Scara robots offer high-speed, precise, and flexible motion primarily in horizontal planes, making them ideal for assembly and packaging tasks requiring rapid, repeatable movements. Cartesian robots, with their straightforward linear axes, provide excellent rigidity and accuracy for applications like 3D printing and CNC machining, where precise, linear positioning is essential.
Table of Comparison
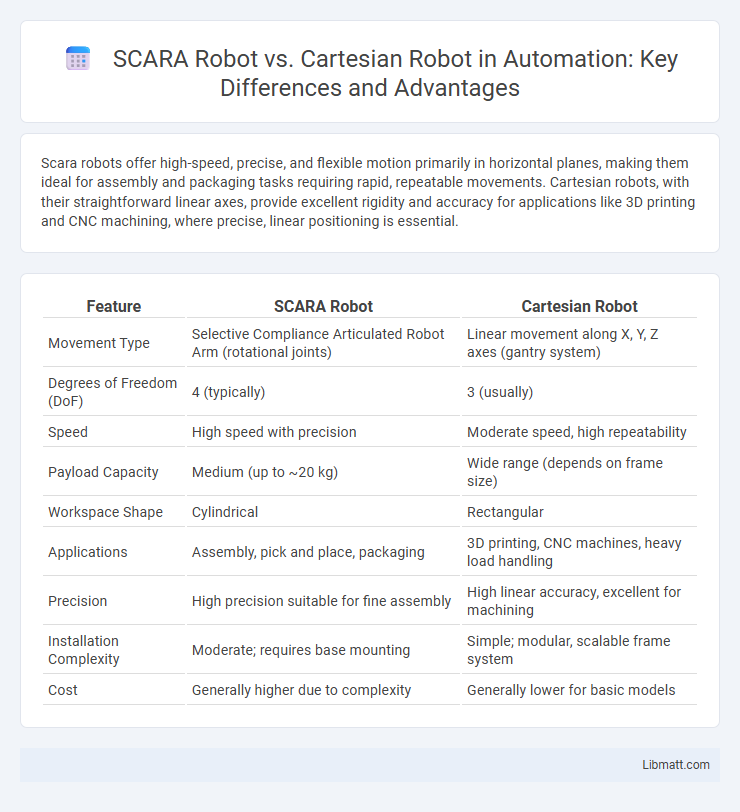
| Feature | SCARA Robot | Cartesian Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Movement Type | Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm (rotational joints) | Linear movement along X, Y, Z axes (gantry system) |
| Degrees of Freedom (DoF) | 4 (typically) | 3 (usually) |
| Speed | High speed with precision | Moderate speed, high repeatability |
| Payload Capacity | Medium (up to ~20 kg) | Wide range (depends on frame size) |
| Workspace Shape | Cylindrical | Rectangular |
| Applications | Assembly, pick and place, packaging | 3D printing, CNC machines, heavy load handling |
| Precision | High precision suitable for fine assembly | High linear accuracy, excellent for machining |
| Installation Complexity | Moderate; requires base mounting | Simple; modular, scalable frame system |
| Cost | Generally higher due to complexity | Generally lower for basic models |
Introduction to SCARA and Cartesian Robots
SCARA robots feature a selective compliance arm ideal for high-speed, precise horizontal movements, commonly used in assembly and packaging tasks. Cartesian robots operate on three linear axes (X, Y, Z), providing straightforward, programmable motion suitable for pick-and-place, CNC machining, and 3D printing applications. Understanding the distinct kinematics and operational strengths of SCARA versus Cartesian robots helps optimize automation solutions tailored to Your manufacturing needs.
Key Differences Between SCARA and Cartesian Robots
SCARA robots feature a rotary arm design offering high-speed pick-and-place capabilities with excellent horizontal movement, ideal for tasks requiring precise lateral motion. Cartesian robots operate on linear axes (X, Y, and Z), providing straightforward, accurate, and repeatable movement suited for applications demanding rigidity and extended reach. Understanding these key structural and operational differences helps you select the most efficient robot type for your automation needs.
Design and Structure Comparison
Scara robots feature a compact, articulated arm design with rotational joints allowing high-speed, precise horizontal movements ideal for assembly tasks. Cartesian robots use linear actuators along X, Y, and Z axes, providing straightforward programming and rigid, stable operation suited for heavy load handling. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize speed and flexibility (Scara) or load capacity and simplicity (Cartesian).
Movement and Degrees of Freedom
Scara robots offer movement with four degrees of freedom, primarily excelling in horizontal plane tasks with vertical motion, suitable for precise assembly and pick-and-place operations. Cartesian robots operate on three linear axes (X, Y, Z), providing straightforward, accurate movement within rectangular workspaces, ideal for applications requiring rigid, repetitive positioning. Your choice depends on whether rotational flexibility (Scara) or linear precision (Cartesian) aligns better with your automation needs.
Speed and Precision Capabilities
Scara robots excel in high-speed assembly and pick-and-place tasks due to their rigid arm structure and limited degrees of freedom, enabling precise horizontal movements with repeatability around +-0.01 mm. Cartesian robots offer exceptional precision in linear axes, typically achieving repeatability within +-0.005 mm, ideal for applications requiring exact positioning along X, Y, and Z coordinates but generally operate at slower speeds compared to Scara robots. The choice between them depends on the trade-off between Scara's rapid cycle times and Cartesian's superior linear accuracy for specific manufacturing needs.
Application Areas: SCARA vs Cartesian
SCARA robots excel in assembly, pick-and-place, and packaging tasks due to their high speed and precision in horizontal movements, making them ideal for electronics manufacturing and small parts handling. Cartesian robots offer superior linear motion control and repeatability, making them suitable for CNC machining, 3D printing, and large-scale material handling in automotive and aerospace industries. The choice between SCARA and Cartesian robots depends on the specific application requirements for speed, range of motion, and payload capacity.
Space Requirements and Footprint
Scara robots generally require less space due to their compact, articulated arm design, making them ideal for applications with limited floor area. Cartesian robots have a larger footprint because of their linear, three-axis movement system, which demands more room for installation and operation. Your choice depends on available workspace, as Scara robots optimize tight environments while Cartesian robots suit setups needing precise, linear motions over larger areas.
Integration and Programming Complexity
Scara robots offer streamlined integration with faster programming due to their specialized arm design, ideal for high-speed, precise pick-and-place tasks. Cartesian robots, featuring linear axes, provide straightforward programming through simple coordinate-based movements, making them suitable for applications requiring large work envelopes and repeatability. Your choice depends on balancing ease of programming against the specific spatial and operational needs of your automation system.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Scara robots typically have lower initial costs and simpler maintenance due to their fewer moving parts and compact design, making them cost-effective for small to medium-scale assembly tasks. Cartesian robots, while often more expensive initially because of their larger frame and complex structure, benefit from straightforward linear motion components that can reduce unexpected downtime and simplify repairs. Both robot types require regular calibration and preventive maintenance, but Scara robots' reduced mechanical complexity generally results in lower long-term operational expenses.
Choosing the Right Robot for Your Needs
Selecting between a Scara robot and a Cartesian robot depends on application requirements such as speed, precision, and workspace geometry. Scara robots excel in high-speed, 3-axis assembly tasks with moderate payloads and compact footprints, making them ideal for electronics or small parts manufacturing. Cartesian robots offer superior precision and repeatability in three linear axes, suited for large workspace automation, pick-and-place, or CNC machining operations where rigidity and scalability are crucial.
Scara Robot vs Cartesian Robot Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com