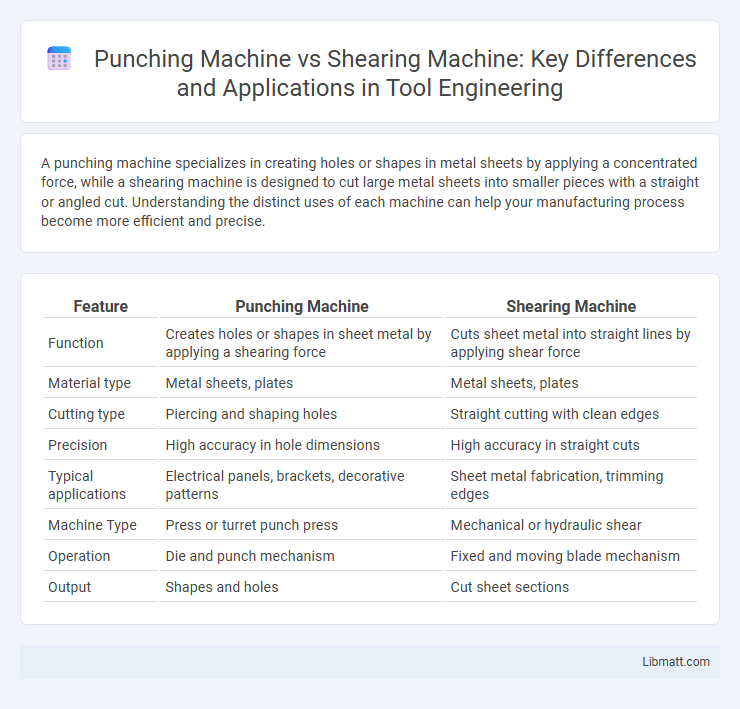
A punching machine specializes in creating holes or shapes in metal sheets by applying a concentrated force, while a shearing machine is designed to cut large metal sheets into smaller pieces with a straight or angled cut. Understanding the distinct uses of each machine can help your manufacturing process become more efficient and precise.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Punching Machine | Shearing Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Creates holes or shapes in sheet metal by applying a shearing force | Cuts sheet metal into straight lines by applying shear force |
| Material type | Metal sheets, plates | Metal sheets, plates |
| Cutting type | Piercing and shaping holes | Straight cutting with clean edges |
| Precision | High accuracy in hole dimensions | High accuracy in straight cuts |
| Typical applications | Electrical panels, brackets, decorative patterns | Sheet metal fabrication, trimming edges |
| Machine Type | Press or turret punch press | Mechanical or hydraulic shear |
| Operation | Die and punch mechanism | Fixed and moving blade mechanism |
| Output | Shapes and holes | Cut sheet sections |
Introduction to Punching and Shearing Machines
Punching machines are industrial tools designed to create holes in metal sheets by applying pressure through a punch and die. Shearing machines cut large metal sheets into smaller sections by applying a linear cutting force along a straight line. Both machines are essential in metal fabrication, offering precision and efficiency for different manufacturing requirements.
Core Operating Principles
Punching machines operate by applying a concentrated force through a punch to create holes or shapes in sheet metal by shearing it against a die. Shearing machines function by exerting a linear blade movement to cut sheet metal along a straight line, separating it into two parts without forming chips or burrs. Both machines utilize mechanical or hydraulic power but differ in their force application methods--punching uses precise localized pressure, while shearing uses a scissor-like action.
Key Differences Between Punching and Shearing
Punching machines create holes or shapes by applying concentrated force to a workpiece with a punch and die set, ideal for precise cut-outs in sheet metal. Shearing machines perform straight-line cutting by applying a high shear force, efficiently producing clean cuts without generating chips or using heat. Key differences include the nature of operation--punching involves material displacement and hole formation, while shearing focuses on cutting entire sections across the workpiece.
Types of Punching Machines
Punching machines come in various types, including mechanical, hydraulic, and CNC punching machines, each designed for specific industrial applications. Mechanical punching machines offer high-speed operations suitable for mass production, while hydraulic types provide greater force for thicker materials. CNC punching machines deliver precision and flexibility, allowing you to customize shapes and sizes efficiently for complex metal fabrication tasks.
Types of Shearing Machines
Shearing machines are primarily classified into mechanical, hydraulic, and pneumatic types, each offering different force applications and precision levels for cutting various metal sheets. Mechanical shearing machines use a flywheel and crank mechanism, providing high speed and durable cutting suitable for thin to medium-thick metals. Hydraulic shearing machines deliver powerful and consistent force through hydraulic cylinders, making them ideal for thicker metal sheets and heavier duty industrial applications.
Material Suitability and Thickness Ranges
Punching machines are ideal for working with thin to medium thickness metals such as aluminum, brass, and mild steel, typically handling materials up to 6 mm thick with high precision and speed. Shearing machines are better suited for cutting thicker and tougher materials, including steel plates and stainless steel, with thickness capacities ranging from 1 mm to over 20 mm, depending on machine power and design. Your choice depends on the material type and thickness, where punching offers detailed shapes and shearing provides straight cuts on heavier gauge metals.
Advantages of Punching Machines
Punching machines offer high precision and speed for creating holes or shapes in metal sheets, making them ideal for mass production. They require less power and produce minimal waste compared to shearing machines, resulting in cost-efficiency and material conservation. Their versatility enables the processing of various thicknesses and materials, enhancing manufacturing flexibility.
Advantages of Shearing Machines
Shearing machines offer precise and clean cuts on metal sheets with minimal material wastage, enhancing manufacturing efficiency. Their high-speed operation and ability to handle thick sheets make them ideal for large-scale production and heavy-duty applications. You benefit from reduced setup time and consistent output quality compared to punching machines, which often require multiple steps and tooling changes.
Applications in Modern Manufacturing
Punching machines excel in creating precise holes and shapes in sheet metal, widely used in automotive body panels, electronics enclosures, and HVAC components manufacturing. Shearing machines are essential for cutting large metal sheets into smaller, manageable pieces, frequently utilized in steel fabrication, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery industries. Both machines optimize production efficiency by streamlining metal processing tasks in modern manufacturing environments.
Choosing the Right Machine for Your Needs
Selecting between a punching machine and a shearing machine depends on the specific metal fabrication requirements; punching machines excel at creating precise holes or intricate shapes by applying concentrated force, while shearing machines efficiently cut straight lines or large pieces by exerting heavy, even pressure. Factors such as material thickness, shape complexity, production volume, and desired edge quality influence the choice, with punching machines preferred for detailed designs and shearing machines ideal for straight cuts on sheet metal. Evaluating operational costs, tool maintenance, and machine versatility ensures alignment with production goals and budget constraints.
Punching machine vs shearing machine Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com