Process automation focuses on controlling and optimizing continuous, complex production processes such as chemical or pharmaceutical manufacturing, while factory automation typically deals with discrete manufacturing tasks like assembling components or packaging products. Understanding these differences helps you select the right automation strategy to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Table of Comparison
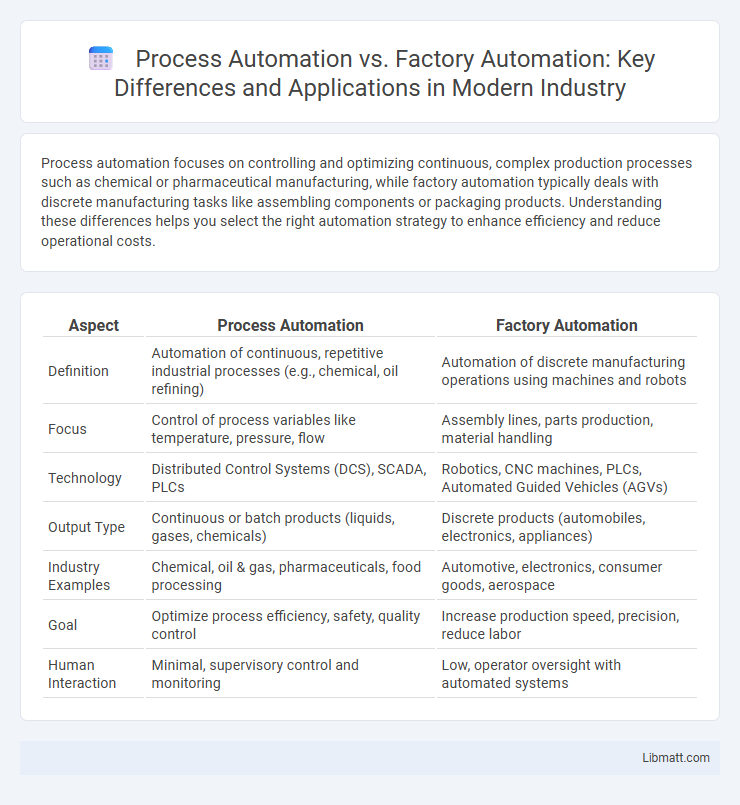
| Aspect | Process Automation | Factory Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automation of continuous, repetitive industrial processes (e.g., chemical, oil refining) | Automation of discrete manufacturing operations using machines and robots |
| Focus | Control of process variables like temperature, pressure, flow | Assembly lines, parts production, material handling |
| Technology | Distributed Control Systems (DCS), SCADA, PLCs | Robotics, CNC machines, PLCs, Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) |
| Output Type | Continuous or batch products (liquids, gases, chemicals) | Discrete products (automobiles, electronics, appliances) |
| Industry Examples | Chemical, oil & gas, pharmaceuticals, food processing | Automotive, electronics, consumer goods, aerospace |
| Goal | Optimize process efficiency, safety, quality control | Increase production speed, precision, reduce labor |
| Human Interaction | Minimal, supervisory control and monitoring | Low, operator oversight with automated systems |
Introduction to Process Automation and Factory Automation
Process Automation involves using technology to control and monitor continuous production processes such as chemical, pharmaceutical, or food manufacturing systems, enhancing efficiency and consistency. Factory Automation focuses on automating discrete manufacturing tasks like assembly, machining, or packaging through robotic systems and programmable logic controllers (PLCs). Understanding these distinctions helps optimize Your industrial operations by selecting appropriate automation solutions tailored to specific production needs.
Key Differences Between Process Automation and Factory Automation
Process Automation primarily targets continuous, chemical, or batch processes in industries like oil refining, pharmaceuticals, and food production, focusing on controlling variables such as temperature, pressure, and flow. Factory Automation involves discrete manufacturing operations in sectors like automotive or electronics, emphasizing robotic assembly, material handling, and machine control. Understanding these distinctions helps you choose the right automation solutions tailored to the specific operational requirements of your production environment.
Core Components of Process Automation
Process automation primarily involves instrumentation, control systems like distributed control systems (DCS), and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems that monitor and manage continuous, batch, or hybrid processes. Core components include sensors, actuators, controllers, and communication networks that facilitate real-time data collection and process regulation. Understanding these elements helps you optimize efficiency, reduce errors, and improve overall process consistency in industries such as chemical, pharmaceutical, and oil refining.
Core Components of Factory Automation
Core components of factory automation include programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), sensors, and robotics systems that work together to streamline production processes. These elements ensure precise control, monitoring, and coordination of machinery, optimizing efficiency and reducing human error. Your integration of these technologies transforms manual factory operations into automated workflows, enhancing productivity and consistency.
Applications of Process Automation in Industry
Process automation in industry primarily enhances chemical manufacturing, oil refining, and pharmaceutical production by optimizing continuous processes through advanced control systems and real-time monitoring. It enables precise regulation of temperature, pressure, and flow rates, ensuring consistent product quality and operational safety. Integration with SCADA and DCS platforms further improves efficiency, reduces human error, and facilitates predictive maintenance.
Applications of Factory Automation in Manufacturing
Factory automation in manufacturing extensively applies robotics, CNC machines, and conveyor systems to enhance production speed, quality, and consistency. These technologies optimize various stages such as assembly, material handling, and packaging, contributing to reduced labor costs and minimized human errors. Your manufacturing process benefits from streamlined operations and increased throughput when leveraging advanced factory automation solutions.
Benefits of Process Automation
Process automation enhances operational efficiency by streamlining repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and increasing productivity across various industries such as manufacturing, finance, and healthcare. It enables real-time data monitoring and analytics, facilitating informed decision-making and predictive maintenance to minimize downtime. By integrating advanced technologies like AI and IoT, process automation improves scalability, consistency, and compliance with industry regulations, driving overall cost savings and business growth.
Benefits of Factory Automation
Factory automation significantly enhances production efficiency by integrating advanced robotics and control systems that reduce human error and increase output consistency. It enables real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which lowers downtime and operational costs. The use of factory automation also improves workplace safety by minimizing direct human involvement in hazardous tasks.
Challenges in Implementing Automation Solutions
Implementing process automation faces challenges such as integration complexity with existing IT infrastructure, ensuring real-time data accuracy, and managing cybersecurity risks across interconnected systems. Factory automation struggles with high initial capital expenditure, equipment compatibility issues, and the need for skilled workforce training to handle advanced robotics and control systems. Both require thorough planning to address scalability, maintenance, and compliance with industry standards for successful deployment.
Choosing the Right Automation for Your Business
Choosing the right automation for your business depends on your specific operational needs and goals. Process automation optimizes repetitive tasks and workflows across various departments, improving efficiency and reducing human error. Factory automation focuses on enhancing manufacturing operations through robotics and control systems, driving higher production accuracy and output.
Process Automation vs Factory Automation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com