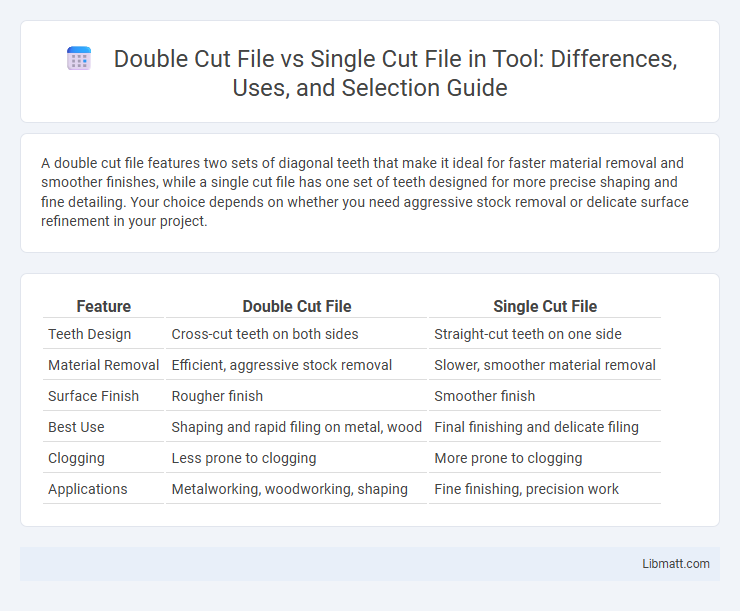
A double cut file features two sets of diagonal teeth that make it ideal for faster material removal and smoother finishes, while a single cut file has one set of teeth designed for more precise shaping and fine detailing. Your choice depends on whether you need aggressive stock removal or delicate surface refinement in your project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Double Cut File | Single Cut File |
|---|---|---|
| Teeth Design | Cross-cut teeth on both sides | Straight-cut teeth on one side |
| Material Removal | Efficient, aggressive stock removal | Slower, smoother material removal |
| Surface Finish | Rougher finish | Smoother finish |
| Best Use | Shaping and rapid filing on metal, wood | Final finishing and delicate filing |
| Clogging | Less prone to clogging | More prone to clogging |
| Applications | Metalworking, woodworking, shaping | Fine finishing, precision work |
Introduction to Double Cut and Single Cut Files
Double cut files feature two sets of diagonal teeth crossing each other, enabling faster material removal and smoothing rough surfaces efficiently. Single cut files contain one set of parallel teeth designed for finer, more precise finishing and shaping tasks. Both file types are essential in metalworking, woodworking, and plastic shaping, with their usage determined by the desired finish quality and material removal rate.
Understanding File Cuts: Definitions and Differences
Double cut files feature two sets of diagonal teeth that intersect, providing aggressive material removal and a smoother finish ideal for shaping and deburring hard metals. Single cut files have parallel rows of teeth that remove less material per stroke, making them suitable for fine finishing and precision work on softer materials like wood and plastic. Understanding the cutting pattern helps select the right file type for specific applications, balancing efficiency and surface quality.
How Double Cut Files Work
Double cut files feature two sets of angled teeth intersecting each other, creating a crisscross pattern that allows for faster material removal compared to single cut files. This design makes double cut files ideal for shaping, deburring, and smoothing rough surfaces on metals, wood, and plastics. Your work benefits from increased efficiency and a smoother finish due to the aggressive, yet controlled, cutting action of double cut files.
How Single Cut Files Work
Single cut files feature a single set of parallel teeth that run straight along the length of the file, designed to remove material efficiently with each stroke. This configuration allows for precise, controlled cutting and smoothing, ideal for sharpening edges or refining hard metals. Their uniform teeth pattern produces a smoother finish compared to double cut files, which have intersecting teeth that remove material more aggressively.
Key Applications for Double Cut Files
Double cut files feature intersecting rows of teeth that efficiently remove material, making them ideal for shaping, deburring, and smoothing rough surfaces in woodworking, metalworking, and plastic fabrication. Their aggressive tooth pattern excels at rapid stock removal and contouring intricate shapes, which is essential for tasks requiring precision and speed. You can rely on double cut files for applications demanding both accuracy and efficiency, such as sharpening tools, refining metal edges, and preparing surfaces for finishing.
Key Applications for Single Cut Files
Single cut files excel in precision tasks like sharpening tools, finishing metal surfaces, and smoothing wood edges due to their linear, parallel teeth design. Their ability to produce fine, controlled cuts makes them ideal for delicate deburring, filing thin material, and creating smooth finishes. When you need accuracy and a clean finish, single cut files provide superior results compared to double cut files, which are more aggressive and suited for rapid material removal.
Comparative Advantages: Double Cut vs Single Cut
Double cut files feature crisscross patterns that enable faster material removal and smoother finishes, making them ideal for shaping and refining surfaces with greater efficiency. Single cut files have parallel teeth that provide precise, controlled cuts, perfect for sharpening tools and fine detailing. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize speed and smoothness (double cut) or accuracy and control (single cut).
Choosing the Right File for Your Task
Selecting the appropriate file depends on the material and the desired finish: double cut files feature intersecting diagonal rows of teeth that efficiently remove material and are ideal for rapid stock removal on metals. Single cut files have a single set of parallel teeth designed for smoother finishing and sharpening tasks on softer materials like wood or plastic. Understanding these differences ensures optimal precision and surface quality in woodworking, metalworking, or sharpening applications.
Maintenance and Longevity of File Types
Double cut files feature intersecting rows of teeth that remove material quickly but require more frequent maintenance to prevent clogging and wear, enhancing their longevity when properly cleaned. Single cut files have a simpler tooth pattern ideal for smoother finishes and easier cleaning, which can extend the life of the file under lighter usage conditions. Your choice between double cut and single cut files influences the maintenance routine and overall durability based on the application intensity and material hardness.
Final Verdict: Which File Suits Your Needs Best?
Double cut files feature a crisscross pattern of ridges that provides aggressive material removal and faster shaping, ideal for rough work and heavy-duty tasks. Single cut files have parallel ridges that deliver smoother finishes and precise control, making them perfect for delicate or fine-tuning jobs. Selecting between double cut and single cut depends on whether efficiency in material removal or surface finish quality is your priority.
Double cut file vs single cut file Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com