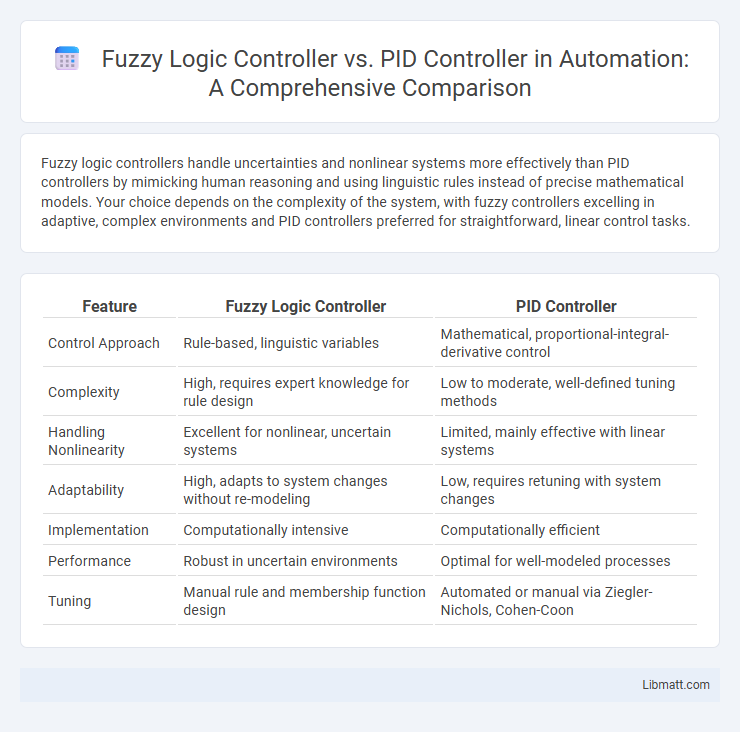
Fuzzy logic controllers handle uncertainties and nonlinear systems more effectively than PID controllers by mimicking human reasoning and using linguistic rules instead of precise mathematical models. Your choice depends on the complexity of the system, with fuzzy controllers excelling in adaptive, complex environments and PID controllers preferred for straightforward, linear control tasks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fuzzy Logic Controller | PID Controller |
|---|---|---|
| Control Approach | Rule-based, linguistic variables | Mathematical, proportional-integral-derivative control |
| Complexity | High, requires expert knowledge for rule design | Low to moderate, well-defined tuning methods |
| Handling Nonlinearity | Excellent for nonlinear, uncertain systems | Limited, mainly effective with linear systems |
| Adaptability | High, adapts to system changes without re-modeling | Low, requires retuning with system changes |
| Implementation | Computationally intensive | Computationally efficient |
| Performance | Robust in uncertain environments | Optimal for well-modeled processes |
| Tuning | Manual rule and membership function design | Automated or manual via Ziegler-Nichols, Cohen-Coon |
Introduction to Control Systems
Fuzzy Logic Controllers (FLC) and PID Controllers are fundamental components in control systems designed to maintain desired output levels. PID Controllers operate using proportional, integral, and derivative terms, providing precise control in linear systems with well-defined models. FLCs handle non-linear, uncertain, or imprecise systems by mimicking human reasoning through linguistic rules and fuzzy sets, offering robustness where traditional PID tuning may struggle.
Overview of PID Controllers
PID controllers operate by continuously calculating an error value as the difference between a desired setpoint and a measured process variable, applying proportional, integral, and derivative terms to minimize this error. Widely used in industrial control systems, PID controllers provide straightforward tuning methods and robust performance in linear and time-invariant processes. Their effectiveness decreases in highly nonlinear or complex dynamic environments, where adaptive approaches like fuzzy logic controllers may offer improved control accuracy.
Understanding Fuzzy Logic Controllers
Fuzzy Logic Controllers use linguistic variables and a rule-based approach to handle uncertainty and imprecision in control systems, making them suitable for complex or nonlinear processes where traditional modeling is challenging. Unlike PID Controllers, which rely on precise mathematical models and fixed parameters for proportional, integral, and derivative actions, Fuzzy Logic Controllers adapt their control actions using fuzzy sets and membership functions. You benefit from enhanced flexibility and robustness in applications like robotics, automotive systems, and industrial automation by implementing fuzzy logic control strategies.
Key Differences Between PID and Fuzzy Logic Controllers
PID controllers rely on precise mathematical models and fixed control parameters (proportional, integral, derivative) to maintain system stability and respond to errors. Fuzzy Logic Controllers use linguistic rules and membership functions to handle uncertainty and nonlinearities, enabling adaptive decision-making without requiring an exact mathematical model. The key difference lies in PID's dependence on exact equations versus Fuzzy Logic's flexibility in managing imprecise inputs and complex system behaviors.
Applications of PID Controllers
PID controllers dominate industrial automation due to their simplicity and effectiveness in controlling temperature, pressure, and flow in manufacturing processes. They excel in applications like robotics, HVAC systems, and automotive engine control by providing precise and stable feedback loops. The widespread use of PID controllers in process industries highlights their reliability for systems requiring consistent, real-time adjustments.
Applications of Fuzzy Logic Controllers
Fuzzy Logic Controllers (FLCs) excel in complex, nonlinear systems where precise mathematical models are difficult to obtain, such as robotics, automotive systems, and home appliances. They are widely used in temperature control, traffic management, and consumer electronics due to their ability to handle uncertainty and approximate reasoning. Your choice of an FLC can improve system robustness and adaptability compared to traditional PID controllers in environments with imprecise or varying parameters.
Performance Comparison: Accuracy and Stability
Fuzzy Logic Controllers exhibit superior adaptability in handling nonlinear systems and uncertainties, often achieving higher accuracy in complex control environments compared to traditional PID Controllers. PID Controllers maintain stable performance in linear, time-invariant systems, providing precise control through well-defined proportional, integral, and derivative actions, but may struggle with system nonlinearities and parameter variations. Stability in Fuzzy Logic Controllers stems from heuristic rule-based tuning, which allows for robust control under varying conditions, while PID Controllers rely on precise mathematical models and tuning methods like Ziegler-Nichols to ensure consistent stability.
Tuning and Implementation Complexity
Fuzzy Logic Controllers offer easier tuning through linguistic rules and do not require an accurate mathematical model, making them suitable for systems with uncertainty and nonlinearities. In contrast, PID Controllers demand precise parameter tuning (proportional, integral, derivative gains) to achieve optimal performance, which can be time-consuming and complex, especially for varying system dynamics. Your choice depends on the implementation complexity you can manage and the nature of the control system; fuzzy logic may simplify tuning but at the cost of designing and maintaining rule sets.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Controller
Fuzzy Logic Controllers excel in handling nonlinear systems and uncertainties with ease, offering robustness and adaptability without requiring precise mathematical models, but they can be complex to design and tune. PID Controllers provide straightforward implementation and effective performance in linear systems with well-defined dynamics, yet they may struggle with nonlinearity and disturbances due to their fixed parameter structure. Both controllers present trade-offs between simplicity and flexibility, making the choice dependent on system characteristics and control objectives.
Choosing the Right Controller for Your System
Selecting the right controller depends on system complexity and performance requirements, where Fuzzy Logic Controllers excel in handling nonlinear, uncertain, or imprecise systems with adaptive control strategies. PID Controllers remain the preferred choice for linear, well-defined processes due to their simplicity, ease of tuning, and robust stability in steady-state control. Evaluating factors such as response time, adaptability, and system modeling accuracy helps determine whether a Fuzzy Logic Controller or a PID Controller is best suited for your specific application.
Fuzzy Logic Controller vs PID Controller Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com