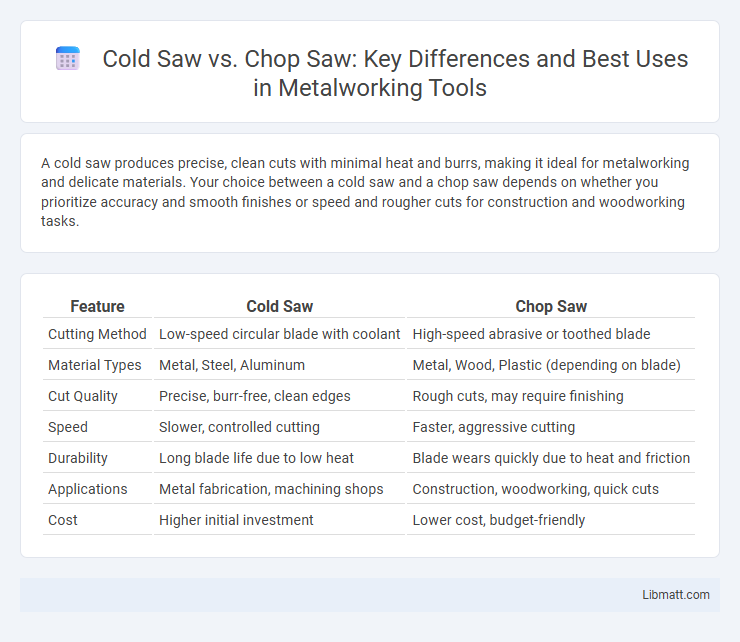
A cold saw produces precise, clean cuts with minimal heat and burrs, making it ideal for metalworking and delicate materials. Your choice between a cold saw and a chop saw depends on whether you prioritize accuracy and smooth finishes or speed and rougher cuts for construction and woodworking tasks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cold Saw | Chop Saw |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | Low-speed circular blade with coolant | High-speed abrasive or toothed blade |
| Material Types | Metal, Steel, Aluminum | Metal, Wood, Plastic (depending on blade) |
| Cut Quality | Precise, burr-free, clean edges | Rough cuts, may require finishing |
| Speed | Slower, controlled cutting | Faster, aggressive cutting |
| Durability | Long blade life due to low heat | Blade wears quickly due to heat and friction |
| Applications | Metal fabrication, machining shops | Construction, woodworking, quick cuts |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
Introduction to Cold Saws and Chop Saws
Cold saws use a circular toothed blade designed to cut metal with minimal heat generation, delivering precise, clean cuts ideal for steel and other hard materials. Chop saws, also known as cut-off saws, typically employ abrasive discs to quickly cut through metal but generate more heat, often causing rougher edges. Understanding the differences in cutting methods and applications will help you choose the right tool for your metalworking needs.
Core Differences Between Cold Saws and Chop Saws
Cold saws utilize a circular saw blade with teeth designed to cut metal precisely through low-speed, high-torque rotation, minimizing heat and material distortion. Chop saws, in contrast, use an abrasive disc that rotates at high speed to cut through metal quickly, but often generate more heat and rougher edges. Selecting the right tool depends on Your need for accuracy and finish quality versus speed and simplicity in metal cutting tasks.
Material Cutting Capabilities
Cold saws excel in cutting ferrous and non-ferrous metals with high precision and minimal heat distortion due to their low cutting speed and toothed circular blades. Chop saws are better suited for cutting abrasive materials like steel pipes and bars quickly but generate more heat and abrasive dust, which can affect cut quality. Choosing between cold saws and chop saws depends on the material hardness, desired cut finish, and tolerance requirements.
Blade Types and Performance
Cold saws use high-speed steel (HSS) or carbide-tipped blades that maintain sharpness and produce precise, burr-free cuts on metal, delivering superior performance for industrial and fabrication tasks. Chop saws typically utilize abrasive or carbide-tipped blades designed for quick, rough cuts on metal and other materials but generate more heat and burrs, reducing cut quality. The blade design and cutting speed of cold saws result in cleaner finishes and less material distortion compared to the aggressive, high-friction cutting action of chop saws.
Precision and Cut Quality
Cold saws deliver superior precision and cut quality by using a circular saw blade with teeth designed to minimize heat buildup, resulting in clean, burr-free cuts and exact tolerances. Chop saws, typically equipped with abrasive discs, produce rougher cuts with increased heat and material deformation, leading to less accurate and less smooth edges. For applications requiring high precision and fine finish, cold saws outperform chop saws significantly in maintaining dimensional accuracy and surface integrity.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Cold saws offer slower cutting speeds but provide superior precision and cleaner cuts with less material waste, making them highly efficient for detailed metalworking tasks. Chop saws excel in speed, delivering quick, rough cuts ideal for high-volume or heavy-duty jobs where finish quality is less critical. Your choice depends on whether speed or accuracy is the priority for your specific project requirements.
Durability and Maintenance Needs
Cold saws offer superior durability due to their robust construction and precision gear-driven mechanisms, making them ideal for heavy-duty, long-term use. Chop saws generally require more frequent maintenance and blade replacements, as their abrasive cutting action generates higher heat and wear. Choosing a cold saw can reduce your maintenance efforts and extend tool lifespan for consistent performance.
Safety Features and Considerations
Cold saws feature enclosed blade designs and coolant systems that reduce sparks, debris, and heat, enhancing operator safety during metal cutting. Chop saws often have exposed abrasive discs, which generate more sparks and dust, requiring robust protective guards and personal protective equipment. Ensuring your workspace includes proper ventilation and safety gear is essential when operating either saw to minimize injury risks.
Cost and Investment Analysis
Cold saws typically demand a higher upfront investment ranging from $1,500 to $5,000 due to precision components and coolant systems, whereas chop saws can cost between $100 and $700, making them more budget-friendly for light to medium tasks. Maintenance expenses for cold saws include regular coolant replacement and blade sharpening, contributing to higher long-term operational costs compared to chop saws, which primarily require blade replacement. When considering production efficiency and material quality, the higher initial and maintenance costs of cold saws can be justified in industrial applications, while chop saws remain a cost-effective choice for occasional or non-critical cutting jobs.
Choosing the Right Saw for Your Needs
Selecting between a cold saw and a chop saw depends on the material type and precision required. Cold saws use a circular saw blade with tungsten carbide tips that reduce heat, making them ideal for cutting metal with high accuracy and minimal burrs. Chop saws, often powered by abrasive discs or metal-cutting blades, excel at quick, rough cuts on steel and other metals but produce more heat and slag, making them suitable for less precise, heavy-duty projects.
Cold saw vs chop saw Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com