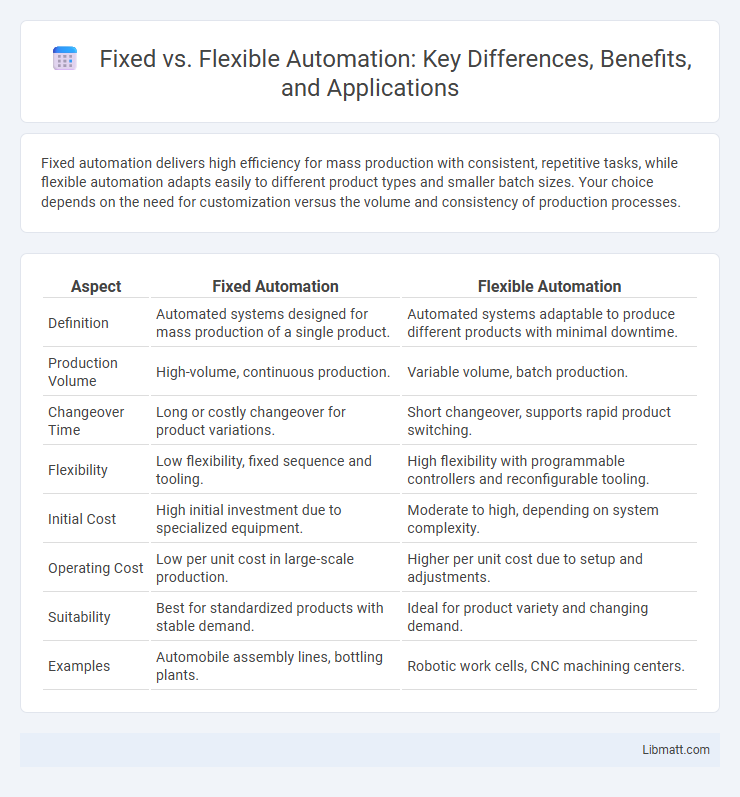
Fixed automation delivers high efficiency for mass production with consistent, repetitive tasks, while flexible automation adapts easily to different product types and smaller batch sizes. Your choice depends on the need for customization versus the volume and consistency of production processes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fixed Automation | Flexible Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated systems designed for mass production of a single product. | Automated systems adaptable to produce different products with minimal downtime. |
| Production Volume | High-volume, continuous production. | Variable volume, batch production. |
| Changeover Time | Long or costly changeover for product variations. | Short changeover, supports rapid product switching. |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility, fixed sequence and tooling. | High flexibility with programmable controllers and reconfigurable tooling. |
| Initial Cost | High initial investment due to specialized equipment. | Moderate to high, depending on system complexity. |
| Operating Cost | Low per unit cost in large-scale production. | Higher per unit cost due to setup and adjustments. |
| Suitability | Best for standardized products with stable demand. | Ideal for product variety and changing demand. |
| Examples | Automobile assembly lines, bottling plants. | Robotic work cells, CNC machining centers. |
Introduction to Fixed and Flexible Automation
Fixed automation involves specialized equipment designed for high-volume production of a single product, optimizing efficiency and consistency but lacking adaptability. Flexible automation employs programmable machines that can quickly adjust to different tasks or products, supporting varied production with reduced downtime. Choosing between fixed and flexible automation depends on factors like production volume, product variety, and cost constraints.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Flexible Automation
Fixed automation is designed for high-volume, repetitive production with specialized equipment tailored to a single task, ensuring efficiency and consistency. Flexible automation uses programmable machines capable of handling various tasks and product types, allowing quick adjustments to manufacturing processes. Your choice depends on production volume, product variety, and the need for adaptability in manufacturing operations.
Advantages of Fixed Automation
Fixed automation offers high production rates and consistent product quality due to its repetitive and predetermined sequence of operations. It reduces labor costs and minimizes errors by using specialized equipment designed for specific tasks. This type of automation is ideal for high-volume manufacturing where demand is stable and long-term production is required.
Advantages of Flexible Automation
Flexible automation offers significant advantages by enabling quick adaptation to different tasks and product variations, which increases production versatility and reduces downtime. It supports customization and small batch production without the need for extensive retooling, ultimately lowering operational costs. Your manufacturing process benefits from enhanced efficiency and responsiveness to market changes through flexible automation systems.
Limitations of Fixed Automation
Fixed automation offers high production rates but is limited by its inflexibility to accommodate design changes or product variety. The high initial investment in specialized equipment and tooling leads to increased costs if production requirements shift. Inability to quickly adapt to market demands restricts fixed automation to long production runs of standardized products.
Limitations of Flexible Automation
Flexible automation offers adaptability but faces limitations such as higher initial investment and complex programming requirements. Production speed may be slower compared to fixed automation, limiting efficiency in high-volume manufacturing. Your operations could also experience challenges with system maintenance and skill requirements for operators.
Ideal Applications for Fixed Automation
Fixed automation is ideal for high-volume production environments where the manufacturing process requires minimal variation and maximum efficiency. Industries such as automotive assembly lines, consumer electronics manufacturing, and packaging frequently utilize fixed automation to achieve consistent product quality and reduced cycle times. Your facility can benefit from fixed automation when repetitive, standardized tasks dominate the production workflow.
Ideal Applications for Flexible Automation
Flexible automation excels in industries requiring frequent product changes and customization, such as automotive assembly lines, electronics manufacturing, and pharmaceutical production. Its adaptability enables efficient handling of low to medium production volumes with varied product types, reducing downtime and reprogramming costs. Ideal applications include tasks involving complex assembly, variable product designs, and rapid response to market demands.
Cost Comparison: Fixed vs Flexible Automation
Fixed automation typically demands higher upfront costs due to custom-designed machinery tailored for repetitive tasks, whereas flexible automation involves lower initial investment with programmable systems adaptable to various products. Your ongoing expenses differ significantly; fixed automation offers lower operating costs for high-volume production, while flexible automation may incur higher maintenance and programming fees but reduces downtime when switching tasks. Evaluating production volume and product variability is essential to determine which automation type offers the best cost efficiency for your manufacturing needs.
Choosing the Right Automation System for Your Business
Selecting between fixed and flexible automation depends on your business's production volume and product variety requirements. Fixed automation offers high efficiency and low unit costs for large-scale, repetitive manufacturing, while flexible automation supports a broader range of products with quicker changeovers at a higher initial investment. Understanding your operational goals and scalability needs ensures you choose the most cost-effective and adaptable system to optimize productivity.
Fixed vs Flexible Automation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com