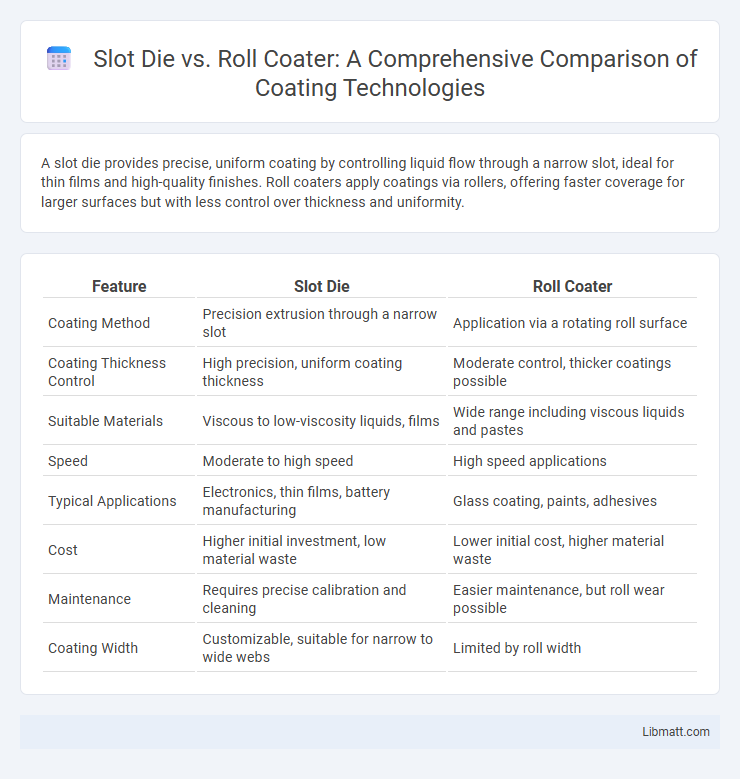
A slot die provides precise, uniform coating by controlling liquid flow through a narrow slot, ideal for thin films and high-quality finishes. Roll coaters apply coatings via rollers, offering faster coverage for larger surfaces but with less control over thickness and uniformity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Slot Die | Roll Coater |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Method | Precision extrusion through a narrow slot | Application via a rotating roll surface |
| Coating Thickness Control | High precision, uniform coating thickness | Moderate control, thicker coatings possible |
| Suitable Materials | Viscous to low-viscosity liquids, films | Wide range including viscous liquids and pastes |
| Speed | Moderate to high speed | High speed applications |
| Typical Applications | Electronics, thin films, battery manufacturing | Glass coating, paints, adhesives |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, low material waste | Lower initial cost, higher material waste |
| Maintenance | Requires precise calibration and cleaning | Easier maintenance, but roll wear possible |
| Coating Width | Customizable, suitable for narrow to wide webs | Limited by roll width |
Introduction to Slot Die and Roll Coater Technologies
Slot die technology offers precise coating control by delivering a uniform liquid film through a narrow slit, ideal for high-quality thin films in electronics and pharmaceuticals. Roll coaters utilize rotating drums or rollers to apply coatings on substrates, providing efficient, high-speed coverage suitable for industrial-scale production. Both methods optimize material use and coating uniformity but differ in application precision and operational scalability.
Principle of Operation: Slot Die vs Roll Coater
Slot die coating utilizes a precision-engineered die to dispense a controlled, continuous film of liquid directly onto a substrate, ensuring uniform thickness through a narrow slit aperture. Roll coating employs one or more rotating rolls to transfer coating fluid onto the substrate by metering the liquid between the roll and substrate surface, providing versatile application for various viscosities. Slot die technology delivers higher accuracy and minimal material waste compared to roll coater systems, which excel in high-speed processing for broader uniform coatings.
Material Compatibility and Application Range
Slot die coating offers precise control over film thickness and works effectively with a wide variety of materials, including polymers, inks, and adhesives, making it suitable for high-precision applications such as electronic display manufacturing. Roll coaters provide greater flexibility for coating thicker layers and are compatible with viscous materials like paints, varnishes, and laminates, commonly used in packaging and decorative coatings. Your choice depends on the specific material properties and application requirements to achieve optimal coating performance.
Coating Uniformity and Thickness Control
Slot die coaters provide superior coating uniformity and precise thickness control due to their ability to dispense a consistent wet film directly onto the substrate with minimal variation. Roll coaters rely on mechanical pressure and rotation, which can lead to uneven coating thickness and less uniform surfaces, especially on substrates with variable textures. Advanced slot die technology enables micron-level thickness adjustments, making it ideal for applications demanding high precision and repeatability.
Speed and Throughput Considerations
Slot die coaters typically offer higher precision at moderate speeds, making them suitable for applications requiring uniform thin films, but their throughput is often limited by the coating width and flow control. Roll coaters excel in high-speed production lines, enabling faster substrate processing and greater throughput, particularly for wide coatings with less stringent uniformity requirements. Choosing between slot die and roll coating depends on the balance between coating speed, film uniformity, and production volume demands.
Maintenance and Operational Complexity
Slot die coaters require precise alignment and regular maintenance of the die lips to prevent clogging and ensure uniform film thickness, demanding skilled operators for effective adjustments. Roll coaters involve multiple moving parts such as rollers and bearings, necessitating frequent inspection and lubrication to avoid wear and maintain coating consistency. Operational complexity in slot die coaters is higher due to the need for tight control over fluid dynamics, while roll coaters are easier to operate but require ongoing mechanical upkeep.
Equipment Cost and Investment
Slot die coating equipment generally requires a higher initial investment compared to roll coaters due to its precise metering and control systems suited for thin film applications. Roll coaters offer a more cost-effective solution for large-scale production, with lower equipment costs but potentially higher material waste and less uniformity. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with the desired coating quality and thickness control.
Energy Efficiency and Waste Management
Slot die coating offers superior energy efficiency due to its precise fluid deposition, minimizing material waste and reducing drying energy requirements. Roll coaters often consume more energy as they rely on excess coating material that must be scraped or recovered, leading to increased waste and higher operational costs. Efficient waste management in slot die systems lowers environmental impact by limiting overspray and recoil losses commonly associated with roll coating processes.
Common Industrial Applications
Slot die coaters are widely used in precision applications such as flexible electronics, battery manufacturing, and pharmaceutical coatings due to their ability to deliver uniform thin films with precise thickness control. Roll coaters find common use in high-speed processes like paper coating, textile finishing, and laminating films where broader coverage and faster production rates are essential. Both technologies enable efficient material deposition but cater to different industrial needs based on coating uniformity and production scale.
Choosing Between Slot Die and Roll Coater
Choosing between a slot die and a roll coater depends on the precision and thickness control required for the coating process. Slot die coaters offer highly uniform films with precise thickness control, ideal for applications like electronics and medical devices, while roll coaters excel in high-speed, large-area coatings such as in packaging and paper industries. Evaluating substrate type, coating viscosity, and production speed helps determine the optimal coating method for specific manufacturing needs.
Slot die vs roll coater Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com