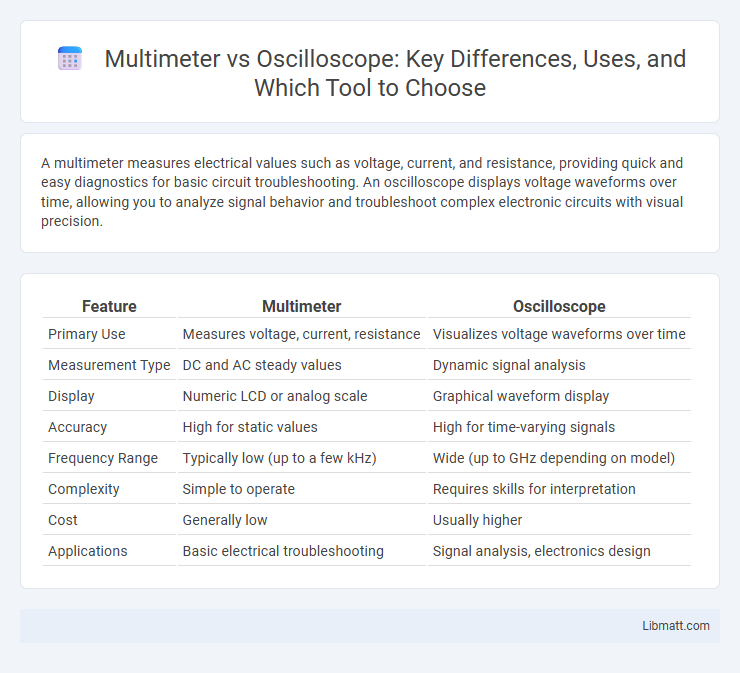
A multimeter measures electrical values such as voltage, current, and resistance, providing quick and easy diagnostics for basic circuit troubleshooting. An oscilloscope displays voltage waveforms over time, allowing you to analyze signal behavior and troubleshoot complex electronic circuits with visual precision.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Multimeter | Oscilloscope |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Measures voltage, current, resistance | Visualizes voltage waveforms over time |
| Measurement Type | DC and AC steady values | Dynamic signal analysis |
| Display | Numeric LCD or analog scale | Graphical waveform display |
| Accuracy | High for static values | High for time-varying signals |
| Frequency Range | Typically low (up to a few kHz) | Wide (up to GHz depending on model) |
| Complexity | Simple to operate | Requires skills for interpretation |
| Cost | Generally low | Usually higher |
| Applications | Basic electrical troubleshooting | Signal analysis, electronics design |
Introduction to Multimeters and Oscilloscopes
Multimeters measure voltage, current, and resistance, providing essential electrical readings for diagnostics and troubleshooting. Oscilloscopes display signal waveforms, enabling analysis of voltage changes over time for complex electronic circuit behavior. Understanding the unique functions of each device helps you select the right tool for accurate electrical testing and diagnostics.
Core Functions and Capabilities
A multimeter primarily measures electrical values such as voltage, current, and resistance with high precision, making it essential for basic circuit diagnostics and troubleshooting. An oscilloscope provides detailed visualization of electrical signals over time, allowing users to analyze waveform shapes, frequencies, and transient events with high temporal resolution. While a multimeter offers quantitative scalar measurements, an oscilloscope delivers qualitative insights into signal behavior, making both instruments complementary tools in electronic testing and diagnostics.
Key Differences in Measurement Techniques
Multimeters measure electrical values using direct sampling of voltage, current, or resistance through analog-to-digital conversion, providing steady-state readings. Oscilloscopes capture and display real-time waveforms by sampling voltage over time with high-frequency sampling rates, enabling analysis of signal shape, frequency, and transient events. The key difference lies in the multimeter's focus on precise numeric measurement versus the oscilloscope's ability to visualize dynamic signal behavior.
Types of Signals Each Instrument Can Analyze
A multimeter is primarily designed to measure static or slowly varying electrical signals such as DC voltage, AC voltage, current, and resistance, making it ideal for basic diagnostics and circuit testing. An oscilloscope excels in analyzing dynamic, time-varying signals like waveforms, transient events, and complex digital signals, offering detailed visualizations of voltage changes over time. While a multimeter provides numerical values for steady-state signals, oscilloscopes display real-time graphical representations, enabling in-depth analysis of signal characteristics such as frequency, amplitude, and noise.
Applications in Electronics and Electrical Work
Multimeters excel in measuring voltage, current, and resistance, making them indispensable for basic troubleshooting and component testing in electronics and electrical work. Oscilloscopes provide detailed waveform analysis, crucial for diagnosing complex signal behavior and timing issues in advanced circuits and electronic design. Your choice depends on whether you need simple pass/fail measurements or in-depth signal visualization for precise diagnostics.
Accuracy and Precision Comparison
Multimeters provide high accuracy in measuring voltage, current, and resistance with typical precision up to 0.5%, making them ideal for straightforward DC measurements. Oscilloscopes offer exceptional precision in waveform analysis, capturing rapid signal changes with high temporal resolution but may have slightly lower absolute accuracy in voltage measurement. The choice between a multimeter and an oscilloscope depends on whether precise static measurements or detailed dynamic waveform observations are prioritized.
Ease of Use and Learning Curve
Multimeters offer straightforward interfaces and simple measurement functions like voltage, current, and resistance, making them highly accessible for beginners and quick diagnostics. Oscilloscopes provide detailed waveform visualization and advanced signal analysis but require more technical knowledge and training to interpret complex data accurately. The learning curve for oscilloscopes is steeper due to intricate settings and menus, while multimeters prioritize ease of use for everyday electrical testing.
Portability and Practical Considerations
A multimeter offers superior portability with a compact, handheld design ideal for fieldwork and quick diagnostics, while oscilloscopes are generally bulkier and require a stable setup, making them less convenient for on-the-go use. Practical considerations include the multimeter's ease of use for measuring voltage, current, and resistance, whereas oscilloscopes provide detailed waveform analysis but demand more technical expertise and space. Your choice depends on the balance between portability needs and the complexity of the measurements required.
Cost and Investment Factors
Multimeters generally cost between $20 and $300, offering an affordable entry point for basic electrical measurements, while oscilloscopes range from $500 to over $10,000 depending on bandwidth and features, reflecting a higher investment for advanced waveform analysis. The choice depends on the specific application: multimeters excel in voltage, current, and resistance measurements, making them cost-effective for routine diagnostics, whereas oscilloscopes provide detailed signal visualization essential for complex electronics troubleshooting and development. Budget constraints and the required precision and functionality significantly influence whether to invest in a multimeter or oscilloscope for electrical measurement tasks.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
Selecting between a multimeter and an oscilloscope depends on the measurement type and level of detail required; a multimeter is ideal for measuring voltage, current, and resistance with straightforward readings, making it perfect for basic electrical diagnostics. An oscilloscope provides a visual representation of signal waveforms, ideal for analyzing complex electronic circuits, transient signals, and frequency changes over time. Evaluating whether your task involves simple measurements or detailed waveform analysis helps determine the most suitable tool for accurate diagnostics and troubleshooting.
Multimeter vs oscilloscope Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com