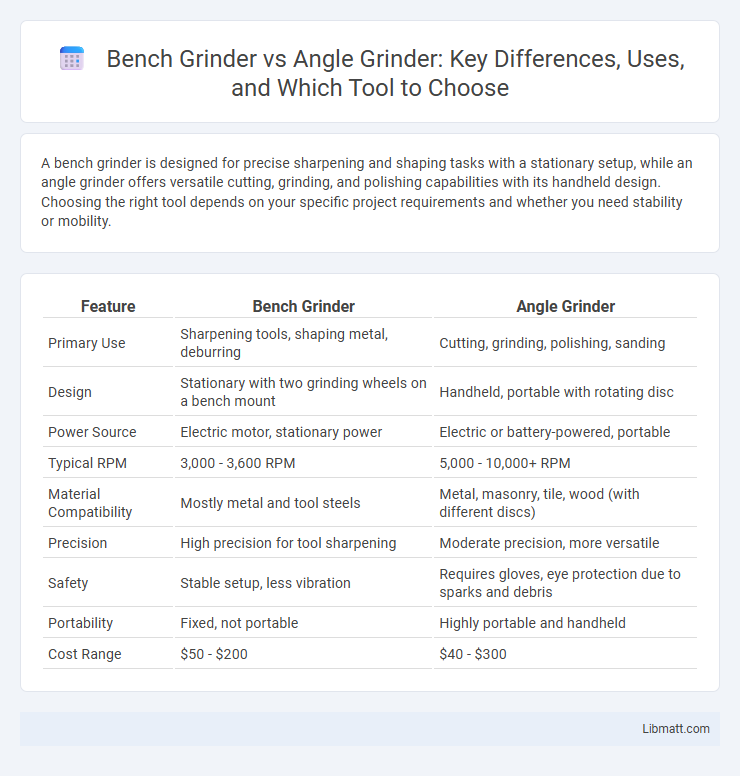
A bench grinder is designed for precise sharpening and shaping tasks with a stationary setup, while an angle grinder offers versatile cutting, grinding, and polishing capabilities with its handheld design. Choosing the right tool depends on your specific project requirements and whether you need stability or mobility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bench Grinder | Angle Grinder |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Sharpening tools, shaping metal, deburring | Cutting, grinding, polishing, sanding |
| Design | Stationary with two grinding wheels on a bench mount | Handheld, portable with rotating disc |
| Power Source | Electric motor, stationary power | Electric or battery-powered, portable |
| Typical RPM | 3,000 - 3,600 RPM | 5,000 - 10,000+ RPM |
| Material Compatibility | Mostly metal and tool steels | Metal, masonry, tile, wood (with different discs) |
| Precision | High precision for tool sharpening | Moderate precision, more versatile |
| Safety | Stable setup, less vibration | Requires gloves, eye protection due to sparks and debris |
| Portability | Fixed, not portable | Highly portable and handheld |
| Cost Range | $50 - $200 | $40 - $300 |
Bench Grinder vs Angle Grinder: Key Differences
Bench grinders provide a stationary grinding solution with a fixed base ideal for sharpening and shaping tools, whereas angle grinders offer a portable, handheld design suited for cutting, grinding, and polishing diverse materials. Bench grinders typically use larger, slower-moving wheels that produce consistent surface finishes, while angle grinders feature faster-spinning discs capable of more aggressive material removal. The choice between the two depends on specific tasks, with bench grinders excelling in precision tool maintenance and angle grinders delivering versatility and mobility for on-the-go applications.
What Is a Bench Grinder?
A bench grinder is a stationary power tool featuring two abrasive wheels mounted on a bench or pedestal, primarily used for sharpening, shaping, and grinding metal objects. It provides precise control and stability for tasks such as sharpening blades, removing rust, or smoothing rough edges. Unlike angle grinders, bench grinders offer consistent speed and balance, making them ideal for detailed or repetitive grinding operations.
What Is an Angle Grinder?
An angle grinder is a versatile handheld power tool designed for grinding, cutting, and polishing materials such as metal, stone, and concrete. It features a rotating abrasive disc or blade that spins at high speeds, enabling precise shaping and smoothing of various surfaces. Common in construction and metalworking, angle grinders accommodate different attachments to perform cutting, grinding, sanding, and polishing tasks efficiently.
Main Applications: When to Use Each Grinder
Bench grinders are ideal for sharpening tools, shaping metal, and removing rust or burrs on stationary objects, making them perfect for precision grinding tasks in workshops. Angle grinders excel in cutting, grinding, and polishing on a variety of materials like metal, stone, and concrete, offering portability and versatility for construction and outdoor projects. You should choose a bench grinder for detailed, controlled work and an angle grinder when flexibility and mobility are required for tough surface preparation or abrasive cutting.
Power and Performance Comparison
Bench grinders typically offer more consistent power output with motor ratings ranging from 1/3 to 1 horsepower for heavy-duty grinding tasks, providing stable performance for sharpening and shaping metal. Angle grinders deliver higher RPMs, often between 5,000 and 11,000, with power sources varying from 4 to 15 amps or cordless options up to 20 volts, making them ideal for versatile cutting, grinding, and polishing on various materials. Your choice depends on whether you need stationary precision and power for bench work or portable, high-speed versatility for on-the-go projects.
Safety Features and Precautions
Bench grinders feature robust wheel guards, adjustable tool rests, and eye shields to protect users from sparks and debris, while angle grinders often include safety clutches, side handles, and protective guards to enhance control and reduce kickback risks. Both tools require the use of personal protective equipment such as safety goggles, gloves, and ear protection to prevent injuries from flying particles and loud noise. Proper maintenance, secure workpiece positioning, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential safety precautions to minimize accidents during grinding operations.
Tool Versatility: Attachments and Accessories
Bench grinders offer a wide range of attachments such as grinding wheels, wire brushes, and polishing pads, making them ideal for detailed sharpening and finishing tasks. Angle grinders support various accessories including cutting discs, flap wheels, and diamond blades, enabling versatile applications like cutting, grinding, and sanding on multiple materials. The choice between these tools depends on specific project requirements, with angle grinders providing greater portability and flexibility through interchangeable accessories.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Bench grinders generally have a higher initial cost compared to angle grinders but require less frequent maintenance due to their stationary design and robust build. Angle grinders, while more affordable upfront, demand regular upkeep such as replacing worn discs and checking for motor wear to ensure longevity. Your choice should factor in not only the purchase price but also ongoing maintenance expenses and the specific tasks you intend to perform.
Pros and Cons of Bench Grinders vs Angle Grinders
Bench grinders provide stable, hands-free grinding with high precision, ideal for sharpening and shaping tools, but they lack portability and versatility. Angle grinders offer portability and versatility for cutting, grinding, and polishing various materials in tight spaces, yet they require more skill to handle safely and can cause less precise finishes. Choosing between bench grinders and angle grinders depends on the specific needs for precision work versus mobile, multi-functional use.
Choosing the Right Grinder for Your Project
Choosing the right grinder for your project depends on the task's precision and material type; bench grinders excel in sharpening, shaping, and heavy-duty grinding with consistent stability, while angle grinders offer versatility for cutting, sanding, and polishing in tight or angled spaces. Your decision should factor in the grinder's power rating, wheel size, and ergonomics to ensure efficiency and safety. Evaluate whether your project requires stationary operation or portability to select the optimal tool for superior performance.
Bench grinder vs angle grinder Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com