A drawbar is a tool used to securely clamp cutting tools into a machine spindle, ensuring precision and stability during machining. Your choice between a drawbar and a retention knob depends on the machine setup; retention knobs are threaded components that pull tooling into the spindle, commonly used in CNC machines for quick tool changes.
Table of Comparison
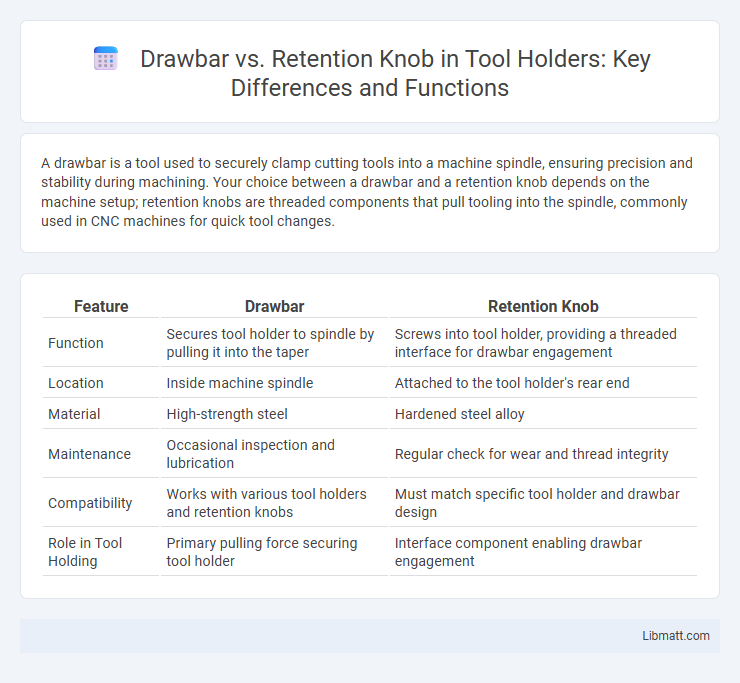
| Feature | Drawbar | Retention Knob |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Secures tool holder to spindle by pulling it into the taper | Screws into tool holder, providing a threaded interface for drawbar engagement |
| Location | Inside machine spindle | Attached to the tool holder's rear end |
| Material | High-strength steel | Hardened steel alloy |
| Maintenance | Occasional inspection and lubrication | Regular check for wear and thread integrity |
| Compatibility | Works with various tool holders and retention knobs | Must match specific tool holder and drawbar design |
| Role in Tool Holding | Primary pulling force securing tool holder | Interface component enabling drawbar engagement |
Introduction to Drawbar and Retention Knob
A drawbar is a tool used in CNC machines to securely hold the tool holder within the spindle by applying axial force, ensuring precise tool alignment and stability during machining. A retention knob, also known as a pull stud, is a component threaded into the end of the tool holder, allowing the drawbar to grip and pull the holder into the spindle taper. Both are critical for maintaining tool retention and spindle-tool connectivity, directly impacting machining accuracy and safety.
What is a Drawbar?
A drawbar is a threaded rod used in CNC machines and milling machines to securely fasten the tool holder inside the spindle, ensuring precise machining and minimizing tool movement. It provides axial clamping force by pulling the tool holder into the spindle taper, offering strong retention during high-speed operations. Drawbars are essential for maintaining tool alignment and enhancing machining accuracy in automated tool change systems.
What is a Retention Knob?
A retention knob, also known as a pull stud, is a mechanical component screwed into the end of a tool holder used in CNC machining to secure the tool holder within the spindle via the drawbar mechanism. It enables precise axial retention and allows the drawbar to firmly clamp the tool holder, ensuring stability and accuracy during high-speed machining operations. Retention knobs come in various standard sizes and shapes tailored to specific machine tool models and spindle tapers, such as CAT, BT, and HSK.
Key Differences Between Drawbar and Retention Knob
Drawbars and retention knobs serve distinct functions in CNC machining; the drawbar applies axial force to secure the tool holder within the spindle taper, while the retention knob connects the tool holder to the drawbar mechanism. The key difference lies in their position and purpose: the drawbar is a spindle-mounted component that pulls the tool holder tightly, whereas the retention knob is attached to the rear of the tool holder to enable this pulling action. Understanding the compatibility of retention knobs with specific machine drawbars is essential for ensuring proper tool clamping and minimizing runout in machining operations.
Function and Purpose in CNC Machines
Drawbars provide secure clamping of tool holders in CNC machine spindles, ensuring precise axial retention and minimizing tool runout during high-speed operations. Retention knobs, also known as pull studs, attach to the tool holder and interface with the drawbar mechanism to enable firm grip and reliable tool change cycles. Together, they optimize tool stability and accuracy, directly impacting machining quality and operational efficiency in CNC systems.
Compatibility with Tool Holders and Spindles
Drawbars and retention knobs both secure tool holders in CNC machine spindles but differ in compatibility aspects. Drawbars are compatible with most tool holders featuring a pull-stud interface, commonly used in CAT, BT, and HSK tool holders, ensuring a firm grip within the spindle. Your choice depends on spindle design and tool holder type; retention knobs must match the tool holder's pull-stud specifications for proper retention and safe operation.
Advantages of Using a Drawbar
Using a drawbar offers superior clamping force and enhanced tool stability compared to retention knobs, reducing tool deflection during high-precision machining. Drawbars enable quicker and more reliable tool changes, improving overall CNC spindle efficiency and minimizing downtime. Your workflow benefits from consistent tool retention, which helps maintain machining accuracy and prolongs tool life.
Benefits of Retention Knobs
Retention knobs offer enhanced tool holding stability by securely locking the tool holder into the spindle, reducing vibration and improving machining precision. Their design allows for quick and repeatable tool changes, increasing overall productivity in CNC operations. The secure fit of retention knobs contributes to extended spindle and tool life by minimizing wear and ensuring consistent tool alignment.
Common Issues and Maintenance Tips
Drawbars often experience wear from frequent tool changes, leading to reduced clamping force and potential tool slippage, while retention knobs may suffer from thread damage or bending. Regularly inspecting both components for signs of wear, cleaning debris, and applying proper torque during installation can extend their lifespan and ensure optimal tool retention. Your maintenance routine should include checking drawbar tension and replacing retention knobs when corrosion or deformation is evident to prevent machining inaccuracies.
Choosing Between Drawbar and Retention Knob
Choosing between a drawbar and a retention knob depends largely on your machine compatibility and tool retention needs. Drawbars are ideal for machines with spindle taper systems like CAT, BT, or HSK, providing strong axial holding force for heavy-duty machining. Your choice should consider the ease of tool changes and the specific retention system designed for your CNC machine to ensure optimal performance and accuracy.
Drawbar vs retention knob Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com