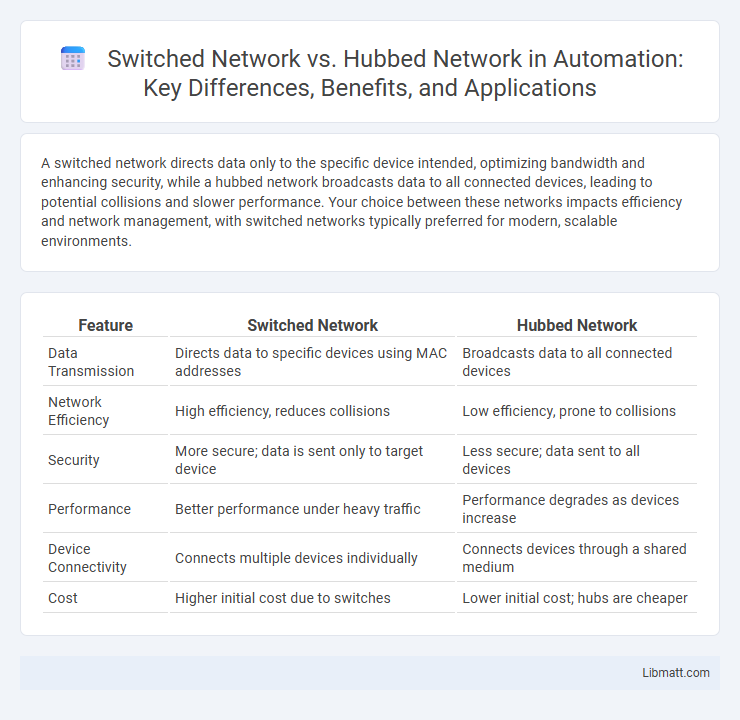
A switched network directs data only to the specific device intended, optimizing bandwidth and enhancing security, while a hubbed network broadcasts data to all connected devices, leading to potential collisions and slower performance. Your choice between these networks impacts efficiency and network management, with switched networks typically preferred for modern, scalable environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Switched Network | Hubbed Network |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transmission | Directs data to specific devices using MAC addresses | Broadcasts data to all connected devices |
| Network Efficiency | High efficiency, reduces collisions | Low efficiency, prone to collisions |
| Security | More secure; data is sent only to target device | Less secure; data sent to all devices |
| Performance | Better performance under heavy traffic | Performance degrades as devices increase |
| Device Connectivity | Connects multiple devices individually | Connects devices through a shared medium |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to switches | Lower initial cost; hubs are cheaper |
Introduction to Switched and Hubbed Networks
Switched networks use network switches to direct data packets only to the intended recipient devices, significantly improving efficiency and reducing collisions compared to hubbed networks. Hubbed networks rely on hubs that broadcast data to all connected devices, causing unnecessary traffic and potential congestion. Your network performance benefits from understanding these differences, as switched networks provide better bandwidth management and security by isolating communication paths.
Key Differences Between Switched and Hubbed Networks
Switched networks use switches to create dedicated communication paths between devices, improving bandwidth efficiency and reducing collisions, whereas hubbed networks rely on hubs that broadcast data to all connected devices, leading to higher collision rates and network congestion. Switches operate at the data link layer, enabling intelligent packet forwarding based on MAC addresses, while hubs function at the physical layer, simply repeating incoming signals to all ports. This fundamental difference results in switched networks offering greater scalability, security, and overall performance compared to hubbed networks.
How Switched Networks Work
Switched networks use network switches to direct data packets to specific devices based on their MAC addresses, improving communication efficiency and reducing collisions. Each device connected to a switch has a dedicated bandwidth, allowing simultaneous data transmission without interference. This targeted data forwarding enhances overall network performance compared to hubbed networks, where data is broadcast to all devices.
How Hubbed Networks Work
Hubbed networks operate by broadcasting incoming data packets to all connected devices regardless of the intended recipient, causing network congestion and potential collisions. This method results in reduced efficiency and slower data transfer compared to switched networks, where data is directed to a specific device. Understanding how your hubbed network functions can help identify limitations impacting overall performance and guide decisions for upgrading to switched networks.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Efficiency
Switched networks offer significantly higher speed and efficiency compared to hubbed networks by directing data packets only to the intended recipient, reducing collisions and network congestion. Hubbed networks broadcast data to all connected devices, resulting in frequent collisions and slower overall performance. The use of switches enables full-duplex communication and better bandwidth utilization, which optimizes network throughput and minimizes latency.
Security Features in Switched vs Hubbed Networks
Switched networks enhance security by isolating data traffic within individual switch ports, preventing unauthorized access and reducing the risk of data interception compared to hubbed networks where data is broadcasted to all connected devices. Switches support features like VLAN segmentation, port security, and MAC address filtering, providing granular control over network access and mitigating risks of eavesdropping and MAC flooding attacks common in hub-based environments. In contrast, hubbed networks lack traffic isolation and encryption capabilities, making them inherently vulnerable to sniffing and unauthorized data capture.
Scalability and Network Expansion
Switched networks offer superior scalability compared to hubbed networks by enabling direct device-to-device communication, which reduces network congestion as more devices are added. Hubbed networks rely on a single collision domain, causing performance degradation and limiting efficient network expansion when increasing the number of connected devices. Your network's growth and performance will benefit significantly from utilizing switches that support segmentation and better traffic management, ensuring smoother scalability.
Cost Considerations: Switched vs Hubbed
Switched networks generally incur higher initial costs due to the price of switches, but they provide better performance and scalability. Hubbed networks are less expensive upfront since hubs are cheaper devices, yet they suffer from limited bandwidth sharing and increased collisions, which can degrade network efficiency. Considering long-term operational costs, switched networks reduce downtime and maintenance expenses, offering a more cost-effective solution for growing or high-traffic environments.
Typical Use Cases for Each Network Type
Switched networks are ideal for environments requiring high data transfer speeds and minimal collisions, such as corporate offices, data centers, and modern enterprise networks, where efficient communication and security are critical. Hubbed networks are more suitable for small, simple setups or legacy systems with minimal traffic, like basic home networks or small laboratories, where cost-effectiveness and ease of installation outweigh performance concerns. Understanding these typical use cases helps you select the right network type based on scalability, bandwidth demands, and network complexity.
Choosing the Right Network for Your Business
Selecting a switched network enhances performance with dedicated points-to-point connections, reducing collisions and improving bandwidth efficiency, ideal for businesses needing high-speed data transfer and reliability. Hubbed networks, while simpler and cost-effective for small setups, broadcast data to all devices, causing network congestion and slower speeds as the network grows. Evaluate your business's scale, traffic volume, and security needs to determine whether the scalability and traffic management of a switched network outweigh the initial lower cost of a hubbed network.
Switched Network vs Hubbed Network Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com