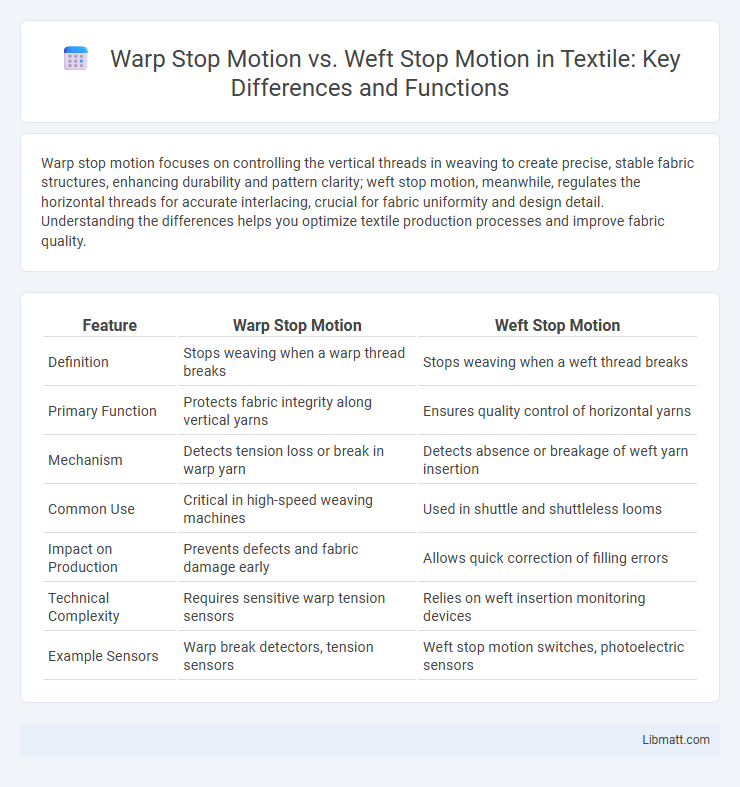
Warp stop motion focuses on controlling the vertical threads in weaving to create precise, stable fabric structures, enhancing durability and pattern clarity; weft stop motion, meanwhile, regulates the horizontal threads for accurate interlacing, crucial for fabric uniformity and design detail. Understanding the differences helps you optimize textile production processes and improve fabric quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Warp Stop Motion | Weft Stop Motion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Stops weaving when a warp thread breaks | Stops weaving when a weft thread breaks |
| Primary Function | Protects fabric integrity along vertical yarns | Ensures quality control of horizontal yarns |
| Mechanism | Detects tension loss or break in warp yarn | Detects absence or breakage of weft yarn insertion |
| Common Use | Critical in high-speed weaving machines | Used in shuttle and shuttleless looms |
| Impact on Production | Prevents defects and fabric damage early | Allows quick correction of filling errors |
| Technical Complexity | Requires sensitive warp tension sensors | Relies on weft insertion monitoring devices |
| Example Sensors | Warp break detectors, tension sensors | Weft stop motion switches, photoelectric sensors |
Introduction to Loom Stop Motions
Loom stop motions are essential techniques used in textile production to control fabric texture and pattern formation. Warp stop motion detects tension breakages or thread issues in the warp yarns running lengthwise, automatically halting the loom to prevent defects. Weft stop motion monitors the weft yarns woven across the fabric's width, ensuring continuous insertion and avoiding incomplete patterns or fabric flaws.
Understanding Warp Stop Motion
Warp stop motion focuses on animating the longitudinal threads held taut in a loom, creating precise control over movement in textile weaving animations. This technique highlights the tension and alignment of warp threads, allowing detailed visualization of fabric formation during weaving processes. Understanding warp stop motion is essential for accurately replicating the structural integrity of woven materials in stop motion animations.
Basics of Weft Stop Motion
Weft stop motion animation relies on manipulating horizontal threads (wefts) woven through vertical warp threads to create motion effects in textiles or backgrounds. This technique involves adjusting or animating the weft threads frame by frame to generate fluid movement or pattern changes within fabric-based animations. Understanding the interaction between weft threads and the static warp threads is essential for achieving precise control over the animated sequences.
Key Differences Between Warp and Weft Stop Motions
Warp stop motion focuses on animating the vertical threads in fabric, creating movement by manipulating the warp threads that run lengthwise. Weft stop motion targets the horizontal threads, controlling the weft yarns that run across the fabric's width to produce distinct animation effects. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the appropriate technique based on whether you want to emphasize vertical or horizontal motion in textile animations.
Working Principle of Warp Stop Motion
Warp stop motion works by detecting the breaking or slackening of warp threads during weaving, triggering an automatic halt to prevent defects in the fabric. This system is essential for maintaining continuous production quality by ensuring that damaged or loose warp yarns do not compromise the textile's integrity. Your weaving process benefits from Warp stop motion by reducing waste and minimizing machine downtime.
Working Principle of Weft Stop Motion
Weft stop motion operates by intermittently advancing the fabric horizontally, aligning the weft yarns precisely during the weaving process. The mechanism controls the weft insertion accurately, ensuring consistent tension and proper fabric density. This precise weft movement is crucial for producing high-quality woven textiles with uniform construction.
Advantages of Warp Stop Motion
Warp stop motion offers precise control over vertical thread movement, resulting in smoother and more detailed animation sequences. This technique enhances the visual depth and texture by manipulating warp threads individually, allowing for high-definition fabric effects. Compared to weft stop motion, warp stop motion reduces motion blur and increases frame consistency, optimizing the overall quality of textile-themed animations.
Advantages of Weft Stop Motion
Weft stop motion offers greater control over fabric tension and alignment, resulting in smoother and more precise animation movements for textile applications. This technique allows for easier manipulation of horizontal threads, enhancing the visual consistency and detail of the final product. Your projects benefit from improved accuracy and reduced distortion when using weft stop motion compared to warp stop motion.
Common Applications in Textile Industry
Warp stop motion and weft stop motion are crucial mechanisms in the textile industry for controlling yarn tension during weaving. Warp stop motion detects breaks or tension changes in the warp yarns, commonly used in producing woven fabrics like denim, upholstery, and technical textiles requiring high tensile strength. Weft stop motion ensures the weft yarn is properly inserted and stops the loom when a weft break occurs, essential in manufacturing fine fabrics, curtains, and patterned textiles where weft consistency impacts quality. Your choice between these mechanisms depends on the fabric type and production precision needed.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Stop Motion System
Warp stop motion excels in precision and vertical control, ideal for intricate animations requiring detailed frame alignment, while weft stop motion offers greater flexibility and horizontal motion, suited for dynamic sequences with broader movements. Assessing project needs such as animation style, frame consistency, and desired motion direction is crucial in selecting the appropriate system. The right stop motion system balances technical capacity and creative demands, enhancing workflow efficiency and final animation quality.
Warp stop motion vs Weft stop motion Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com