Metrology is the science of measurement that establishes standards and ensures accuracy across various instruments, while calibration is the practical process of adjusting and verifying those instruments against these standards to maintain their precision. Your equipment's reliability depends on regular calibration based on the principles and benchmarks defined by metrology.
Table of Comparison
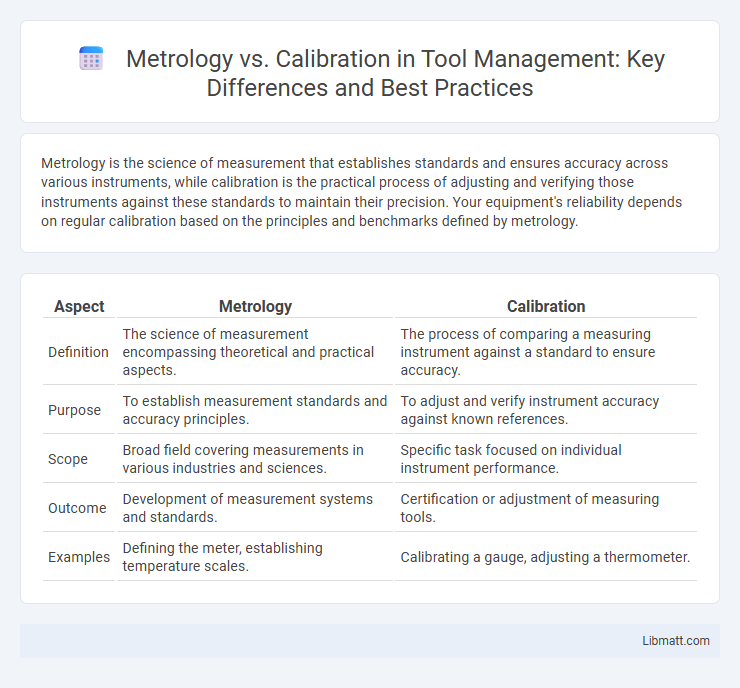
| Aspect | Metrology | Calibration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The science of measurement encompassing theoretical and practical aspects. | The process of comparing a measuring instrument against a standard to ensure accuracy. |
| Purpose | To establish measurement standards and accuracy principles. | To adjust and verify instrument accuracy against known references. |
| Scope | Broad field covering measurements in various industries and sciences. | Specific task focused on individual instrument performance. |
| Outcome | Development of measurement systems and standards. | Certification or adjustment of measuring tools. |
| Examples | Defining the meter, establishing temperature scales. | Calibrating a gauge, adjusting a thermometer. |
Introduction to Metrology and Calibration
Metrology is the science of measurement that establishes standards and ensures accuracy and consistency in various industries. Calibration is a critical process within metrology that adjusts and verifies the precision of measuring instruments against established standards. Together, they maintain measurement integrity, enabling reliable data and quality control across manufacturing, engineering, and scientific research.
Defining Metrology: Scope and Importance
Metrology is the science of measurement encompassing all theoretical and practical aspects of measurement accuracy, units, and standards. It plays a crucial role in ensuring reliable and consistent measurements across industries, enabling quality control, product development, and regulatory compliance. Defining metrology establishes the foundation for understanding calibration, which involves the verification and adjustment of measuring instruments against established standards.
Understanding Calibration: Key Concepts
Calibration is the process of comparing an instrument's measurements against a known standard to ensure accuracy and consistency in results. It involves adjusting the measuring device to minimize errors and maintain traceability to national or international measurement standards. Understanding calibration fundamentals is essential for quality assurance across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and aerospace.
Fundamental Differences Between Metrology and Calibration
Metrology is the science of measurement encompassing theoretical and practical aspects, while calibration is a process that ensures the accuracy of measuring instruments by comparing them to a known standard. Metrology establishes the fundamental principles, units, and methods for measurement, whereas calibration applies these principles to verify and adjust instruments within specified tolerances. Your understanding of their fundamental differences enhances measurement reliability and instrument performance in technical applications.
The Role of Metrology in Quality Assurance
Metrology plays a critical role in quality assurance by providing precise measurement standards and techniques essential for manufacturing consistency and product reliability. Calibration ensures that measurement instruments conform to these metrology standards, maintaining accuracy across production processes. Together, metrology and calibration enable companies to meet regulatory requirements and achieve high-quality outputs.
Calibration Processes and Procedures
Calibration processes and procedures involve comparing measuring instruments against known standards to ensure accuracy and traceability. Metrology encompasses the broader science and systematic approach that defines how calibration is performed, including establishing measurement methods, uncertainty evaluation, and documentation standards. Your calibration ensures instruments maintain precision within specified tolerances, supporting reliable measurement results critical for quality control.
Traceability in Metrology and Calibration
Traceability in metrology ensures measurement results are linked to international or national standards through an unbroken chain of comparisons, providing confidence in accuracy and consistency across measurements. Calibration establishes and verifies this traceability by comparing an instrument's output against a reference standard under specified conditions. Effective traceability in both metrology and calibration is critical for maintaining measurement reliability, regulatory compliance, and quality assurance in scientific and industrial applications.
Standards and Regulations Influencing Both Fields
Standards such as ISO/IEC 17025 and regulations from bodies like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) shape metrology and calibration processes globally. Metrology establishes measurement traceability to primary standards, ensuring consistency, while calibration aligns measuring instruments with these standards to maintain accuracy. Compliance with regulatory frameworks including the European Union's Measuring Instruments Directive (MID) reinforces quality control and legal metrological requirements in both domains.
Applications Across Industries: Metrology vs Calibration
Metrology serves as the foundational science of measurement, ensuring accuracy and consistency across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and pharmaceuticals by developing precise measurement techniques and standards. Calibration focuses on adjusting and verifying instruments to maintain their accuracy in fields like manufacturing, healthcare, and electronics, preventing errors and ensuring regulatory compliance. Both metrology and calibration are critical for quality control, impacting product reliability and operational efficiency in diverse industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Measurement Needs
Selecting the appropriate method between metrology and calibration hinges on the specific measurement requirements and accuracy levels desired for your application. Metrology encompasses the science of measurement, including establishing measurement standards and ensuring traceability, while calibration focuses on adjusting and verifying instruments against known standards to maintain precision. Evaluating factors such as measurement range, tolerances, and industry regulations will guide the optimal choice for reliable and consistent measurement results.
Metrology vs calibration Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com