing.
Impact on Fabric Properties
Compact spinning enhances fabric strength, smoothness, and uniformity by reducing fiber hairiness and imperfections compared to conventional spinning. Fabrics produced through compact spinning exhibit improved abrasion resistance and better pilling performance, increasing their durability and visual appeal. Your textiles gain a higher quality finish with consistent thickness and softer hand feel, making compact spinning ideal for premium fabric production.
Environmental Considerations
Compact spinning reduces fiber waste and energy consumption compared to conventional spinning, leading to a lower environmental footprint in textile production. The process minimizes air pollution by generating less fiber fly and dust, improving workplace air quality and reducing emissions. Your choice of compact spinning technology supports sustainable manufacturing practices by optimizing resource efficiency and lowering overall environmental impact.
Application Areas and Market Trends
Compact spinning offers superior yarn strength and reduced hairiness, making it ideal for high-quality textiles in fashion and technical fabrics, while conventional spinning remains prevalent in mass production of basic textiles and home furnishings. Market trends show a growing preference for compact spinning in premium segments due to its efficiency and enhanced fabric performance, driving innovation in smart textiles and sustainable production. The conventional spinning market holds steady in volume but faces pressure from compact technology adoption, especially in developing regions prioritizing cost and output scalability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Spinning Method
Choosing the right spinning method depends on specific production goals, with compact spinning offering superior yarn quality and strength due to reduced hairiness and fewer imperfections. Conventional spinning remains cost-effective for high-volume manufacturing where extreme yarn performance is less critical. Evaluating factors like fiber type, end-use requirements, and budget constraints ensures the optimal spinning technology aligns with operational needs.
Compact spinning vs Conventional spinning Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com